(Press-News.org) New York University chemists have developed a computational approach for determining the viability and suitability of complex molecular structures--an advancement that could aid in the development of pharmaceuticals as well as a range of other materials.
"Understanding how molecules interact and achieve stable conformations in different environments is vital to many industries," says Mark Tuckerman, a professor in NYU's Department of Chemistry and the senior author of the study, which appears in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. "However, the number of possible configurations is enormous, and the pathways leading to the most stable ones are complex, which makes these favored structures difficult to nail down in computational searches."
"Our results offer an approach that can aid in predicting these optimal structures, providing the potential to enhance the production of everything from over-the-counter drugs to new LED materials," adds Tuckerman, also a professor at NYU's Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences and the NYU-East China Normal University Center for Computational Chemistry at NYU Shanghai.
Manufacturers need to know how to choose chemical compounds for a given function from a vast space of all possible compounds--dissolving once ingested, and not in the bottle, in the case of pharmaceuticals, or maintaining their form under harsh weather conditions in the case of construction materials.
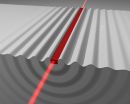
In order to understand the how best to go about predicting these structures, researchers rely on a construct called the free energy surface, a multidimensional mathematical object that reveals optimal spatial or geometrical configurations of a given system--whether it pertains to pharmaceuticals or computer chips. However, because the molecular constituents of such systems of interest and their interactions are often remarkably complex, elucidating these multi-dimensional free energy surfaces in order to derive the best "molecular answers" has presented significant challenges to scientists.
To help overcome this, the NYU team focused on a particular aspect of free energy surfaces: landmarks, which are considered, chemically and/or structurally, the most important features of these extremely complex, or high-dimensional, surfaces.
Specifically, relying on a computer simulation of free energy surfaces, they developed an algorithm designed to spot these landmarks while "seeing over" the terrain's high dimensionality.
The method, Tuckerman explains, "gives a rendering of a complex terrain that is computationally tractable by generating the most important and useful facets of free energy surfaces. From these facets, we can ultimately determine not only the most favored conformations of the constituent molecules and their spatial arrangements, but also the relative stability of these conformations and the likelihood of random conversions between them."
INFORMATION:
The paper's other authors are Ming Chen and Tang-Qing Yu, both doctoral candidates in NYU's Department of Chemistry.
The study was supported, in part, by a grant from the National Science Foundation (CHE-1301314)
Scientists from the University of Southampton have found that ocean tides have changed significantly over the last century at many coastal locations around the world.
Increases in high tide levels and the tidal range were found to have been similar to increases in average sea level at several locations.
The findings of the study are published online in the journal Earth's Future.
It is well documented that global average sea levels are rising; but tide levels, have generally been considered to have undergone little change on decadal time scales. It is also often ...
New Haven, Conn. - For once, slower is better in a new piece of technology.
A Yale lab has developed a new, radio frequency processing device that allows information to be controlled more effectively, opening the door to a new generation of signal processing on microchips. One of the keys to the technology involves slowing information down.
The new system, described in the March 5 edition of the journal Nature Communications, combines photons and phonons -- electromagnetic energy and sound energy -- to conduct sophisticated signal processing tasks by harnessing the properties ...
Dr. Liang Luo and associate prof. Jianchao Cai, a renowned researcher on fractal and capillarity and guest chief editor of FRACTALS, have published their latest paper entitled Numerical simulation of tortuosity for fluid flow in two-dimensional pore fractal models of porous media.
The tortuosity of different generations of Sierpinski carpet is calculated and analyzed by the finite volume method. A simple linear relation between the generations and tortuosity in pore fractal model of porous media is obtained. The results show a more realistic tortuosity predication for ...
Weight loss surgery does not stunt the growth of obese children when applied within a clinical pathway. It is a safe option to use and provides hope for youngsters who are unable to shed pounds through weight management programs that include counseling and lifestyle changes. So says Professor Aayed Alqahtani of King Saud University (KSU) in Saudi Arabia, after tracking the progress of almost 300 children who had all undergone such surgery through a standardized clinical pathway that was created and applied by Alqahtani in his practice at KSU. The findings are published ...
Over the next two centuries, climate change is likely to impact everything from industrial agriculture to the shape of our coastlines. The changing climate will certainly cause huge changes around the world, and the challenge is to predict exactly what impact those changes will have.
In the world of marine science, this means grappling with a process called ocean acidification. As human activity pumps carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, some of the carbon dioxide gets absorbed into the sea, which raises its acidity.
Scientists have been concerned about this for more than ...
The planet candidate was spotted using a spectrometer which measures the 'wobble', small changes in the wavelength of light emitted by a star, caused as a planet orbits it. In 2014 researchers revisiting the data said that the 'planet' was actually just noise in the data caused by starspots. The possible existence of the planet was widely dismissed without further questioning.
But now researchers from Queen Mary University of London (QMUL) and University of Hertfordshire have questioned the methods used to challenge the planet's existence. The statistical technique used ...
LOS ANGELES (March 5, 2015) - The benefits of weight loss surgery, along with a treatment plan that includes exercise and dietary changes, are well documented. In addition to a significant decrease in body mass, many patients find their risk factors for heart disease are drastically lowered and blood sugar regulation is improved for those with Type 2 diabetes.
Some patients, however, do not experience the optimal weight loss from bariatric surgery. The presence of a specific methane gas-producing organism in the gastrointestinal tract may account for a decrease in optimal ...
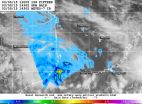
Tropical Cyclone 15S formed in the Mozambique Channel of the Southern Indian Ocean, and the Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core satellite gathered data on its rainfall rates.
The GPM (core satellite) flew over the northwestern half of newly formed Tropical Cyclone 15S on March 5 at 15:36 UTC (10:36 a.m. EST). The GPM satellite is managed by both NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency known as JAXA.
GPM's Microwave Imager (GMI) instrument found that the heaviest precipitation was then occurring on the western side of the circulation center. Powerful ...
Bubbles gushing from melting glaciers and their icebergs make fjords the noisiest places in the oceans, a new study of waters near Alaska and Antarctica shows.
The underwater noise is much louder than previously thought, researchers found. That led them to ask how the noise affects the behavior of harbor seals and whales in Alaska's fjords.
"The ocean ambient sound gives us clues to the physical processes going on, but it also is an important aspect of the environment in which marine mammals and fish live. Like teenagers at a loud rock concert, the seals and whales modify ...
No one really knows how the High Plains got so high. About 70 million years ago, eastern Colorado, southeastern Wyoming, western Kansas and western Nebraska were near sea level. Since then, the region has risen about 2 kilometers, leading to some head scratching at geology conferences.
Now researchers at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) and the Department of Geological Sciences at the University of Colorado Boulder have proposed a new way to explain the uplift: Water trapped deep below Earth's crust may have flooded the lower ...