Melting glaciers create noisiest places in ocean, study says
Gushing bubbles create underwater soundscape
2015-03-06
(Press-News.org) Bubbles gushing from melting glaciers and their icebergs make fjords the noisiest places in the oceans, a new study of waters near Alaska and Antarctica shows.
The underwater noise is much louder than previously thought, researchers found. That led them to ask how the noise affects the behavior of harbor seals and whales in Alaska's fjords.
"The ocean ambient sound gives us clues to the physical processes going on, but it also is an important aspect of the environment in which marine mammals and fish live. Like teenagers at a loud rock concert, the seals and whales modify their behavior depending on the ambient sound levels," said Erin Pettit, a glaciologist from the University of Alaska Fairbanks Department of Geosciences.
Pettit conducted the study with researchers from the University of Texas at Austin, the University of Washington in Seattle and the U.S. Geological Survey. The results were published by Geophysical Research Letters, one of the American Geophysical Union's journals.
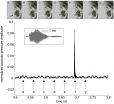
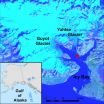
The team used underwater microphones to hear and record the average noise levels in three bays where glaciers flow into ocean fjords -- Icy Bay, Alaska; Yakutat Bay, Alaska; and Andvord Bay, Antarctica. All of the fjords have many icebergs from glacial calving.
The researchers found that the average underwater noise level from bubbles in these fjords exceeded ocean noise levels generated by all other sources, including weather, the movement and communication of fish, and machines such as ships and sonar devices. The team measured sound waves at frequencies between 300 and 20,000 Hertz, which covers most of the average human's hearing range.
Glacial calving contributed some of the noise, but the loud sounds were short-lived. When looking at overall noise levels for a long period of time, Pettit said it was the consistent melting of ice from the glaciers and their icebergs that was the real noise generator. Air trapped within the glacier ice escapes rapidly as it melts into saltwater, forming bubbles in the water that pop as they pinch off from the ice.
Pettit said their findings raise questions about how the underwater noise in the fjords will affect animals as climate change increases the rate at which glaciers melt into the ocean and then stops the process altogether as the glaciers retreat onto land.
She said fjords with glaciers are foraging hotspots for seabirds and marine mammals as well as important breeding locations for harbor seals. Seals might use the underwater noise to help hide from killer whales, which listen to locate their prey, she said. As glaciers retreat onto land, the seals would lose the acoustic camouflage, which might explain why harbor seal populations are declining in fjords where glaciers have retreated onto land, she said.
She said further studies are needed to investigate the relationship between the underwater noise levels and the fjord ecosystem. The team will continue listening to glaciers to see if they can develop a method of predicting glacier melt based on the underwater sounds.
INFORMATION:
ADDITIONAL CONTACT: Erin Pettit, glaciologist with the UAF Department of Geosciences, College of Natural Science and Mathematics, Erin Pettit: pettit@gi.alaska.edu
NOTE TO EDITORS: A movie of the bubbles in a lab setting and other multimedia content is available at the following links:
Bubbles in a lab video: http://www.explore-ice.gi.alaska.edu/bubble-movies/
Sounds of melting ice and calving: http://www.explore-ice.gi.alaska.edu/#/ice-ocean/
To see the paper: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2014GL062950/abstract?campaign=wlytk-41855.5282060185
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-06
No one really knows how the High Plains got so high. About 70 million years ago, eastern Colorado, southeastern Wyoming, western Kansas and western Nebraska were near sea level. Since then, the region has risen about 2 kilometers, leading to some head scratching at geology conferences.
Now researchers at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) and the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder have proposed a new way to explain the uplift: Water trapped deep below Earth's crust may have flooded the lower ...
2015-03-06
This news release is available in German. The water content of soil has a great impact on the regional climate, but many of the connections are still not clear. Researchers at ETH Zurich's Institute for Atmospheric and Climate Science, together with colleagues from Belgium and the Netherlands, examined when and where it rains most frequently on summer afternoons. They wanted to clarify whether more rain fell on days when the soil was dry or moist. And where exactly it was most likely to rain on these days. The contradictory findings of other scientists was the reason ...
