Heat boosts phthalate emissions from vinyl crib mattress covers
2014-12-17
(Press-News.org) The U.S. continues to look at the use and regulation of phthalates, which have been associated with health problems. Of particular concern is the safety of these plastic additives to children. A new study aims to improve our understanding of one possible exposure route for babies: vinyl crib mattress covers. Scientists report in ACS' Environmental Science & Technology that as these covers warm up, they emit more phthalates into the air.
Ying Xu and Yirui Liang note that previous studies have linked phthalates, which soften plastics, to potential health effects, including reproductive issues and an increased risk for asthma and allergies. In response, the U.S. Congress banned six kinds of phthalates from toys in 2008, and manufacturers have been turning to alternative plasticizers, which are different phthalates. But little is known about the toxicity of these replacements or whether they waft into the air infants breathe for 12 to 14 hours per day at potentially harmful levels. Xu and Liang decided to find out whether infants, who breathe in far more air (given their low body weight) than adults, might be getting exposed to high levels of alternative phthalates.
The researchers tested the amounts of the alternative-phthalate plasticizers released from vinyl crib mattress covers at different temperatures and estimated how much of that the infants might breathe in. They found that, under warm conditions, the covers emitted significantly higher levels of phthalates that could cause a baby's exposure to increase four-fold. They say the preliminary study is an essential first step to investigating the potential risk posed by these new phthalates.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Science Foundation.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-17
A new study by a team of researchers that includes University of Notre Dame scientists Joshua Shrout and Mark Alber provides new insights into the behavior of an important bacterial pathogen.
Alber, Vincent J. Duncan Family Professor of Applied Mathematics, and Schrout, an associate professor of civil and environmental engineering and earth sciences, studied Pseudomonas aeruginosa, an opportunistic pathogen responsible for both acute and persistent infections.
"While this ubiquitous environmental bacterium rarely infects healthy people, it is a common pathogen among ...
2014-12-17
ALAMEDA, Calif. - December 17, 2014 - Penumbra, Inc., the market leader in intra-arterial stroke treatment, announced that an independent study published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine found that intra-arterial stroke treatment, including the company's clot extraction technology, was shown to be significantly more effective than medical management with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), which is the current standard of care. The findings of this randomized, controlled comparative effectiveness trial of stroke treatment have the potential to change ...
2014-12-17
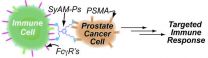
New Haven, Conn. - A Yale University lab has crafted the first synthetic molecules that have both the targeting and response functions of antibodies.
The new molecules -- synthetic antibody mimics (SyAMs) -- attach themselves simultaneously to disease cells and disease-fighting cells. The result is a highly targeted immune response, similar to the action of natural human antibodies.
"Unlike antibodies, however, our molecules are synthetic organic compounds that are approximately one-twentieth the size of antibodies," said David A. Spiegel, a professor of chemistry at ...
2014-12-17
Promising treatments known as biologics are on the market and under development for many serious illnesses such as cancer, but some of them come with high risks, even lethal ones. Now scientists have produced a novel class of molecules that could be as effective but without the dangerous side effects. They report their work on these compounds, which they tested on prostate cancer cells, in ACS' Journal of the American Chemical Society.
David A. Spiegel and colleagues explain that biologics are protein-based therapies that have revolutionized cancer treatment over the ...
2014-12-17
It takes some cooking, but turning farm waste into biofuels is now possible and makes economic sense, according to preliminary research from the University of Guelph.
Guelph researchers are studying how to make biofuels from farm waste, especially "wet" waste that is typically difficult to use. They have developed a fairly simple procedure to transport waste and produce energy from it.
Scientists have struggled to find uses for wet and green waste, including corn husks, tomato vines and manure. Dry farm waste, such as wood chips or sawdust, is easier to use for generating ...
2014-12-17
Many consumers seek out shampoos, soaps and cosmetics that are labeled "hypoallergenic" or "dermatologist tested," words that imply the products are safe to use. But recent research gives shoppers reason to question what those labels really mean. Now some scientists and consumer advocates are calling for change, according to an article in Chemical & Engineering News (C&EN), the weekly newsmagazine of the American Chemical Society.
Britt E. Erickson, a senior editor at C&EN, notes that the definitions of the terms "hypoallergenic" and "dermatologist tested/recommended" ...
2014-12-17
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- It may be beneficial for employers to not only encourage office Christmas parties but also celebrate holidays and festivals from a variety of religions, according to a Kansas State University researcher.
Sooyeol Kim, doctoral student in psychological sciences, was involved in a collaborative study that found that employees who openly discuss their religious beliefs at work are often happier and have higher job satisfaction than those employees who do not.
"For many people, religion is the core of their lives," Kim said. "Being able to express important ...
2014-12-17
SAN FRANCISCO--A new study is helping to answer a longstanding question that has recently moved to the forefront of earth science: Did our planet make its own water through geologic processes, or did water come to us via icy comets from the far reaches of the solar system?
The answer is likely "both," according to researchers at The Ohio State University-- and the same amount of water that currently fills the Pacific Ocean could be buried deep inside the planet right now.
At the American Geophysical Union (AGU) meeting on Wednesday, Dec. 17, they report the discovery ...
2014-12-17
SAN FRANCISCO--Of the many weather-related factors that contribute to harmful algal blooms (HABs) in Lake Erie, a new study has identified one as most important: the wind.
Over a 10-year period in Lake Erie, wind speed contributed more consistently to HABs than sunshine or even precipitation, researchers at The Ohio State University and their colleagues found.
The ongoing study is unusual, in that researchers are building the first detailed analyses of how the various environmental factors influence each other--in the context of satellite studies of Lake Erie.
They ...
2014-12-17
Singapore, Date - A more effective treatment for tuberculosis (TB) could soon be available as scientists have discovered that Metformin (MET), a drug for treating diabetes, can also be used to boost the efficacy of TB medication without inducing drug resistance.
This discovery was made by a team of international scientists led by the Singapore Immunology Network (SIgN), a research institute under the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore.
TB is an air-borne infectious disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Heat boosts phthalate emissions from vinyl crib mattress covers