New treatment strategy for epilepsy
Chemical chaperones correct the misfolding of the mutant protein
2014-12-09
(Press-News.org) Researchers found out that the conformational defect in a specific protein causes Autosomal Dominant Lateral Temporal Lobe Epilepsy (ADLTE) which is a form of familial epilepsy. They showed that treatment with chemical corrector called "chemical chaperone" ameliorates increased seizure susceptibility in a mouse model of human epilepsy by correcting the conformational defect. This was published in Nature Medicine (December 8, 2014 electronic edition).
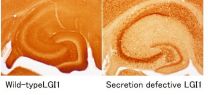
Mutations in the gene LGI1, encoding a secreted protein, cause familial temporal lobe epilepsy. The research group of Professor Masaki Fukata, Associate Professor Yuko Fukata, and Assistant Professor Norihiko Yokoi of the National Institute for Physiological Sciences (NIPS), National Institutes of Natural Sciences (NINS), in collaboration with the group of Professor Masahiko Watanabe of the Hokkaido University Graduate School of Medicine, Professor Dies Meijer of the Erasmus University Medical Center in the Netherlands, and Professor Takao Hamakubo of the Research Center for Advanced Science and Technology, The University of Tokyo, investigated 22 mutations in the LGI1 gene found in patients with human epilepsy. In 19 mutations, LGI1 mutant protein was secretion-defective. One of these mutations was introduced to mice which produced symptoms of epilepsy. In LGI1 mutant mice, there was a decrease in the amount of LGI1 functioning normally outside the cell (i.e., synapse) due to the degradation by an intrinsic quality control system that rapidly degrades and eliminates mutant proteins.
A small molecule called chemical chaperone (4-phenylbutyrate) was administrated to LGI1 mutant mice with a view to correct the misfolding of the LGI1 mutant protein and to cause normal secretion to the synapse. It was found that the mice had decreased seizure susceptibility.
Epilepsy is a common brain disorder that affects 1% of the population. In some cases, current antiepileptic drugs have a limited role in the treatment. According to Professor Masaki Fukata, "Chemical chaperone treatment focused on correcting the misfolding in proteins has been tried in inherited diseases including cystic fibrosis and lysosome disease. This is the first for chemical chaperones to be applied as a therapeutic option for epilepsy. The same therapeutic strategy may also be of benefit to epilepsy caused by genetic mutations other than LGI1 gene. We propose a novel therapeutic strategy for epilepsy."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-09
ALBUQUERQUE, N.M. -- Changing flesh to stone sounds like the work of a witch in a fairy tale.
But a new technique to transmute living cells into more permanent materials that defy rot and can endure high-powered probes is widening research opportunities for biologists who are developing cancer treatments, tracking stem cell evolution or even trying to understand how spiders vary the quality of the silk they spin.
The simple, silica-based method also offers materials scientists the ability to "fix" small biological entities like red blood cells into more commercially ...
2014-12-09
As sand dunes march across the Sahara, vast dunes cross the surface of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. New research from a refurbished NASA wind tunnel reveals the physics of how particles move in Titan's methane-laden winds and could help to explain why Titan's dunes form in the way they do. The work is published online Dec. 8 in the journal Nature.
"Conditions on Earth seem natural to us, but models from Earth won't work elsewhere," said Bruce White, professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at the University of California, Davis, and a co-author on the study. ...
2014-12-09
ATLANTA - December 9, 2014- A new American Cancer Society study finds that despite significant drops in smoking rates, cigarettes continue to cause about three in ten cancer deaths in the United States. The study, appearing in the Annals of Epidemiology, concludes that efforts to reduce smoking prevalence as rapidly as possible should be a top priority for the U.S. public health efforts to prevent cancer deaths.
More than 30 years ago, a groundbreaking analysis by famed British researchers, Richard Doll and Richard Peto, calculated that 30 percent of all cancer deaths ...
2014-12-09
Whether we're paying attention to something we see can be discerned by monitoring the firings of specific groups of brain cells. Now, new work from Johns Hopkins shows that the same holds true for the sense of touch. The study brings researchers closer to understanding how animals' thoughts and feelings affect their perception of external stimuli.
The results were published Nov. 25 in the journal PLoS Biology.
"There is so much information available in the world that we cannot process it all," says Ernst Niebur, Ph.D., a professor of neuroscience in the Johns Hopkins ...
2014-12-09
LIVERMORE, Calif. -- Large-scale storage of low-pressure, gaseous hydrogen in salt caverns and other underground sites for transportation fuel and grid-scale energy applications offers several advantages over above-ground storage, says a recent Sandia National Laboratories study sponsored by the Department of Energy's Fuel Cell Technologies Office.
Geologic storage of hydrogen gas could make it possible to produce and distribute large quantities of hydrogen fuel for the growing fuel cell electric vehicle market, the researchers concluded.
Geologic storage solutions ...
2014-12-09
Neuro-rehabilitation (physical therapy, occupational therapy, etc.) helps hemaparetic stroke patients confronted with loss of motor skills on one side of their body, to recover some of their motor functions after a cerebrovascular accident. One of the most promising tracks in neuro-rehabilitation consists in amplifying the motor learning ability after a stroke, in other words how to learn (again) how to make movements with the parts of the human body impacted after a stroke.
Pilot studies have shown at this matter that tDCS (transcranial direct current stimulation) - ...
2014-12-09
Nidelric pugio fossil dates to half a billion years ago and teaches us about the diversity of life in Earth's ancient seas
In life the animal was a 'balloon' shape and was covered in spines, but the squashed fossil resembles a bird's nest
Named in honour of Professor Richard Aldridge from the University of Leicester
A rare 520 million year old fossil shaped like a 'squashed bird's nest' that will help to shed new light on life within Earth's ancient seas has been discovered in China by an international research team - and will honour the memory of a University of ...
2014-12-09
Montreal, Canada, November x, 2014 - Angiochem, a clinical stage biotechnology company creating and developing drugs that cross the blood-brain barrier, today announced the publication in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics demonstrating that ANG4043, a peptide-monoclonal antibody (mAb) conjugate, entered the brain at therapeutic concentrations, resulting in significantly prolonged survival in mice. The antibody is directed against HER2, which is the protein targeted by Herceptin®. Because the mAb is conjugated to Angiopep-2, it is recognized by the LRP1 receptor and takes ...
2014-12-09
Phoenix, AZ (December 9th, 2014) - Healthy, elderly research participants who report being more sleepy and less rested have higher levels of amyloid deposition in regions of the brain that are affected in Alzheimer's disease, according to a report presented today at the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology annual meeting in Phoenix (Arizona). If sleep disturbance is a cause of amyloid accumulation, it may be an early target for intervention to prevent the progression of cognitive deficits in late life.
Numerous studies have shown the importance of sleep and the ...
2014-12-09
Phoenix, AZ (December 9th, 2014) - Abnormalities in the prefrontal cortex and related brain areas are observed in adolescents who have attempted suicide, according to a report today at the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology annual meeting in Phoenix Arizona. The study suggests that deficits in frontal systems may be associated with risk for suicide attempts in youths with mood disorders.
Most suicide attempts occur in the context of mood disorders, including bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder. Bipolar disorder has a prevalence of 3-4% in the U.S. population, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New treatment strategy for epilepsy
Chemical chaperones correct the misfolding of the mutant protein