Animal research sheds light on harmful mood disorders in new mothers
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) In the days shortly after giving birth, most mothers experience a period of increased calmness and decreased stress responses, but around 20% of mothers experience anxiety. Some women may become depressed, and around one in a thousand can develop psychosis. The latest evidence indicates that these distressing responses to motherhood are still poorly understood, but that animal research could provide valuable clues to their causes.
Writing in the British Journal of Pharmacology, Dr David Slattery and Dr Clara Perani highlight that anxiety, depression and psychosis during this 'postpartum' period of life not only affect the well-being of the mother but also place at risk the long-term health of the infant. Infant care and bonding can also be altered, which in turn may lead to long-term behavioural and emotional problems for the child.
Despite the seriousness of the situation, little is known about the causes of postpartum disorders. Slattery and Perani believe animal research could play a greater role. "All female mammals give birth, produce milk and adapt their behaviour in order to care for the offspring. Research in rodents shows that they too experience a host of important behavioural and physiological alterations during this time. For example, just like most breastfeeding mothers, rodents are generally calmer and show a smaller increase in the stress hormone cortisol when subjected to stress," says Slattery.
Factors like smoking, drinking alcohol throughout pregnancy and marital status, all influence the likelihood of a mother developing these sorts of postpartum mood and anxiety disorders, and having a previous history of a mood condition places a woman at greater risk. "While we know this from observing women, what we need now is a greater understanding of the underlying causes and mechanisms so that we can begin to identify mothers who are at risk and start to provide them with preventative advice and effective therapies," says Slattery.
While it is very difficult to impose experimental restraints on women, some of the factors such as diet or repeated exposure to stress during pregnancy can be explored in research involving animals.
Identification of such causes could lead to better treatment and faster diagnosis of the disorders, which would help both the mother and her child. "Long-term, we hope that increased study, involving both animals and humans, will improve our understanding of postpartum psychiatric disorders, and lead to improved, earlier diagnosis and to novel treatment approaches for this particular time period of a woman's life," says Slattery, who has previously published a number of studies assessing how pregnancy stress effects the normal adaptations that occur immediately before or after giving birth.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
Wind turbine developments have no effect on property values of nearby homes and farms, according to new research from the University of Guelph.
Published in a recent issue of the Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics, the study is believed the first peer-reviewed study on this issue in Canada.
It was conducted by Richard Vyn, a professor in the Department of Food, Agricultural and Resource Economics, and Ryan McCullough, a former U of G graduate student and now a policy analyst for Health Canada.
They analyzed more than 7,000 home and farm sales in Melancthon ...
2014-12-08
PORTICI, ITALY - As water becomes scarcer in arid and semiarid regions across the globe, the floriculture industry is looking for ways to reduce water usage and produce ornamental plants more efficiently. Chiara Cirillo and members of an Italian research team coordinated by Professor Stefania De Pascale, say that understanding flowering plants' response to water management is critical for optimizing the production of high-quality potted ornamentals. "Water-saving irrigation management strategies are among the options available to horticultural growers to reduce water consumption ...
2014-12-08
DURHAM, N.C. -- By identifying the most efficient fishing practices and behaviors, a new model developed by economists at Duke University and the University of Connecticut could help fishermen land larger paychecks while reducing the risk of fishery depletion.
"We're not talking about a trivial improvement. In some cases, we found that identifying the most efficient practices led to a 20 percent annual increase in total revenues if the fishery is managed differently," said Martin D. Smith, professor of environmental economics at Duke's Nicholas School of the Environment.
"Under ...
2014-12-08
The same research team that developed the first laser based on a living cell has shown that use of fluorescent proteins in a solid form rather than in solution greatly increases the intensity of light produced, an accomplishment that takes advantage of natural protein structures surrounding the light-emitting portions of the protein molecules. The findings from investigators Seok Hyun Yun, PhD, of the Wellman Center for Photomedicine at Massachusetts General Hospital and Malte Gather, PhD, of the University of St. Andrews in the U.K. appear in the online journal Nature ...
2014-12-08
CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. -- The majority of streams in the Chesapeake Bay region are warming, and that increase appears to be driven largely by rising air temperatures. These findings are based on new U.S. Geological Survey research published in the journal Climatic Change.
Researchers found an overall warming trend in air temperature of 0.023 C (0.041 F) per year, and in water temperature of 0.028 C (0.050 F) per year over 51 years. This means that air temperature has risen 1.1 C (1.98 F), and water temperature has risen 1.4 C (2.52 F) between 1960 and 2010 in the Chesapeake ...
2014-12-08
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...
2014-12-08
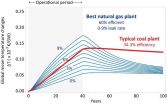
Washington, D.C.-- Natural gas power plants produce substantial amounts of gases that lead to global warming. Replacing old coal-fired power plants with new natural gas plants could cause climate damage to increase over the next decades, unless their methane leakage rates are very low and the new power plants are very efficient.
These are the principal findings of new research from Carnegie's Ken Caldeira and Xiaochun Zhang, and Nathan Myhrvold of Intellectual Ventures that compares the temperature increases caused by different kinds of coal and natural gas power plants. ...
2014-12-08
Washington, DC (December 8, 2014) - Scrolling through the comments section on a news site is like seeing a verbal war before your eyes. Internet trolls flourish in an anonymous world, so much so that sites like Reuters and Popular Science have done away with the comment sections altogether. But there has to be a better way to let the audience engage in a civil manner. A recent study published in the Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication by researchers at the University of Texas, Purdue University, and University of Wyoming, found that having a journalist engage with ...
2014-12-08
A technique that can identify causes of cancer invisible to genetic sequencing has uncovered large sets of previously unknown pancreatic cancer genes. It is hoped that this study will boost research into a disease that is still poorly understood and for which five-year survival rates have stood at around 5 per cent for the past four decades.
The technique works by introducing sections of DNA called piggyBac transposons into the mouse genome. Transposons jump around within the genome, reinserting themselves at random and causing a different mutation in each cell of the ...
2014-12-08
ITHACA, N.Y. - There is cloud hanging over climate science, but one Cornell University expert on communication and environmental issues says he knows how to help clear the air.
In the December issue of Nature Climate Change, Jonathon Schuldt, assistant professor of communication, argues that only by creating a "science of climate diversity" can climate science and the larger climate change movement overcome a crippling lack of ethnic and racial diversity.
"There is an invisible, but very real barrier to climate engagement," Schuldt said. "We need to engage with all ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Animal research sheds light on harmful mood disorders in new mothers