(Press-News.org) Athens, Ga. - New University of Georgia research shows that while on the job, public servants contribute not just to mandated sustainability but also to discretionary eco-friendly initiatives of their own.
"Some people are born with a higher intrinsic need to serve the public," said study co-author Robert K. Christensen, an associate professor in the School of Public and International Affairs. "They have a desire to help others and serve society. Government and nonprofit managers, for example, typically have higher levels of public service motivation than business managers."
The study in the American Review of Public Administration used a survey of hundreds of public servants in a large southeastern city to examine their environmental and organizational behaviors.
Authored by Justin M. Stritch, a former doctoral student in public administration and policy, and Christensen, who also is the school's Ph.D. director in the department of public administration and policy, the research found that public servants were likely to engage in eco initiatives.
"Eco initiatives are discretionary, pro-environmental behaviors that an employee can participate in during the day," said Stritch, who is now an assistant professor at Arizona State University. "Eco initiatives involve things like recycling or energy conservation. Reusing water bottles and turning off your computer screen are examples."
Eco initiatives include sustainable micro-level behaviors, small tasks that are done voluntarily by the employee. When an employee chooses to do things like save paper or turn off lights at work, they are participating in eco initiatives. Eco initiatives are done because employees choose to do them, not because they're enforced.
In the survey, public servants in the southeastern city from departments like neighborhood and business services, fire, police, human resources and the city manager's office reported their environmental and workplace behaviors. The results showed that eco initiatives had to do with how motivated these public servants were to help society.
Public service motivation, a type of altruism, determines how people feel about the public and how they want to service public values. People with public service motivation can fulfill their desire to help society by choosing a job in government or a job in the private sector that helps citizens.
"Eco initiatives are correlated with the public service motivation of an individual," Christensen said. "Public servants with high public service motivation engage in micro citizenship behaviors to benefit society on a broader basis."
Along with public service motivation, two other predictors indicate a person's likeliness to perform eco initiatives.
"The three key drivers are public service motivation, organizational commitment and environmental connectedness," Stritch said. "The three work together to determine whether a person engages in eco initiatives."
Environmental connectedness describes an individual's attachment to nature. Having a strong connection to nature will increase an employee's likelihood of performing environmental initiatives. An employee's concern for the environment will help predict whether, and to what extent, they engage in eco initiatives.
"Even after accounting for an individual's connectedness to nature, an employee's public service motivation is a key factor in understanding voluntary, eco initiatives in the public workplace," Christensen said.
Stritch and Christensen hope that future studies will examine how institutional arrangements and mandated sustainability initiatives in cities change environmental commitment and behavior.
"Our hope is that people begin to think about stewardship and public resources in a broader way," Stritch said. "We want to see how public servants consider the environment over time and in different places."
"We have some compelling, if not preliminary, evidence that government workers often have the motivation to go above and beyond to benefit the environment while working in jobs that benefit society," Christensen said.
INFORMATION:
The full article, published online ahead of print, is available at http://arp.sagepub.com/content/early/2014/09/29/0275074014552470.full.pdf+html.
For more information on the School of Public and International Affairs, see http://spia.uga.edu/.
Triple-negative breast cancer is as bad as it sounds. The cells that form these tumors lack three proteins that would make the cancer respond to powerful, customized treatments. Instead, doctors are left with treating these patients with traditional chemotherapy drugs that only show long-term effectiveness in 20 percent of women with triple-negative breast cancer. Now, researchers at The Johns Hopkins University have discovered a way that breast cancer cells are able to resist the effects of chemotherapy -- and they have found a way to reverse that process.
A report of ...
CLEVELAND: Researchers from Seidman Cancer Center at University Hospitals (UH) Case Medical Center and Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine presented new research findings this weekend at the 56th Annual Meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) in San Francisco.
In a poster presentation (Abstract #4053), Jane Little, MD, and colleagues presented promising findings related to a novel biochip aimed at improving outcomes for patients with sickle cell disease. Although it is well-known that red cell interactions are important in sickle cell disease, ...
