INFORMATION:
Jia and Wisniewski also worked with Heng Xu, associate professor of information sciences and technology; Mary Beth Rosson, professor of information science and technology and interim Dean of the College of Information Sciences and Technology and John M. Carroll, distinguished professor of information sciences and technology.
The National Science Foundation supported this work.
Teens' approach to social media risk is different from adults'
2015-03-17
(Press-News.org) For every parent who ever wondered what the heck their teens were thinking when they posted risky information or pictures on social media, a team of Penn State researchers suggests that they were not really thinking at all, or at least were not thinking like most adults do.
In a study, the researchers report that the way teens learn how to manage privacy risk online is much different than how adults approach privacy management. While most adults think first and then ask questions, teens tend to take the risk and then seek help, said Haiyan Jia, post-doctoral scholar in information sciences and technology.
"Adults often find this very difficult to understand and paradoxical because they are so used to considering possible risks of disclosing information online first and then taking the necessary precautions, based on those concerns," said Jia. "What our model suggests is that teens don't think this way -- they disclose and then evaluate the consequences. The process is more experiential in nature for teens."
This disclose-first-and-then-make-corrections model may lend insight into what researchers refer to as the privacy paradox, according to Pamela Wisniewski, a post-doctoral scholar in information sciences and technology, who worked with Jia.
Wisniewski said that the privacy paradox suggests that there is a disconnect between the privacy concerns of teens and what information they disclose.
"For adults, the basic model is that different factors contribute to an individual's concern for his or her information privacy and based on that privacy concern the user takes certain actions, for example, disclosing less information," said Wisniewski. "This is a very rational, adult-focused model, however, that doesn't seem applicable to teens."
When teens begin to struggle with privacy concerns, they often try to find possible protective actions to mitigate risk, according to the researchers. Those remedies include seeking advice from adults, removing online information, or going offline completely.
Teens are often more exposed to online risks because they are using social media as a platform for self-expression and as a way to gain acceptance from their peers. This desire for expression and acceptance can lead teens to disclose too much information. They may disclose vital contact information, or exchange photographs with strangers, for example.
"Adults don't know how big of a deal this is for teens," said Jia. "Before I worked on these papers, I was drawn to the issue because I heard about so many tragedies of teens who were exploring their identities online and that led them to very risky situations, often with terrible consequences."
A parent's first impulse may be to forbid Internet or social media access, but completely avoiding risks may cause other problems, according to the researchers, who present their findings today (March 17) at the Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing conference.
"First, I can't imagine a teen growing up and avoiding the Internet and online communications in this age," said Jia. "But there's also a danger that without taking on the minimum risks, teens will not have access to all the positive benefits the Internet can provide, nor will they learn how to manage risk and how to safely navigate this online world."
Jia said swimming lessons may be the best model for parents who want to encourage their teens to use the Internet and social media safely.
"It's a lot like learning to swim," Jia said. "You make sure they enter the water slowly and make sure they know how to swim before you let them swim on their own and in the deeper parts."
The researchers used data from the Pew Research Center's 2012 Teens and Privacy Management Survey. The survey gathered information on social media behaviors from 588 teens in the United States, most of whom were active users of sites such as Facebook.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
West Coast waters shifting to lower-productivity regime, new NOAA report finds
2015-03-17
Large-scale climate patterns that affect the Pacific Ocean indicate that waters off the West Coast have shifted toward warmer, less productive conditions that may affect marine species from seabirds to salmon, according to the 2015 State of the California Current Report delivered to the Pacific Fishery Management Council.
The report by NOAA Fisheries' Northwest Fisheries Science Center and Southwest Fisheries Science Center assesses productivity in the California Current from Washington south to California. The report examines environmental, biological and socio-economic ...
New cystic fibrosis research takes aim at deadly pathogen
2015-03-17
AUSTIN, Texas - A new method of testing the most common cause of life-threatening infection in people with cystic fibrosis could improve efforts to study and combat the illness.
The bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a leading contributor to hospitalizations, serious illness and early death for people with cystic fibrosis (CF). Scientists at The University of Texas at Austin have found a way to re-create conditions specific to the environment in which the bacterium spreads in the lungs of a person with CF, allowing them to identify several genes that appear to be necessary ...
