High photosensitivity 2D-few-layered molybdenum diselenide phototransistors
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials are now attracting a lot of interest due to their unique optoelectronic properties at atomic thicknesses. Among them, graphene has been mostly investigated, but the zero-gap nature of graphene limits its practical applications. Therefore, 2D layered materials with intrinsic band gaps such as MoS2, MoSe2, and MoTe2 are of interest as promising candidates for ultrathin and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
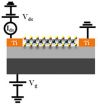
Here, Pil Ju Ko and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan have fabricated back-gated field-effect phototransistors made of MoSe2 crystals having a thickness of only twenty nanometers. The devices were fabricated by mechanical cleavage of MoSe2 crystals into few-layered flakes, followed by transfer onto a silicon wafer with pre-deposited titanium electrodes.
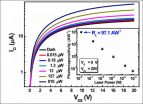
Despite their ultra-thin physical size, the devices showed excellent field-effect phototransistor characteristics. The measured photoresponsivity of 97.1 AW-1 at zero back gate voltage was higher than previous reports of photodetectors fabricated using GaS, GaSe, MoS2, and InSe. The photoresponse of the MoSe2 was much faster (less than 15 msec) than ultrasensitive photodetectors based on monolayer MoS2. Furthermore, the theoretical external quantum efficiency was 280-fold higher than of commercial Si and InGaAs photodiodes.
The research shows that MoSe2 is a promising material for photodetector applications. The group is optimization the device performance by studying thickness-dependent of the photosensitivity.
INFORMATION:
Reference:
Authors: Abdelkader Abderrahmane, Pil Ju Ko, Tran Viet Thu, Shunji Ishizawa, Tsukasa Takamura and Adarsh Sandhu.
Title of original paper: High photosensitivity few-layered MoSe2 back-gated field-effect phototransistors.
Journal, volume, pages and year: Nanotechnology 25 365202 (1-5) (2014).
Digital Object Identifier (DOI): 10.1088/0957-4484/25/36/365202.
Affiliations: Electronics-Inspired Interdisciplinary Research Institute (EIIRIS) and Department of Electrical and Electronic Information Engineering, Toyohashi University of Technology, 1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku, Toyohashi, Aichi 441-8580, Japan
Department website: http://www.sandhu.jp/
This article is featured in the December 2014 issue of the Toyohashi Tech e-Newsletter:
http://www.tut.ac.jp/english/newsletter/research_highlights/research05.html
Further information
Toyohashi University of Technology
1-1 Hibarigaoka, Tempaku
Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, 441-8580, JAPAN
Inquiries: Committee for Public Relations
E-mail: press@office.tut.ac.jp
About Toyohashi University of Technology:
Founded in 1976 as a National University of Japan, Toyohashi University of Technology is a vibrant modern institute with research activities reflecting the modern era of advanced electronics, engineering, and life sciences.
Website: http://www.tut.ac.jp/english/
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
Physical activity increases oxidative stress, and therefore, as an antioxidant vitamin C might have particularly evident effects on people who are participating in vigorous exercise. In several studies, vitamin C administration attenuated the increases in oxidative stress markers caused by exercise. Furthermore, vitamin C is involved in the metabolism of histamine, prostaglandins, and cysteinyl leukotrienes, all of which appear to be mediators in the pathogenesis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
A meta-analysis of three studies found that vitamin C halved post-exercise ...
2014-12-08
A new analysis of an important trial of the blood pressure-lowering procedure, renal denervation, shows that the main results may have been affected by a number of confounding factors that partially explain the unexpected blood pressure responses in patients.
The analysis, published in the European Heart Journal [1], identified factors in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial, such as variations in the way the procedure was performed and changes in patients' medications and drug adherence, which may have had a significant impact on the results.
Results of the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 ...
2014-12-08
An international research team that includes researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has captured the highest-resolution protein snapshots ever taken with an X-ray laser, revealing how a key protein in a photosynthetic bacterium changes shape when hit by light.
Human biology is a massive collection of chemical reactions and all involve proteins, known as the molecules of life. Scientists have been moving steadily toward their ultimate goal of following these life-essential reactions step by step in real time, at the scale of atoms and electrons.
"These ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - Novel treatments that harness the body's own immune cells to attack cancer cells demonstrate safe and durable responses in patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant blood cancers, according to data presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Therapies designed to target the immune system and ignite the body's own disease-fighting mechanisms have become an increasingly promising field of study, particularly in blood cancers. While the immune system can easily recognize viruses ...
2014-12-08
Researchers from North Carolina State University have developed a new lithography technique that uses nanoscale spheres to create three-dimensional (3-D) structures with biomedical, electronic and photonic applications. The new technique is significantly less expensive than conventional methods and does not rely on stacking two-dimensional (2-D) patterns to create 3-D structures.
"Our approach reduces the cost of nanolithography to the point where it could be done in your garage," says Dr. Chih-Hao Chang, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering ...
2014-12-08
Nature's ingenious systems: A layer of cells called endothelial cells lines the interior of blood vessels. When blood flows through the vessels, such cells only divide to replace dead cells. However, if there is a blood clot preventing blood from flowing across the endothelial cells, they begin to divide more actively. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates that cell division is very ordered. The new cells move away from each other and create a dynamic movement with eddies in a large area. This presumably helps to widen the vessel around the blockage. The ...
2014-12-08
A new study by researchers at the University of Exeter has found early warning signals of a reorganisation of the Atlantic oceans' circulation which could have a profound impact on the global climate system.
The research, published today in the journal Nature Communications, used a simulation from a highly complex model to analyse the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), an important component of the Earth's climate system.
It showed that early warning signals are present up to 250 years before it collapses, suggesting that scientists could monitor ...
2014-12-08
Cancer Research UK scientists have discovered a new line of defence used by cancer cells to evade cell death, according to research published in Nature Communications* today (Monday).
The team identified a critical pathway of molecular signals which throw a lifeline to cancer cells, enabling them to survive even though they contain vast DNA errors which would usually trigger cell death.
The PKCƐ signal pathway**, which is used by cancer cells but rarely by normal cells, could be important in targeting some cancer cells as they rely on this pathway to survive.
The ...
2014-12-08
UPTON, NY-A team of scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, Columbia Engineering, Columbia Physics and Kyoto University has discovered an unusual form of electronic order in a new family of unconventional superconductors. The finding, described in the journal Nature Communications, establishes an unexpected connection between this new group of titanium-oxypnictide superconductors and the more familiar cuprates and iron-pnictides, providing scientists with a whole new family of materials from which they can gain deeper insights ...
2014-12-08
A new analysis has found that while clinical trial data support omitting radiation treatments in elderly women with early stage breast cancer, nearly two-thirds of these women continue to receive it. The findings are published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Results published in 2004 from a large, randomized clinical trial showed that adding radiation therapy to surgery plus tamoxifen does not reduce 5-year recurrence rates or prolong survival in elderly women with early stage tumors. Despite the findings, many doctors still ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] High photosensitivity 2D-few-layered molybdenum diselenide phototransistors