INFORMATION:
CONTACT: SAN DIEGO ZOO GLOBAL
PUBLIC RELATIONS
619-685-3291
WEB SITE: http://www.sandiegozoo.org
With experience, people can tell bears apart
2014-12-10
(Press-News.org) Studying the social interaction of bears through the use of camera traps and visual observations requires that humans be able to tell individuals apart. A study done using volunteers to study the vulnerable Andean bear indicates that people can learn to identify individual bears, given a little practice. The research, done by San Diego Zoo conservationists with international collaborators using photos spanning many years, also indicates that young bears usually retain many of their unique markings as they grow older.
"Knowing, scientifically, that people who have been trained to identify individual bears can do so with a reasonable expectation of accuracy helps us to know that the work we are doing to learn about these bears is based on good science, not just personal opinion" said Russ Van Horn, Ph.D., a lead researcher on the study and a research scientist for the San Diego Zoo Institute for Conservation Research. "It also allows us more freedom to engage local citizen scientists in the effort to save the species around them."
Published in a recent issue of "Wildlife Biology," the study used photos of Andean bears in many different zoos.
Bringing species back from the brink of extinction is the mission of San Diego Zoo Global. As a leader in conservation, the work of San Diego Zoo Global includes onsite wildlife conservation efforts (representing both plants and animals) at the San Diego Zoo, San Diego Zoo Safari Park, and San Diego Zoo Institute for Conservation Research, as well as international field programs on six continents. The important conservation and science work of these entities is made possible by the San Diego Zoo Wildlife Conservancy and is supported in part by the Foundation of the Zoological Society of San Diego.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
German researchers propose better substances for treating the dengue virus
2014-12-10
Researchers from Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) and the Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg are proposing potential new active substances for treating the dengue virus. Just like Ebola, dengue fever is also caused by a virus for which there is currently no cure and no vaccine and can be fatal.
In the quest for medication to treat the dengue virus, the scientific community is focusing on a particular enzyme of the pathogen, the protease known as NS2B/NS3. The reason for this is that inhibitors of similar proteases have been revealed to be very effective ...
Immune function marker does not predict benefit of trastuzumab in HER-2+ breast cancer
2014-12-10
JACKSONVILLE, Fla. -- A marker of immune function that predicts for better outcomes in patients treated with chemotherapy for triple negative breast cancer is also linked to improved prognosis in patients treated with chemotherapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. But that marker -- the quantity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (S-TILs) in a biopsy -- appears irrelevant when trastuzumab is used.
And since trastuzumab, and not chemotherapy alone, is the standard of care for the HER2-positive sub-class of breast cancer, there is no need to test for these lymphocytes in ...
Early trial of new drug shows promise for patients with triple-negative breast cancer
2014-12-10
In patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer--a disease with no approved targeted therapies--infusion of pembrolizumab produced durable responses in almost one out of five patients enrolled in a phase-Ib clinical trial, according to data presented Dec. 10, at the 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium.
The multi-center, non-randomized trial was designed to evaluate the safety, tolerability and antitumor activity of bi-weekly infusions of pembrolizumab (MK-3475, marketed as Keytruda®). The researchers enrolled 27 patients, aged 29 to 72 years, who had ...
Link between power lines and ill-health called into question
2014-12-10
Several past studies have suggested that the magnetic fields created by phones, high-voltage power lines and other electrical equipment are harmful for humans.
Research first carried out in the 1970's and again subsequently, found an association between people living near overhead power lines and an increased risk of childhood leukaemia. Although some later studies have failed to find such a link, the International Agency for Research on Cancer has categorised low frequency magnetic fields as "possibly carcinogenic."
But a mechanism for this association has never been ...
Brain inflammation a hallmark of autism, large-scale analysis shows
2014-12-10
While many different combinations of genetic traits can cause autism, brains affected by autism share a pattern of ramped-up immune responses, an analysis of data from autopsied human brains reveals. The study, a collaborative effort between Johns Hopkins and the University of Alabama at Birmingham, included data from 72 autism and control brains. It will be published online Dec. 10 in the journal Nature Communications.
"There are many different ways of getting autism, but we found that they all have the same downstream effect," says Dan Arking, Ph.D. , an associate professor ...
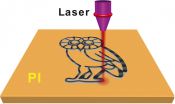
Defects are perfect in laser-induced graphene
2014-12-10
HOUSTON - (Dec. 10, 2014) - Researchers at Rice University have created flexible, patterned sheets of multilayer graphene from a cheap polymer by burning it with a computer-controlled laser. The process works in air at room temperature and eliminates the need for hot furnaces and controlled environments, and it makes graphene that may be suitable for electronics or energy storage.
Under a microscope, what the researchers call laser-induced graphene (LIG) doesn't look like a perfect chicken wire-like grid of atoms. Instead, it's a jumble of interconnected graphene flakes ...
Brain reward circuits respond differently to 2 kinds of sugar
2014-12-10
Phoenix, AZ (December 10th, 2014) - The brain responds differently to two kinds of sugar, according to a report today at the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology annual meeting in Phoenix Arizona. The study suggests that fructose heightens the response of brain reward circuits to food cues, promoting feeding behavior.
Currently, roughly two out of three U.S. adults are overweight and one out of three is obese. Changes in lifestyle and dietary intake during the past quarter century are thought to be the main culprits, with the increase in fructose consumption of ...
Alcohol-control law may curb partner abuse
2014-12-10
PISCATAWAY, NJ - Communities with fewer places to buy or drink alcohol also tend to have lower rates of intimate partner violence, new evidence suggests.
The research, published in the January issue of the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs, suggests that laws limiting what is called "alcohol outlet density" could offer one way to address violence within intimate relationships.
States and communities throughout the United States have enacted various laws to reduce excessive use of alcohol, including limiting outlet density, limiting hours and days of sale, and ...
Saving old information can boost memory for new information
2014-12-10
The simple act of saving something, such as a file on a computer, may improve our memory for the information we encounter next, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The research suggests that the act of saving helps to free up cognitive resources that can be used to remember new information.
Our findings show that people are significantly better at learning and remembering new information when they save previous information," says psychological scientist and study author Benjamin Storm of ...
Drug developed at Pitt proves effective against antibiotic-resistant 'superbugs'
2014-12-10
PITTSBURGH, Dec. 9, 2014 - A treatment pioneered at the University of Pittsburgh Center for Vaccine Research (CVR) is far more effective than traditional antibiotics at inhibiting the growth of drug-resistant bacteria, including so-called "superbugs" resistant to almost all existing antibiotics, which plague hospitals and nursing homes.
The findings, announced online in the journal Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy and funded by the National Institutes of Health, provide a needed boost to the field of antibiotic development, which has been limited in the last four ...