Scientists reveal breakthrough in optical fiber communications
2014-12-19
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the University of Southampton have revealed a breakthrough in optical fibre communications.
Academics from the University's Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) have collaborated with colleagues at Eblana Photonics Inc, in Ireland, to develop an approach that enables direct modulation of laser currents to be used to generate highly advanced modulation format signals.
The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, explores a radically new approach to the generation of spectrally-efficient advanced modulation format signals as required in modern optical communication systems.
This new technology, patented by the University of Southampton and licensed to Eblana Photonics Inc, avoids the need for costly and power-inefficient external modulator schemes that are currently used to generate such signals.
Dr Radan Slavik, Principal Research Fellow at the ORC, said: "Our paper highlights the exquisite control that we have achieved over the optical field generated directly from a current-modulated semiconductor laser."
Direct current modulated lasers are of huge commercial relevance and are already widely used in optical communications, telecommunications and sensor and high power fibre laser systems. However, the inability to accurately control the full optical field emitted directly from such lasers has been a fundamental problem limiting applications.
Dr Slavik explains: "The new capability we have demonstrated will be of relevance and could be of significant impact within many scientific and engineering communities that are directly concerned with or exploit laser radiation.
"We have previously presented some of the results included in this paper at conferences, including a post-deadline presentation at Optical Fibre Communications (OFC), and at an international symposium and this has already generated a lot of interest from senior academics in our community, as well as from leading industrial players."
Dr Rob Lennox, Director of Sales at Eblana Photonics Ltd., Dublin, said: "We are very pleased to have collaborated on this innovative development work performed by the ORC team and are looking towards making this new approach a commercial reality."
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-19
Carnivorous plants catch and digest tiny animals in order and derive benefits for their nutrition. Interestingly the trend towards vegetarianism seems to overcome carnivorous plants as well. The aquatic carnivorous bladderwort, which can be found in many lakes and ponds worldwide, does not only gain profit from eating little animals but also by consuming algae and pollen grains. This results in survival in aquatic habitats where prey animals are rare, and in increased fitness if the animals and algae are caught in a well-balanced diet. An Austrian research group around ...
2014-12-19
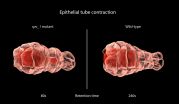
Researchers at the Mechanobiology Institute (MBI), National University of Singapore (NUS) have identified a novel mechanosensitive regulation of epithelial tube contraction. These findings are published on 19 December 2014 in Current Biology (Pei Yi Tan and Ronen Zaidel-Bar. Transient membrane localization of SPV-1 drives cyclical actomyosin contractions in the C. elegans spermatheca, Current Biology, 19 Dec 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.033)
Regulating tube constriction
Many of the fundamental processes of life rely on biological structures known as epithelial ...
2014-12-19
Over the past decade, ocean acidification has received growing recognition not only in the scientific area. Decision-makers, stakeholders, and the general public are becoming increasingly aware of "the other carbon dioxide problem". It is time to reflect on the successes and deficiencies of ocean acidification research and to take a look forward at the challenges the fastest growing field of marine science is facing. In the January issue of the journal Nature Climate Change Ulf Riebesell, professor for Biological Oceanography at GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research ...
2014-12-19
Bremerhaven/Germany, 18 December 2014. Ingestion of microplastic particles does not mechanically affect marine isopods. This was the result of a study by biologists at the North Sea Office of the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) that was published recently in the journal Environmental Science and Technology. The study marks the launch of a series of investigations aimed at forming a risk matrix on the sensitivity of different marine species to microplastic pollution.
Uptake of large plastic items by birds and fish may cause ...
2014-12-19
In a recent study from Lund University in Sweden, researchers have used new technology to study extremely fast processes in solar cells. The research results form a concrete step towards more efficient solar cells.
The upper limit for the efficiency of normal solar cells is around 33 per cent. However, researchers now see a possibility to raise that limit to over 40 per cent, thereby significantly improving the potential of this energy source.
The experiments in the present study involved 'juggling' on quantum level with photons, i.e. light particles, and electrons. ...
2014-12-19
In everyday life, the global positioning system (GPS) can be employed to reliably determine the momentary location of one en route to the desired destination. Scientists from the Institute of Physical and Theoretical Chemistry of the University of Bonn have now developed a molecular "GPS" with which the whereabouts of metal ions in enzymes can be reliably determined. Such ions play important roles in all corners of metabolism and synthesis for biological products. The "molecular GPS" is now being featured in the journal Angewandte Chemie.
There would be no life on our ...
2014-12-19
Bethesda, MD (Dec. 19, 2014) -- A new formulation of oral budesonide suspension, a steroid-based treatment, is safe and effective in treating pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE), according to a new study in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association. Eosinophilic esophagitis is a chronic immune system disease caused by a buildup of white blood cells in the lining of the esophagus. This build up, which is a reaction to food, allergens or acid reflux, can inflame or injure ...
2014-12-19
The changes can be measured, but their reasons were unknown. For several decades, scientists have carefully observed that the oxygen minimum zones (OMZ) in the tropical oceans are expanding. These zones are a paradise for some specially adapted microorganisms, but for all larger marine organisms such as fish and marine mammals they are uninhabitable. Thus, their expansion has already narrowed down the habitat of some fish species.
Marine scientists from the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel and the Kiel Collaborative Research Centre (Sonderforschungsbereich, ...
2014-12-19
PITTSBURGH--University of Pittsburgh researchers have shared their findings from three studies related to shale gas in a recent special issue of the journal Energy Technology, edited by Götz Veser, the Nickolas A. DeCecco Professor of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering in Pitt's Swanson School of Engineering.
In the special issue focusing on shale gas, Pitt faculty authors look at "smart wells" that use wireless communication, wastewater management, and information gaps between legislators, regulators, industry representatives, researchers, and the public on the ...
2014-12-19
Scientists from the Southwest University, Chongqing, China have found a new species and a new subspecies of cockroach. What makes these creepy crawlies distinctive from the cockroaches most of us know is that they don't infest human houses, on the contrary they prefer to live a hermit life drilling logs, hidden away from human eyes. The study was published in the open access journal ZooKeys.
Out of around 4,600 species worldwide, only 30 are the cockroaches associated with human habitats that gives the bad fame of these creatures. The representatives of the genus Panesthia, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists reveal breakthrough in optical fiber communications