EARTH Magazine: El Niño disaster stunted children's growth
2015-03-06
(Press-News.org) Alexandria, VA-- Children born during, and up to three years after, the devastating 1997-1998 El Niño event in northern Peru were found to be shorter than their peers in a new study covered in EARTH Magazine. The rising waters wiped out crops, drowned livestock, cut off bridges, and caused prolonged famine in many rural villages. Now, a new study that tracked long-term health impacts on children from the affected region has found that a decade later, the children continue to bear signs of the hardship endured early in their lives.
Learn how the children's health was impacted by El Niño, and how geoscience can be used to help communities better plan and prepare for environmental disasters in the March issue of EARTH Magazine: http://www.earthmagazine.org/article/el-nino-disaster-stunted-childrens-growth....
For more stories about the science of our planet, check out EARTH magazine online or subscribe at http://www.earthmagazine.org. The March issue, now available for download features stories on the asbestos controversy unfolding in Nevada, new satellite maps of carbon dioxide sources, and an ongoing, multi-million dollar treasure hunt in the U.S. Rocky Mountains.
INFORMATION:
Keep up to date with the latest happenings in Earth, energy and environment news with EARTH magazine online at: http://www.earthmagazine.org/. Published by the American Geosciences Institute, EARTH is your source for the science behind the headlines.
The American Geosciences Institute is a nonprofit federation of geoscientific and professional associations that represents more than 250,000 geologists, geophysicists and other earth scientists. Founded in 1948, AGI provides information services to geoscientists, serves as a voice of shared interests in the profession, plays a major role in strengthening geoscience education, and strives to increase public awareness of the vital role the geosciences play in society's use of resources, resiliency to natural hazards, and interaction with the environment.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-06
(Boston)--In a review article recently published in the journal Clinical and Translational Medicine, researchers from Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) shed new light on the underlying processes of tumor metastasis and highlight the role of epigenetics in this process. By comparing embryogenesis with cancer metastasis they hypothesize that reversible epigenetic events regulate the development of different types of metastatic cancers. They also describe that the surrounding cells of the tumors (stromal cells) play a significant role in this process.
The BUSM ...
2015-03-06
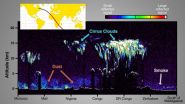
From Saharan dust storms to icy clouds to smoke on the opposite side of the continent, the first image from NASA's newest cloud- and aerosol-measuring instrument provides a profile of the atmosphere above Africa.
The Cloud-Aerosol Transport System instrument (CATS), was launched Jan. 10 aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, and was installed on the International Space Station on Jan. 22. From its berth on the station, CATS sends laser pulses toward Earth, detecting the photons that bounce off of particles in the atmosphere to measure clouds, volcanic ash, pollutants, dust ...
2015-03-06
If you walk into your local drug store and ask for a supplement to help you sleep, you might be directed to a bottle labeled "melatonin." The hormone supplement's use as a sleep aid is supported by anecdotal evidence and even some reputable research studies. However, our bodies also make melatonin naturally, and until a recent Caltech study using zebrafish, no one knew how--or even if--this melatonin contributed to our natural sleep. The new work suggests that even in the absence of a supplement, naturally occurring melatonin may help us fall and stay asleep.
The study ...
2015-03-06
(Boston)--Racial and ethnic disparities in the receipt of health care (typically referring to minorities not receiving needed care) are well known. A recent review in the journal Milbank Memorial Quarterly has now found that while race/ethnicity is not consistently associated with the overuse of medical care (unnecessary care that does not improve patient outcomes). However, when overuse occurs, a substantial proportion occurs among white patients. These findings may lead to a better understanding of how and why race/ethnicity might be associated with overuse and may result ...
2015-03-06
(WASHINGTON, March, 6, 2015) - A report, released today from the American Society of Hematology (ASH) in its journal, Blood, presents an innovative, sustainable new role for hematologists, particularly those specializing in non-malignant blood diseases, for today's rapidly changing U.S. health-care system. The report, published online as a Blood Forum article, outlines several models for a "systems-based clinical hematologist," a centralized position within hospitals and health-care systems specializing in non-malignant blood disorders.
In the report, "The Role of Hematologists ...
2015-03-06
Researchers have identified more than 100 areas within U.S. waters that should be considered biologically important when making management and regulatory decisions about human activities that could affect whales, dolphins and porpoises.
The creation of Biologically Important Areas (BIAs) are described in a special issue of the journal Aquatic Mammals. Expert judgment was combined with published and unpublished data to identify 131 BIAs covering 24 species, stocks or populations in seven regions of the U.S. It is the first time so much information has been brought together ...
2015-03-06
Having a high sense of purpose in life may lower your risk of heart disease and stroke, according to a new study led by researchers at Mount Sinai St. Luke's and Mount Sinai Roosevelt and presented on March 6 at the American Heart Association's EPI/Lifestyle 2015 Scientific Sessions in Baltimore.
The new analysis defined purpose in life as a sense of meaning and direction, and a feeling that life is worth living. Previous research has linked purpose to psychological health and well-being, but the new Mount Sinai analysis found that a high sense of purpose is associated ...
2015-03-06
Using a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis, scientists have discovered that a form of cellular immunotherapy by intravenous administration of monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells, or M-MDSCs, might be an effective treatment for the disease in humans. In a report published in the March 2015 issue of the Journal of Leukocyte Biology, researchers show that M-MDSCs are capable of inhibiting T cell proliferation, as well as B cell proliferation and antibody production. As a result, the arthritic mice experienced improvements in their symptoms.
"I hope this study will ...
2015-03-06
Tropical Cyclone 15S continued to meander in the Mozambique Channel of the Indian Ocean when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and captured a picture of it. The storm's lack of direction is short-lived, however, as forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center or JTWC expect that the storm will move in a southwesterly direction and landfall in west central Madagascar by March 9.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Cyclone 15S on March 5 at 11:25 UTC (6:25 ...
2015-03-06
San Diego, CA--Among prescriptions filled for menopausal hormone therapy (HT) in the U.S., almost half now are custom-compounded "bioidentical" hormones, according to analysis of a recent survey of nearly 500 pharmacists. The study results will be presented Friday March 6th at the Endocrine Society's 97th annual meeting in San Diego.
Custom-compounded prescriptions, which are mixed for an individual according to a doctor's prescription, are not well-regulated or monitored by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
"Despite the increased quality risks and the lack ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] EARTH Magazine: El Niño disaster stunted children's growth