Punishing kids for lying just doesn't work
Children more likely to tell the truth either to please an adult or because they believe it is the right thing to do
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) If you want your child to tell the truth, it's best not to threaten to punish them if they lie. That's what researchers discovered through a simple experiment involving 372 children between the ages of 4 and 8.
How the Experiment was Done
The researchers, led by Prof. Victoria Talwar of McGill's Dept. of Educational and Counselling Psychology, left each child alone in a room for 1 minute with a toy behind them on a table, having told the child not to peek during their absence.
While they were out of the room, a hidden video camera filmed what went on.
When the researchers returned, they asked the child, a simple question: "When I was gone, did you turn around and peak at the toy?"
What the researchers discovered was that:
Slightly more than 2/3 of the children peeked at the toy (67.5 % or 251 children out of the 372 who were involved in the experiment). For every 1-month increase in age, children became slightly less likely to peek.
When the children were asked whether or not they had peeked, again about 2/3 of them lied (167 children or 66.5%) - and month-by-month as children aged, they both become more likely to tell lies and more adept at maintaining their lies
But what was more interesting to the researchers was that:
Children were less likely to tell the truth if they were afraid of being punished than if they were asked to tell the truth either because it would please the adult, or because it was the right thing to do and would make the child feel good.
The researchers expected and found that while younger children were more focused on telling the truth to please the adults, the older children had better internalized standards of behaviour which made them tell the truth because it was the right thing to do.
"The bottom line is that punishment does not promote truth-telling," says Victoria Talwar, the lead researcher on the study. "In fact, the threat of punishment can have the reverse effect by reducing the likelihood that children will tell the truth when encouraged to do so. This is useful information for all parents of young children and for the professionals like teachers who work with them and want to encourage young children to be honest."
INFORMATION:
To read the full article in the Journal of Experimental Child Psychology: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022096514001817
To contact the researcher directly: Victoria.talwar@mcgill.ca
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
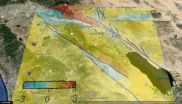
AMHERST, Mass. - New three-dimensional (3D) numerical modeling that captures far more geometric complexity of an active fault segment in southern California than any other, suggests that the overall earthquake hazard for towns on the west side of the Coachella Valley such as Palm Springs and Palm Desert may be slightly lower than previously believed.
New simulations of deformation on three alternative fault configurations for the Coachella Valley segment of the San Andreas Fault conducted by geoscientists Michele Cooke and Laura Fattaruso of the University of Massachusetts ...
2014-12-08
Hamilton, ON (Dec. 8, 2014) - Researchers from McMaster University have identified an important hormone that is elevated in obese people and contributes to obesity and diabetes by inhibiting brown fat activity.
Brown adipose tissue, widely known as brown fat, is located around the collarbone and acts as the body's furnace to burn calories. It also keeps the body warm. Obese people have less of it, and its activity is decreased with age. Until now, researchers haven't understood why.
There are two types of serotonin. Most people are familiar with the first type in the ...
2014-12-08
Recently, the researchers had constructed several single molecules with dual hormone action. Now, for the first time, the researchers succeeded in designing a substance that combines three metabolically active hormone components (GLP-1, GIP and glucagon) and offers unmatched potency to fight metabolic diseases in pre-clinical trials.
The team headed by physician scientist Matthias Tschöp (Helmholtz Diabetes Center at HMGU and Metabolic Diseases Chair at TUM) and peptide chemist Richard DiMarchi (Indiana University) has been cooperating for almost a decade to invent ...
2014-12-08
Harvard Stem Cell Institute researchers at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital have taken what they are describing as "the first step toward a pill that can replace the treadmill" for the control of obesity - though it of course would not provide all the additional benefits of exercise.
Chad Cowan, an HSCI Principal Faculty Member and his HSCI team report that they have created a system using human stem cells to screen for compounds that have the potential to turn white, or 'bad', fat cells into brown, or 'good' fat cells, and have already identified two compounds ...
2014-12-08
Titan, Saturn's largest moon, is a peculiar place. Unlike any other moon, it has a dense atmosphere. It has rivers and lakes made up of components of natural gas, such as ethane and methane. It also has windswept dunes that are hundreds of yards high, more than a mile wide and hundreds of miles long--despite data suggesting the body to have only light breezes.
Research led by Devon Burr, an associate professor in the Earth and Planetary Sciences Department at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, shows that winds on Titan must blow faster than previously thought to ...
2014-12-08
New nanopore DNA sequencing technology on a device the size of a USB stick could be used to diagnose infection - according to new research from the University of East Anglia and Public Health England.
Researchers tested the new technology with a complex problem - determining the cause of antibiotic resistance in a new multi-drug resistant strain of the bacterium that causes Typhoid.
The results, published today in the journal Nature Biotechnology, reveal that the small, accessible and cost effective technology could revolutionise genomic sequencing.
Current technology ...
2014-12-08
For a small percentage of cancer patients, treatment aimed at curing the disease leads to a form of leukemia with a poor prognosis. Conventional thinking goes that chemotherapy and radiation therapy induce a barrage of damaging genetic mutations that kill cancer cells yet inadvertently spur the development of acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a blood cancer.
But a new study at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis challenges the view that cancer treatment in itself is a direct cause of what is known as therapy-related AML.
Rather, the research suggests, ...
2014-12-08
BOSTON and CAMBRIDGE -- The genetic tumult within cancerous tumors is more than matched by the disorder in one of the mechanisms for switching cells' genes on and off, scientists at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard report in a new study. Their findings, published online today in the journal Cancer Cell, indicate that the disarray in the on-off mechanism - known as methylation - is one of the defining characteristics of cancer and helps tumors adapt to changing circumstances.
The researchers also showed that derangement in ...
2014-12-08
BOSTON -- Small cell lung cancer - a disease for which no new drugs have been approved for many years - has shown itself vulnerable to an agent that disables part of tumor cells' basic survival machinery, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology reported.
In a study published today in the journal Cancer Cell, the investigators found that the agent THZ1 caused human-like small cell lung tumors in mice to shrink significantly, with no apparent side effects. The compound is now being developed into a drug for testing ...
2014-12-08
COLUMBUS, OH - As interest in organic agricultural and horticultural practices continues to grow, so does the need to identify alternative weed control practices. Mulching, a common practice used to control weeds and reduce the need for tillage, can also reduce insect pollinators' exposure to harmful pesticides; however, finding the right mulch materials that allow pollinators to flourish can be challenging. Caitlin E. Splawski, from The Ohio State University Department of Horticulture and Crop Science, researched the effects of several types of organic mulch on squash ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Punishing kids for lying just doesn't work
Children more likely to tell the truth either to please an adult or because they believe it is the right thing to do