(Press-News.org) San Diego, CA--A treatment known as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) may decrease fasting glucose and improve quality of life in overweight and obese women, new research suggests. The results will be presented in a poster Friday, March 6, at ENDO 2015, the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society in San Diego.
MBSR is a secular mindfulness meditation program that was developed by Jon Kabat-Zinn, PhD at the University of Massachusetts Medical School. The practice of MBSR involves paying attention to one's thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations in the present moment in a nonjudgmental and nonreactive manner through mindfulness exercises such as breathing awareness. MBSR may be beneficial for overweight and obese women as it has been shown to reduce stress and improve quality of life.
"In overweight and obese women, stress may contribute to increased diabetes and cardiovascular disease," said Nazia Raja-Khan, MD, assistant professor of medicine and obstetrics and gynecology at the Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, Pennsylvania. "MBSR significantly reduces fasting glucose and improves quality of life without changing body weight or insulin resistance. Increased mindfulness and reduced stress may lead to physiological changes in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and/or sympathetic nervous system that result in lower glucose levels."
Dr. Raja-Khan and her colleagues conducted a pilot randomized controlled trial of 86 overweight or obese women who were similar in age and body mass index. The women received 8 weeks of either MBSR or health education control (HEC) and underwent fasting blood work and completed questionnaires at baseline, 8 weeks and 16 weeks.
The MBSR group's mindfulness scores significantly increased and its perceived stress scores significantly decreased, compared to the HEC group's scores. While sleep, depression, anxiety and overall psychological distress improved in both groups, fasting glucose dropped significantly and quality of life improved significantly in the MBSR group, but not in the HEC group.
Weight, body mass index, blood pressure, lipid profile, hemoglobin A1c, fasting insulin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) remained similar with MBSR.
"Given the increasing epidemics of obesity and diabetes, this study is particularly relevant to the general public, as it demonstrates that stress management, specifically with mindfulness-based interventions such as MBSR, may be beneficial for reducing perceived stress and blood glucose and improving quality of life in overweight or obese women," said Raja-Khan. "This research supports the integration of mindfulness-based interventions with conventional medical approaches to obesity and diabetes prevention and treatment."
The NIH National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (NCCAM) and the NIH National Center for Research Resources and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences funded the study.
INFORMATION:
Founded in 1916, the Endocrine Society is the world's oldest, largest and most active organization devoted to research on hormones and the clinical practice of endocrinology. Today, the Endocrine Society's membership consists of over 18,000 scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. Society members represent all basic, applied and clinical interests in endocrinology. The Endocrine Society is based in Washington, DC. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at http://www.endocrine.org. Follow us on Twitter at https://twitter.com/#!/EndoMedia.
San Diego, CA--A mother's age at childbirth may affect her male baby's birth weight as well as his adult glucose metabolism, new research shows. The results will be presented Friday, March 6, at ENDO 2015, the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society in San Diego.
"Our findings indicate that women giving birth at a very young (under 25 years) or older (over 34 years) age might result in less favorable sugar handling and thus possibly higher risk for developing type 2 diabetes in their sons," said Charlotte Verroken, MD, of the Department of Endocrinology of Ghent University ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. - March 6, 2015) The St. Jude Children's Research Hospital--Washington University Pediatric Cancer Genome Project reports that a highly aggressive form of leukemia in infants has surprisingly few mutations beyond the chromosomal rearrangement that affects the MLL gene. The findings suggest that targeting the alteration is likely the key to improved survival. The research appeared online ahead of print this week in the scientific journal Nature Genetics.
The study is the most comprehensive analysis yet of this rare but aggressive subtype of pediatric acute ...
Alexandria, VA-- Children born during, and up to three years after, the devastating 1997-1998 El Niño event in northern Peru were found to be shorter than their peers in a new study covered in EARTH Magazine. The rising waters wiped out crops, drowned livestock, cut off bridges, and caused prolonged famine in many rural villages. Now, a new study that tracked long-term health impacts on children from the affected region has found that a decade later, the children continue to bear signs of the hardship endured early in their lives.
Learn how the children's health ...
(Boston)--In a review article recently published in the journal Clinical and Translational Medicine, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) shed new light on the underlying processes of tumor metastasis and highlight the role of epigenetics in this process. By comparing embryogenesis with cancer metastasis they hypothesize that reversible epigenetic events regulate the development of different types of metastatic cancers. They also describe that the surrounding cells of the tumors (stromal cells) play a significant role in this process.
The BUSM ...
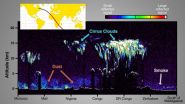
From Saharan dust storms to icy clouds to smoke on the opposite side of the continent, the first image from NASA's newest cloud- and aerosol-measuring instrument provides a profile of the atmosphere above Africa.
The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System instrument (CATS), was launched Jan. 10 aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, and was installed on the International Space Station on Jan. 22. From its berth on the station, CATS sends laser pulses toward Earth, detecting the photons that bounce off of particles in the atmosphere to measure clouds, volcanic ash, pollutants, dust ...
If you walk into your local drug store and ask for a supplement to help you sleep, you might be directed to a bottle labeled "melatonin." The hormone supplement's use as a sleep aid is supported by anecdotal evidence and even some reputable research studies. However, our bodies also make melatonin naturally, and until a recent Caltech study using zebrafish, no one knew how--or even if--this melatonin contributed to our natural sleep. The new work suggests that even in the absence of a supplement, naturally occurring melatonin may help us fall and stay asleep.
The study ...
(Boston)--Racial and ethnic disparities in the receipt of health care (typically referring to minorities not receiving needed care) are well known. A recent review in the journal Milbank Memorial Quarterly has now found that while race/ethnicity is not consistently associated with the overuse of medical care (unnecessary care that does not improve patient outcomes). However, when overuse occurs, a substantial proportion occurs among white patients. These findings may lead to a better understanding of how and why race/ethnicity might be associated with overuse and may result ...
(WASHINGTON, March, 6, 2015) - A report, released today from the American Society of Hematology (ASH) in its journal, Blood, presents an innovative, sustainable new role for hematologists, particularly those specializing in non-malignant blood diseases, for today's rapidly changing U.S. health-care system. The report, published online as a Blood Forum article, outlines several models for a "systems-based clinical hematologist," a centralized position within hospitals and health-care systems specializing in non-malignant blood disorders.
In the report, "The Role of Hematologists ...
Researchers have identified more than 100 areas within U.S. waters that should be considered biologically important when making management and regulatory decisions about human activities that could affect whales, dolphins and porpoises.
The creation of Biologically Important Areas (BIAs) are described in a special issue of the journal Aquatic Mammals. Expert judgment was combined with published and unpublished data to identify 131 BIAs covering 24 species, stocks or populations in seven regions of the U.S. It is the first time so much information has been brought together ...
Having a high sense of purpose in life may lower your risk of heart disease and stroke, according to a new study led by researchers at Mount Sinai St. Luke's and Mount Sinai Roosevelt and presented on March 6 at the American Heart Association's EPI/Lifestyle 2015 Scientific Sessions in Baltimore.
The new analysis defined purpose in life as a sense of meaning and direction, and a feeling that life is worth living. Previous research has linked purpose to psychological health and well-being, but the new Mount Sinai analysis found that a high sense of purpose is associated ...