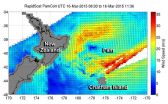
RapidScat eyes Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam's winds near Chatham Islands
2015-03-17
The New Zealand Meteorological Service issued a Storm Warning for the Chatham Islands today as NASA's RapidScat instrument found that winds in one quadrant of Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam is still generating tropical-storm-force winds east of its center.
The International Space Station's RapidScat instrument captured data on Ex-Tropical Cyclone Pam's winds on March 16 from 08:30 to 11:36 UTC. RapidScat revealed sustained winds over 30 meters per second (108 kph/67 mph) were still occurring southeast of the center.
The forecast calls for southwesterly winds to 50 knots (57 ...
Genetic markers play role in who benefits from aspirin, NSAIDs to lower colon cancer risk
2015-03-17
INDIANAPOLIS - An Indiana University cancer researcher and her colleagues have identified genetic markers that may help determine who benefits from regular use of aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for lowering one's risk of developing colorectal cancer.
Previous studies have shown that regular use of aspirin and NSAIDs lower one's risk of colorectal cancer, but their use is not recommended as a way to prevent the disease because of uncertainty about the risks and benefits. Thus, the researchers set out to examine the interrelationship between genetic ...
The need for a more open attitude towards invasive alien species data
2015-03-17
New research published with the support of the FP7 large-scale bioinformatics project Building the European Biodiversity Observation Network (EU BON) and the Alien Challenge COST action reveals the importance of open data in the study and control of invasive alien species. The study was published online in open access in the journal Management of Biological Invasions.
Invasive alien species cause a wide variety of problems, including issues related to conservation; to human and animal health; to agriculture and to fisheries management. But how can science be useful to ...
Chronic bowel inflammation is diagnosed too late in children and adolescents
2015-03-17
Cramping abdominal pains, diarrhea, bloody stools--these are common symptoms of chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Every year, up to 1470 children and adolescents in Germany develop the disease. But chronic inflammatory bowel disease is mostly diagnosed too late in these patients, as Stephan Buderus, Dietmar Scholz, and colleagues show in an original article in the current issue of Deutsches Ärzteblatt International (Dtsch Arztebl Int 2015; 112: 121-7). The average delay between initial symptoms and diagnosis is four to six months. In most cases, the inflammation ...
Study: Erectile dysfunction drug relieves nerve damage in diabetic mice
2015-03-17
DETROIT - New animal studies at Henry Ford Hospital found that sildenafil, a drug commonly used to treat erectile dysfunction, may be effective in relieving painful and potentially life-threatening nerve damage in men with long-term diabetes.
The research targeted diabetic peripheral neuropathy, the most common complication of diabetes, affecting as many as 70 percent of patients.
The study was recently published online in PLOS ONE.
Lei Wang, M.D., the Henry Ford neuroscientist who led the research, said that although numerous drugs have been shown to be effective in ...
Hormones with statins may help women's hearts after menopause
2015-03-17
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 17, 2015)--Hormones may not protect women from heart disease or stroke after menopause, but when combined with cholesterol-lowering statin drugs, they may help protect women from these killers, shows a population study from Sweden to be published in the April issue of Menopause, the journal of The North American Menopause Society (NAMS). During the study, women who took both hormones and statins had a significantly lower risk of dying of any cause and a moderately lower risk of dying of cardiovascular disease.
Using health information from national ...
Social media training works best for student-athletes, study shows
2015-03-17
CLEMSON, S.C. -- Placing less reliance on monitoring software and modifying new media training to align with student-athletes' habits and input will promote more positive and responsible usage of social networks.
This is the key finding by researchers from Clemson University, Baylor University and the University of Florida and published in the International Journal of Sport Communication.
The study explored college athletes' social media use and their experiences with and attitudes about a rising trend in college athletics: social media education.
Given the media ...
Finding a new test for children with concussions
2015-03-17
This news release is available in French. Researchers at the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital -The Neuro, at McGill University and the MUHC, are working to develop a much needed tool for helping diagnose concussions or mild traumatic brain injuries suffered by thousands of young Canadians ---hockey and football players among them. Post-concussion symptoms can include physical ailments, emotional disturbances and sleep disruption. Objective methods for predicting how severely mild brain trauma can affect a young person's brain are sorely needed. The potential ...