According to a new NOAA-sponsored study, natural oceanic and atmospheric patterns are the primary drivers behind California's ongoing drought. A high pressure ridge off the West Coast (typical of historic droughts) prevailed for three winters, blocking important wet season storms, with ocean surface temperature patterns making such a ridge much more likely. Typically, the winter season in California provides the state with a majority of its annual snow and rainfall that replenish water supplies for communities and ecosystems.
Further studies on these oceanic conditions ...
Using one of the most powerful lasers in the world, researchers have accelerated subatomic particles to the highest energies ever recorded from a compact accelerator.
The team, from the U.S. Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Lab (Berkeley Lab), used a specialized petawatt laser and a charged-particle gas called plasma to get the particles up to speed. The setup is known as a laser-plasma accelerator, an emerging class of particle accelerators that physicists believe can shrink traditional, miles-long accelerators to machines that can fit on a table.
The ...
If you want your child to tell the truth, it's best not to threaten to punish them if they lie. That's what researchers discovered through a simple experiment involving 372 children between the ages of 4 and 8.
How the Experiment was Done
The researchers, led by Prof. Victoria Talwar of McGill's Dept. of Educational and Counselling Psychology, left each child alone in a room for 1 minute with a toy behind them on a table, having told the child not to peek during their absence.
While they were out of the room, a hidden video camera filmed what went on.
When the ...
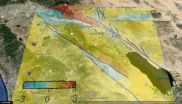
AMHERST, Mass. - New three-dimensional (3D) numerical modeling that captures far more geometric complexity of an active fault segment in southern California than any other, suggests that the overall earthquake hazard for towns on the west side of the Coachella Valley such as Palm Springs and Palm Desert may be slightly lower than previously believed.
New simulations of deformation on three alternative fault configurations for the Coachella Valley segment of the San Andreas Fault conducted by geoscientists Michele Cooke and Laura Fattaruso of the University of Massachusetts ...
Hamilton, ON (Dec. 8, 2014) - Researchers from McMaster University have identified an important hormone that is elevated in obese people and contributes to obesity and diabetes by inhibiting brown fat activity.
Brown adipose tissue, widely known as brown fat, is located around the collarbone and acts as the body's furnace to burn calories. It also keeps the body warm. Obese people have less of it, and its activity is decreased with age. Until now, researchers haven't understood why.
There are two types of serotonin. Most people are familiar with the first type in the ...
Recently, the researchers had constructed several single molecules with dual hormone action. Now, for the first time, the researchers succeeded in designing a substance that combines three metabolically active hormone components (GLP-1, GIP and glucagon) and offers unmatched potency to fight metabolic diseases in pre-clinical trials.
The team headed by physician scientist Matthias Tschöp (Helmholtz Diabetes Center at HMGU and Metabolic Diseases Chair at TUM) and peptide chemist Richard DiMarchi (Indiana University) has been cooperating for almost a decade to invent ...
Harvard Stem Cell Institute researchers at Harvard and Massachusetts General Hospital have taken what they are describing as "the first step toward a pill that can replace the treadmill" for the control of obesity - though it of course would not provide all the additional benefits of exercise.
Chad Cowan, an HSCI Principal Faculty Member and his HSCI team report that they have created a system using human stem cells to screen for compounds that have the potential to turn white, or 'bad', fat cells into brown, or 'good' fat cells, and have already identified two compounds ...
Titan, Saturn's largest moon, is a peculiar place. Unlike any other moon, it has a dense atmosphere. It has rivers and lakes made up of components of natural gas, such as ethane and methane. It also has windswept dunes that are hundreds of yards high, more than a mile wide and hundreds of miles long--despite data suggesting the body to have only light breezes.
Research led by Devon Burr, an associate professor in the Earth and Planetary Sciences Department at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, shows that winds on Titan must blow faster than previously thought to ...