Study offers future hope for tackling signs of aging
Team identifies 'markers' to spot old cells in the body -- offering hope in the fight against cancer and aging
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) A new advance in biomedical research at the University of Leicester could have potential in the future to assist with tackling diseases and conditions associated with ageing - as well as in treating cancer.
The research, which has shown promise in clinical samples, has been published in the prestigious scientific journal, Cell Death and Disease.
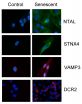
The group of scientists coordinated by Dr Salvador Macip from the Mechanisms of Cancer and Ageing Lab and the Department of Biochemistry of the University of Leicester carried out the study to find new ways of identifying old cells in the body.
This is important because the accumulation of old cells (called "senescent") in human tissue can contribute to symptoms of ageing. But old cells can also appear as a result of the activation of the internal anti-cancer mechanisms of the human body.
Dr Macip said: "What we have found is a series of novel markers - a way to detect senescent cells. What is more, we have shown that they can be used to predict increased survival in certain types of cancer.
"Until now, good protocols to help spot these cells have been sadly lacking. Our research has described new markers located on the surface of the old cells. This makes these markers particularly useful to quickly identify these cells in laboratory and human samples using a range of techniques."
As a first clinical application of these markers, the researchers observed that they were present in high numbers in samples from different types of cancer and that this correlated with a better prognosis of the disease. This was particularly evident in breast cancer.
Dr Macip said: "These markers could be useful tools not only to study senescent cells in the lab but also they could be developed into diagnostics to help predict survival in cancer patients.
"Moreover, they could also be used in the future to define strategies to selectively eliminate the old cells from the tissues and thus reduce their effects on promoting ageing in healthy subjects."
INFORMATION:
The work was funded by the MRC, the University of Leicester, the Saudi Arabian Government and the RSCF and involved scientists from the Departments of Biochemistry and Cancer Studies of the University of Leicester, the Umm AL-Qura University and the Russian Academy of Sciences.
Link to the paper: http://www.nature.com/cddis/journal/v5/n11/full/cddis2014489a.html
Lab webpage: http://lab.macip.org
Note to newsdesk:
For more information, please contact: Salvador Macip, sm460@le.ac.uk
The Medical Research Council has been at the forefront of scientific discovery to improve human health. Founded in 1913 to tackle tuberculosis, the MRC now invests taxpayers' money in some of the best medical research in the world across every area of health. Twenty-nine MRC-funded researchers have won Nobel prizes in a wide range of disciplines, and MRC scientists have been behind such diverse discoveries as vitamins, the structure of DNA and the link between smoking and cancer, as well as achievements such as pioneering the use of randomised controlled trials, the invention of MRI scanning, and the development of a group of antibodies used in the making of some of the most successful drugs ever developed. Today, MRC-funded scientists tackle some of the greatest health problems facing humanity in the 21st century, from the rising tide of chronic diseases associated with ageing to the threats posed by rapidly mutating micro-organisms. http://www.mrc.ac.uk
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...
2014-12-08
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- MIT chemists have devised a new way to wirelessly detect hazardous gases and environmental pollutants, using a simple sensor that can be read by a smartphone.
These inexpensive sensors could be widely deployed, making it easier to monitor public spaces or detect food spoilage in warehouses. Using this system, the researchers have demonstrated that they can detect gaseous ammonia, hydrogen peroxide, and cyclohexanone, among other gases.
"The beauty of these sensors is that they are really cheap. You put them up, they sit there, and then you come around ...
2014-12-08
Researchers have long wondered if there is an upper limit to our capacity to store memories and how we manage to remember so many events without mixing up events that are very similar.
To explore this issue, researchers at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology's (NTNU) Kavli Institute for Systems Neuroscience and Centre for Neural Computation and colleagues from the Czech Republic and Italy tested the ability of rats to remember a number of distinct but similar locations. Their findings are published in the 8 December edition of the Proceedings of the National ...
2014-12-08
Technology that can map out the genes at work in a snake or lizard's mouth has, in many cases, changed the way scientists define an animal as venomous. If oral glands show expression of some of the 20 gene families associated with "venom toxins," that species gets the venomous label.
But, a new study from The University of Texas at Arlington challenges that practice, while also developing a new model for how snake venoms came to be. The work, which is being published in the journal Molecular Biology and Evolution, is based on a painstaking analysis comparing groups of ...
2014-12-08
(BOSTON and CAMBRIDGE, Massachusetts) - One of the reasons cancer is so deadly is that it can evade attack from the body's immune system, which allows tumors to flourish and spread. Scientists can try to induce the immune system, known as immunotherapy, to go into attack mode to fight cancer and to build long lasting immune resistance to cancer cells. Now, researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering and Harvard's School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) show a non-surgical injection of programmable biomaterial that spontaneously assembles ...
2014-12-08
BUFFALO, N.Y. - A new study has shown that smoking can inhibit the success of treatment for alcohol abuse, putting people who are addicted to both tobacco and alcohol in a double bind.
According to findings by the University at Buffalo Research Institute on Addictions (RIA), clients who smoke have shorter stays in alcohol treatment programs than non-smokers and may have poorer treatment outcomes than non-smokers.
Kimberly Walitzer, PhD, deputy director and senior research scientist at RIA, led the study, which analyzed more than 21,000 adult treatment seekers from ...
2014-12-08
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Some infections after prostate biopsy due to drug-resistant Escherichia coli can be thwarted by simple rectal swab cultures prior to the procedure. The cultures test for antibiotic-resistant E. coli, and the findings are used to direct the selection of antimicrobial prophylaxis used for the procedure, according to Rhode Island Hospital researchers. The study was recently published in Urology.
For patients undergoing transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided biopsies, Ciprofloxacin may not be the best prophylactic option to use for patients colonized with ...
2014-12-08
NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites flew over Typhoon Hagupit from Dec. 6 through Dec. 8 and the MODIS instrument that flies aboard both satellites provided images of the storm as it moved through the country.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Aqua satellite caught a picture of Hagupit on Dec. 6 before it made landfall. On Dec. 7, the MODIS instrument aboard NASA's Terra satellite took an image of the storm as it was making landfall in the eastern Philippines.
On Dec. 8 at 04:50 UTC (Dec. 7 at 11:50 p.m. EST) when NASA's ...
2014-12-08
Scientists at the Medical College of Wisconsin (MCW) have discovered a link between sleep loss and cell injury. Results of a new study find sleep deprivation causes the damage to cells, especially in the liver, lung, and small intestine. Recovery sleep following deprivation heals the damage.
The findings are published in the December issue of Sleep, a joint publication of the Sleep Research Society and the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. The lead author is Carol Everson, Ph.D., professor of neurology, cell biology, neurobiology and anatomy at MCW. Co-authors are Christopher ...
2014-12-08
Athens, Ga. - New University of Georgia research shows that while on the job, public servants contribute not just to mandated sustainability but also to discretionary eco-friendly initiatives of their own.
"Some people are born with a higher intrinsic need to serve the public," said study co-author Robert K. Christensen, an associate professor in the School of Public and International Affairs. "They have a desire to help others and serve society. Government and nonprofit managers, for example, typically have higher levels of public service motivation than business managers."
The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study offers future hope for tackling signs of aging
Team identifies 'markers' to spot old cells in the body -- offering hope in the fight against cancer and aging




