Macrophages chase neutrophils away from wounds to resolve inflammation
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) Macrophages are best known for their Pac Man-like ability to gobble up cellular debris and pathogens in order to thwart infection. A new study in The Journal of Cell Biology describes how these immune cells also help resolve inflammation by inducing white blood cells called neutrophils to leave wounded tissue.
Neutrophils are "first responders" that are attracted to wounds by signaling molecules called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that activate a protein kinase. When neutrophils finish their work, inflammation is partly resolved through apoptosis, or cell suicide, and the subsequent engulfment of the neutrophils' remains by macrophages. But neutrophils can also elect to leave wounded tissue in a process known as reverse migration. Whether macrophages promote this mode of inflammation resolution is unclear.
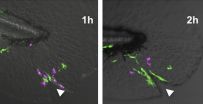
Taking advantage of transparent zebrafish larvae, Anna Huttenlocher and colleagues from the University of Wisconsin-Madison found that neutrophils were generally recruited to wounds before macrophages, but, once they arrived, macrophages often contacted neutrophils and appeared to shepherd them away from the damaged tissue. Neutrophils remained in wounds for longer times in zebrafish larvae lacking macrophages, the researchers discovered. Like neutrophils, macrophages were attracted to wounds by ROS and protein kinase signaling, and macrophages lacking the ROS-generating enzyme Nox2 were unable to migrate into wounds and induce the departure of neutrophils.
VIDEO:
In this video, neutrophils (magenta) are contacted and chased from a wound by macrophages (green).
Click here for more information.
Interestingly, patients lacking the human equivalent of Nox2 suffer from recurring infections and exaggerated inflammation, a disorder known as chronic granulomatous disease. This new study suggests that one cause of the patients' symptoms may be the inability of macrophages to migrate to sites of inflammation to induce neutrophil reverse migration and inflammation resolution.
INFORMATION:
Tauzin, S., et al. 2014. J. Cell Biol. doi:10.1083/jcb.201408090
About The Journal of Cell Biology
The Journal of Cell Biology (JCB) is published by The Rockefeller University Press. All editorial decisions on manuscripts submitted are made by active scientists in conjunction with our in-house scientific editors. JCB content is posted to PubMed Central, where it is available to the public for free six months after publication. Authors retain copyright of their published works, and third parties may reuse the content for non-commercial purposes under a creative commons license. For more information, please visit http://www.jcb.org.
Research reported in the press release was supported by the American Heart Association and National Institutes of Health.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
What does it mean for expectant mothers and hospitals when there are large-scale closures of maternity units? A new study led by researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia provides an inside view from hospital staff members in Philadelphia, where 13 out of 19 obstetric units closed in a 15-year period.
The researchers found that sharp surges in patient volume in the remaining units strained the healthcare system, eroded workforce morale, and fragmented care for mothers and babies until hospitals adjusted to added demands.
"While the degree of obstetric ...
2014-12-08
WASHINGTON, DC (December 8, 2014)-- Despite the promise of health reform, millions of U.S. children still lack quality health coverage or have trouble getting the services they need to stay healthy or to develop properly, according to two articles published in the December issue of Health Affairs. To address these gaps in coverage, broad reforms aimed at improving the quality of coverage for all children are needed, according to the authors.
In the first article, Sara Rosenbaum, JD, the Harold and Jane Hirsh Professor of Health Law and Policy at Milken Institute School ...
2014-12-08
WASHINGTON, DC - December 9, 2014 - Seasonal flu vaccines may protect individuals not only against the strains of flu they contain but also against many additional types, according to a study published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology.
The work, directed by researchers at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tenn., found that some study participants who reported receiving flu vaccines had a strong immune response not only against the seasonal H3N2 flu strain from 2010, when blood samples were ...
2014-12-08
San Francisco children living in non-redeveloped public housing are 39 percent more likely to repeatedly visit emergency rooms, according to new research from UC San Francisco and UC Berkeley.
"The average emergency department (ED) visit costs two to five times more than an office visit, and many children visit EDs for potentially preventable reasons," said Nancy Adler, PhD, senior author of the research, and vice chair of the department of psychiatry and director of the Center for Health and Community at UCSF. "There is a clear need to better understand the range of ...
2014-12-08
(SALT LAKE CITY)- It's a virus that has long been characterized as dangerous and even deadly, but new research shows infant deaths from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) are actually quite uncommon in the 21st century.
Researchers at the University of Utah have shown there are approximately 42 deaths annually associated with RSV in the United States, and of those deaths, the majority are in infants and young children that have complex preexisting chronic conditions.
"The news is very good for parents and their babies," says Carrie Byington, M.D., professor of pediatrics ...
2014-12-08
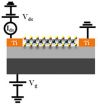
Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials are now attracting a lot of interest due to their unique optoelectronic properties at atomic thicknesses. Among them, graphene has been mostly investigated, but the zero-gap nature of graphene limits its practical applications. Therefore, 2D layered materials with intrinsic band gaps such as MoS2, MoSe2, and MoTe2 are of interest as promising candidates for ultrathin and high-performance optoelectronic devices.
Here, Pil Ju Ko and colleagues at Toyohashi University of Technology, Japan have fabricated back-gated field-effect phototransistors ...
2014-12-08
Physical activity increases oxidative stress, and therefore, as an antioxidant vitamin C might have particularly evident effects on people who are participating in vigorous exercise. In several studies, vitamin C administration attenuated the increases in oxidative stress markers caused by exercise. Furthermore, vitamin C is involved in the metabolism of histamine, prostaglandins, and cysteinyl leukotrienes, all of which appear to be mediators in the pathogenesis of exercise-induced bronchoconstriction.
A meta-analysis of three studies found that vitamin C halved post-exercise ...
2014-12-08
A new analysis of an important trial of the blood pressure-lowering procedure, renal denervation, shows that the main results may have been affected by a number of confounding factors that partially explain the unexpected blood pressure responses in patients.
The analysis, published in the European Heart Journal [1], identified factors in the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial, such as variations in the way the procedure was performed and changes in patients' medications and drug adherence, which may have had a significant impact on the results.
Results of the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 ...
2014-12-08
An international research team that includes researchers from Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory has captured the highest-resolution protein snapshots ever taken with an X-ray laser, revealing how a key protein in a photosynthetic bacterium changes shape when hit by light.
Human biology is a massive collection of chemical reactions and all involve proteins, known as the molecules of life. Scientists have been moving steadily toward their ultimate goal of following these life-essential reactions step by step in real time, at the scale of atoms and electrons.
"These ...
2014-12-08
(SAN FRANCISCO, December 6, 2014) - Novel treatments that harness the body's own immune cells to attack cancer cells demonstrate safe and durable responses in patients with relapsed and treatment-resistant blood cancers, according to data presented today at the 56th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition.
Therapies designed to target the immune system and ignite the body's own disease-fighting mechanisms have become an increasingly promising field of study, particularly in blood cancers. While the immune system can easily recognize viruses ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Macrophages chase neutrophils away from wounds to resolve inflammation