2015-03-06
Good supervisors aren't easily duped by the motives of underlings who go the extra mile - they know when an employee is sucking up to them because of personal ambition, or when such actions truly have what's best for the organization at heart. This is one of the insights from a study in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology, led by Magda Donia of the University of Ottawa in Canada.
Supervisors play an important role in making decisions about rewards and promotions within an organization. They should therefore be able to effectively distinguish between so-called ...
2015-03-06
About four billion years ago, the young planet would have had enough water to cover its entire surface in a liquid layer about 140 metres deep, but it is more likely that the liquid would have pooled to form an ocean occupying almost half of Mars's northern hemisphere, and in some regions reaching depths greater than 1.6 kilometres.
"Our study provides a solid estimate of how much water Mars once had, by determining how much water was lost to space," said Geronimo Villanueva, a scientist working at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, USA, and lead ...
2015-03-06
PITTSBURGH--The ancient Mongols have a reputation for having been fierce warriors. A new study out of the University of Pittsburgh shows them to have been unmatched polluters.
Graduate student Aubrey Hillman recently published a paper in the journal Environmental Science & Technology that shows copper and silver production in southwest China produced tremendous quantities of harmful heavy metals, such as lead, silver, zinc, and cadmium, starting in 1500 BC and continuing through the era of the Mongol Yuan Dynasty (1271-1368 AD). Hillman is near to earning her PhD from ...
2015-03-06
(BOSTON and CAMBRIDGE) - In nature, pores can continuously control how a living organism absorbs or excretes fluids, vapors and solids in response to its environment; for example, tiny holes invisible to the naked eye called stomata cover a plant's leaves and stems as gated openings through which oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapors are transported in and out during photosynthesis and respiration. And some scientists have proposed that micropores in the tissues of the air sacs of human lungs can open or close to modulate fluid flow based on changes in air pressure or ...
2015-03-06
PITTSBURGH--"Why doesn't she just leave?" is a timeworn question about women trapped in relationships that are physically and/or emotionally abusive to them. Economic dependence is clearly part of the story--many women lack the financial means to leave and find themselves trapped by both poverty and abuse.
Of the women who do attempt to escape the abuse, some opt to petition a judge for a civil restraining order, also called a Protection From Abuse (PFA) order, for protection from abuse, harassment, threats, or intimidation. Research shows that PFAs can promote women's ...
2015-03-06
Fast food ads aimed at kids fail to de-emphasize toy premiums, making them deceptive by industry self-regulation standards. They also fail to emphasize healthy menu items, investigators at Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center have found. The research was published in the March 4 edition of the journal PLOS ONE.
"Kids were just as likely to notice the toy premiums in the kid's ads as they were the food, when their own standards require a de-emphasis on premiums compared to foods," said James D. Sargent, MD, researcher at Dartmouth-Hitchcock's Norris Cotton ...
2015-03-06
African American men at elevated risk for developing type 2 diabetes may have fewer beneficial and more harmful intestinal bacteria, according to research presented by University of Illinois at Chicago endocrinologist Dr. Irina Ciubotaru at the ENDO 2015 meeting in San Diego.
"The 'signature' of the gut microbiota - the relative abundance of various bacteria and other microbes in the digestive system - could be another useful tool in assessing a person's risk for developing diabetes," said Ciubotaru. Ciubotaru and her colleagues, including principal investigator Dr. Elena ...
2015-03-06
San Diego, CA--Losing as little as 30 minutes of sleep per day on weekdays can have long-term consequences for body weight and metabolism, a new study finds. The results will be presented Thursday, March 5, at ENDO 2015, the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society in San Diego.
"While previous studies have shown that short sleep duration is associated with obesity and diabetes, we found that as little as 30 minutes a day sleep debt can have significant effects on obesity and insulin resistance at follow up," said lead study author Professor Shahrad Taheri, MBBS, PhD, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Melting glaciers create noisiest places in ocean, study says
Gushing bubbles create underwater soundscape