(Press-News.org) Women whose loved ones are critical of their weight tend to put on even more pounds, says a new study on the way people's comments affect our health.
Professor Christine Logel from Renison University College at the University of Waterloo led the study, which appears in the December issue of the journal Personal Relationships.
"When we feel bad about our bodies, we often turn to loved ones--families, friends and romantic partners--for support and advice. How they respond can have a bigger effect than we might think," said Professor Logel, who teaches social development studies.
The study found that women who received a higher number of what the researchers called acceptance messages about their weight saw better weight maintenance and even weight loss than their counterparts who did not receive this positive messaging from their loved ones.
The researchers studied university-age women, a demographic often dissatisfied with personal weight. The team of social psychologists asked the women their height and weight, and how they felt about what they see on the scale. About five months later, they asked them if they had talked to their loved ones about their concerns, and if so, how they had responded. About three months after that, they tracked whether their weight and their concerns about it changed in that time.
"On average, the women in the study were at the high end of Health Canada's BMI recommendations, so the healthiest thing is for them to maintain the weight they have and not be so hard on themselves, " said Professor Logel. "But many of the women were still very concerned about how much they weigh, and most talked to their loved ones about it."
Overall, the women in the sample gained some weight over time, which is not uncommon for young adults. But if the women got the message from their loved ones that they look fine, then they maintained or even lost a bit of weight. Women who received comparatively few weight acceptance messages from their loved ones gained almost 4.5 pounds on average, whereas women who received comparatively more weight acceptance messages lost a pound.
The results showed that when women concerned about their weight heard that their loved ones accepted them as they are, they felt better about their bodies, and subsequently they did not gain like other women did.
"Lots of research finds that social support improves our health," said Professor Logel. "An important part of social support is feeling that our loved ones accept us just the way we are."
Pressure from loved ones about weight loss was not helpful for women already concerned about it. And it actually led women who weren't originally concerned about their weight to gain some weight.
"We all know someone who points out our weight gain or offers to help us lose weight. These results suggest that these comments are misguided," said Professor Logel.
The research suggests that feeling better about themselves caused the women to be more active or eat more sensibly. Receiving unconditional acceptance might have lowered their stress, a known cause of weight gain.
INFORMATION:
WASHINGTON D.C., December 19, 2014 - Researchers at Montana State University and Brandenburg University of Applied Sciences in Germany have created a simple mathematical model based on optical measurements that explains the stunning colors of Yellowstone National Park's hot springs and can visually recreate how they appeared years ago, before decades of tourists contaminated the pools with make-a-wish coins and other detritus.
The model, and stunning pictures of the springs, appear today in the journal Applied Optics, which is published by The Optical Society (OSA).
If ...
Despite showing interest in web or mobile apps to help manage their Type 2 diabetes, only a small number of older adults actually use them, says a new study from the University of Waterloo. Approximately 2.2 million Canadians are living with Type 2 diabetes, 2 million of whom are age 50 or older.
The study, which appears in the online edition of the Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, found that although more than 90 per cent of research participants owned a computer or had daily Internet access, just 18 per cent used applications on this technology to help manage ...
The lithium-ion batteries that mobilize our electronic devices need to be improved if they are to power electric vehicles or
store electrical energy for the grid. Berkeley Lab researchers looking for a better understanding of liquid electrolyte may have found a pathway forward. A team led by Richard Saykally, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Chemical Sciences Division, David Prendergast, a theorist with Berkeley Lab's Molecular Foundry, and Steven Harris, a chemist with the Lab's Materials Sciences Division, found surprising results in the first X-ray absorption spectroscopy ...
It's like a scene from a gamer's wildest dreams: 12 high-definition, 55-inch 3D televisions all connected to a computer capable of supporting high-end, graphics-intensive gaming.
On the massive screen, images are controlled by a Wii remote that interacts with a Kinnect-like Bluetooth device (called SmartTrack), while 3D glasses worn by the user create dizzying added dimensions.
But this real-life, computer-powered mega TV is not for gaming. It's for engineering.
Welcome to Brigham Young University's VuePod, a 3D immersive visualization environment run by BYU's Department ...
New research indicates that reducing emergency surgery for three common procedures by 10 percent could cut $1 billion in health care costs over 10 years.
As hospitals and health systems increasingly focus on addressing the rising cost of health care in the United States, and with the expense of surgical care playing a major role, physician researchers and others across the healthcare industry are working to identify innovative ways to reduce surgical costs.
In new findings published online in the journal Annals of Surgery on December 19, 2014, researchers determined ...
Researchers from the University of Southampton have revealed a breakthrough in optical fibre communications.
Academics from the University's Optoelectronics Research Centre (ORC) have collaborated with colleagues at Eblana Photonics Inc, in Ireland, to develop an approach that enables direct modulation of laser currents to be used to generate highly advanced modulation format signals.
The research, published in the journal Nature Communications, explores a radically new approach to the generation of spectrally-efficient advanced modulation format signals as required ...
Carnivorous plants catch and digest tiny animals in order and derive benefits for their nutrition. Interestingly the trend towards vegetarianism seems to overcome carnivorous plants as well. The aquatic carnivorous bladderwort, which can be found in many lakes and ponds worldwide, does not only gain profit from eating little animals but also by consuming algae and pollen grains. This results in survival in aquatic habitats where prey animals are rare, and in increased fitness if the animals and algae are caught in a well-balanced diet. An Austrian research group around ...
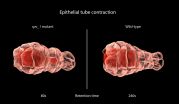
Researchers at the Mechanobiology Institute (MBI), National University of Singapore (NUS) have identified a novel mechanosensitive regulation of epithelial tube contraction. These findings are published on 19 December 2014 in Current Biology (Pei Yi Tan and Ronen Zaidel-Bar. Transient membrane localization of SPV-1 drives cyclical actomyosin contractions in the C. elegans spermatheca, Current Biology, 19 Dec 2014, doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2014.11.033)
Regulating tube constriction
Many of the fundamental processes of life rely on biological structures known as epithelial ...
Over the past decade, ocean acidification has received growing recognition not only in the scientific area. Decision-makers, stakeholders, and the general public are becoming increasingly aware of "the other carbon dioxide problem". It is time to reflect on the successes and deficiencies of ocean acidification research and to take a look forward at the challenges the fastest growing field of marine science is facing. In the January issue of the journal Nature Climate Change Ulf Riebesell, professor for Biological Oceanography at GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research ...
Bremerhaven/Germany, 18 December 2014. Ingestion of microplastic particles does not mechanically affect marine isopods. This was the result of a study by biologists at the North Sea Office of the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) that was published recently in the journal Environmental Science and Technology. The study marks the launch of a series of investigations aimed at forming a risk matrix on the sensitivity of different marine species to microplastic pollution.
Uptake of large plastic items by birds and fish may cause ...