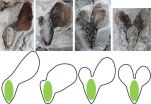
Time-lapse snapshots of a nova's fading light
2015-03-17
(Press-News.org) Scientists in a collaboration led by Dai Takei of the RIKEN SPring-8 Center in Japan have, for the first time, examined a detailed 'time lapse' X-ray image of the expansion of a classical nova explosion using the GK Persei nova -- a binary star system which underwent a nova explosion in 1901.
Through this work, they hope to gain a better understanding of the expansion of gases in the universe, including not only in classical novae but also in supernovae--tremendous stellar explosions that are believed to be responsible for the creation of heavy elements such as uranium which cannot be produced by normal stars.
There is great interest in understanding the dynamics of stellar explosions and especially supernovae, which are among the most powerful events that we know of in the universe. In these explosions, a collapsing star can outshine an entire galaxy. These events take place over enormous spans of time--the whole written history of mankind--so it is unfortunately impossible to observe the whole process as the remnant of the exploding star spreads out into the interstellar medium around it. As a result, scientists have traditionally relied on comparing snapshots taken of different supernova believed to be in different stages of evolution, as well as computer simulations.
Takei says, "I wanted to understand how these explosions unfold, but there were many obstacles. We thus took on the challenge of, instead of looking at supernovae, studying the expansion of a classical nova explosion, since this process is expected to develop within approximately a human lifetime." Though classical novae and supernovae are different processes, the fundamental mechanism through which we see them--a shock wave created by an explosion--is essentially the same.
"The GK Persei nova," Takei continued, "which was discovered in 1901, provided the perfect model for our study." GK Persei is believed to be a binary star system consisting of a white dwarf--a dead star in the sense that it has reached the end of its thermonuclear phase--and a companion, which may be a red dwarf that is still alive, meaning that hydrogen is still burning on its surface. The matter from the companion accretes onto the surface of the white dwarf, and occasionally, when it reaches a certain critical point, thermonuclear runaway starts, ejecting the white dwarf layer outward into an explosion.
Taking advantage of the fact that the development of the nova remnant is relatively rapid, the team examined X-ray snapshots of the nova taken in 2000 and 2013 by the same telescope, NASA's space-based Chandra observatory, and compared the X-ray emissions--created as the expanding gases heat the interstellar medium into a plasma--between the two eras.
What they found from the study was that although the nova remnant had expanded by approximately 90 billion kilometers during the 14 years--an amazingly precise measurement considering the star system is roughly 1,500 light years away, and implying that it is expanding by approximately 300 kilometers per second--the temperature of the plasma remained at a nearly constant 1 million degrees Celsius. The light was fading but the energy of the dominant photons had not changed, implying that the nova remnant is expanding into a region of lower density. "For the first time," says Takei, "we have a detailed image of how the nova propagates through space. Through this kind of study, we hope to be able to understand exactly how these powerful explosions expand into interstellar space, and it may ultimately give us new insights into the history of the cosmos."
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-17
Vitamin D may play a vital role in the prevention and treatment of diseases associated with aging, according to researchers at Loyola University Chicago Marcella Niehoff School of Nursing (MNSON). These findings were published in the latest issue of the Journal of Aging and Gerontology.
Researchers reviewed evidence that suggests an association between vitamin D deficiency and chronic diseases associated with aging such as cognitive decline, depression, osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, high blood pressure, Type 2 diabetes and cancer.
"Vitamin D deficiency is a ...
2015-03-17
Hamilton, ON (March 17, 2015) - It's long been known that obese men are more likely to develop type two diabetes than obese women, but researchers at McMaster University have discovered it may be related to a difference between the sexes in the activity of a protein in the muscle.
As people become overweight, their skeletal muscle develops insulin resistance that can lead to type two diabetes. In a paper published by Scientific Reports today, the research team found the activity of this protein, called PTEN (for Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10), ...
2015-03-17
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Young, inexperienced drivers have always gotten into more automobile accidents, but if you add in a lot of distractions, it's a recipe for disaster - and a new Pacific Northwest research program is learning more about these risks while identifying approaches that may help reduce them.
Distractions have been an issue since the age of the Model T, whether a driver was eating a sandwich or talking to a passenger. But the advent of cell phones, text messaging and heavy urban traffic has taken those distractions to a historic level, say researchers, who ...
2015-03-17
The whirling, winged seeds of today's conifers are an engineering wonder and, as University of California, Berkeley, scientists show, a result of about 270 million years of evolution by trees experimenting with the best way to disperse their seeds.
The first conifer species that produced seeds that whirl when they fall used a variety of single- and double-winged designs. Whirling, or helicoptering, keeps a seed aloft longer, increasing the chance that a gust of wind will carry a seed to a clearing where it can sprout and grow unimpeded by competitors
"Winged seeds may ...
2015-03-17
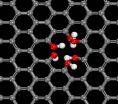
The honeycomb structure of pristine graphene is beautiful, but Northwestern University scientists, together with collaborators from five other institutions, have discovered that if the graphene naturally has a few tiny holes in it, you have a proton-selective membrane that could lead to improved fuel cells.
A major challenge in fuel cell technology is efficiently separating protons from hydrogen. In a study of single-layer graphene and water, the Northwestern researchers found that slightly imperfect graphene shuttles protons -- and only protons -- from one side of the ...
2015-03-17
An atomically thin membrane with microscopically small holes may prove to be the basis for future hydrogen fuel cells, water filtering and desalination membranes, according to a group of 15 theorists and experimentalists, including three theoretical researchers from Penn State.
The team, led by Franz Geiger of Northwestern University, tested the possibility of using graphene, the robust single atomic layer carbon, as a separation membrane in water and found that naturally occurring defects, essentially a few missing carbon atoms, allowed hydrogen protons to cross the ...
2015-03-17
An analysis of genetic and lifestyle data from 10 large epidemiologic studies confirmed that regular use of aspirin or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) appears to reduce the risk of colorectal cancer in most individuals. The study being published in the March 17 issue of JAMA found that a few individuals with rare genetic variants do not share this benefit. The study authors note, however, that additional questions need to be answered before preventive treatment with these medications can be recommended for anyone.
"Previous studies, including randomized ...
2015-03-17
Among approximately 19,000 individuals, the use of aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) was associated with an overall lower risk of colorectal cancer, although this association differed according to certain genetic variations, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
Considerable evidence demonstrates that use of aspirin and other NSAIDs is associated with a lower risk of colorectal cancer. However, the mechanisms behind this association are not well understood. Routine use of aspirin, NSAIDs, or both for prevention of cancer is not currently ...
2015-03-17
In a study in which pathologists provided diagnostic interpretation of breast biopsy slides, overall agreement between the individual pathologists' interpretations and that of an expert consensus panel was 75 percent, with the highest level of concordance for invasive breast cancer and lower levels of concordance for ductal carcinoma in situ and atypical hyperplasia, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
Approximately 1.6 million women in the United States have breast biopsies each year. The accuracy of pathologists' diagnoses is an important and inadequately ...
2015-03-17
Older adults who had spine imaging within 6 weeks of a new primary care visit for back pain had pain and disability over the following year that was not different from similar patients who did not undergo early imaging, according to a study in the March 17 issue of JAMA.
When to image older adults with back pain remains controversial. Many guidelines recommend that older adults undergo early imaging because of the higher prevalence of serious underlying conditions. However, there is not strong evidence to support this recommendation. Adverse consequences of early imaging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Time-lapse snapshots of a nova's fading light