NASA-JAXA's GPM satellite close-up of Cyclone Pam's rainfall
2015-03-18
(Press-News.org) As one of the strongest cyclones every recorded in the South Pacific Ocean, Cyclone Pam devastated the island archipelago of Vanuatu. The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core observatory provided data on rain rates throughout the storm. At the end of Pam's life on March 17, NASA's RapidScat provided a look at the winds of the waning storm.
As the cyclone bore down on Vanuatu's central islands on the afternoon (local time) of March 13, 2015, Pam's maximum sustained winds were estimated to have increased to 270 kph (~167 mph) by the U.S. Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC), making it a category 5 storm on the U.S. Saffir-Simpson Wind Scale.
The storm caused immense, widespread damage with the islands of Erromango and Tanna suffering a direct hit. Although damage is still being assessed, the number of reported fatalities fortunately has been rather low at 11 considering the power of the storm.
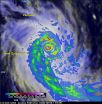
NASA's GPM Core observatory satellite passed over Pam as the cyclone began pulling away from Vanuatu on the 14th. The image was taken at 03:51 UTC (2:51 p.m. local time) on March 14, 2015 and showed rain rates within Cyclone Pam observed from GPM's microwave (GMI, in the outer swath) and radar (DPR, inner swath) instruments. GPM showed that Pam was still a very powerful storm. A well-defined, closed inner eyewall denoted by the annulus of intense rain rates up to 50 mm/2 inches per hour, is indicative of a well-formed intense cyclonic circulation. Typically the faster the winds, the more symmetrical the precipitation features around the storm's center. At that time, Pam's maximum sustained winds were still estimated at 135 knots (~155 mph) by JTWC, putting it near the top of the Saffir-Simpson category 4 scale.
TRMM and GPM are joint missions between NASA and the Japanese space agency JAXA.
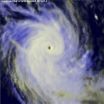
After the GPM image was taken, Pam continued moving southward, tracking east of New Caledonia, and continued to weaken further.
By March 17, Pam had already moved past northern New Zealand and had become an extra-tropical cyclone.
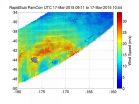
The RapidScat instrument aboard the International Space Station (ISS) measures surface winds. When the ISS passed over Extra-tropical Cyclone Pam on March 17 RapidScat gathered data on surface winds that showed the strongest winds stretched over the northern quadrant and were near 25 m/s (56 mph/90 kph). Pam continued to weaken while moving in a southerly direction on March 18 through the southern Pacific Ocean.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-18
New research shows that courtship rituals evolve very fast in cichlid fish in Lake Malawi. Whenever species evolve to feed at different depths, their courtship evolves as well. In the shallows where the light is good, males build sand castles to attract females. Males of deep-dwelling species dig less elaborate pits and compensate with longer swimming displays. The results are published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
"Lake Malawi cichlids are famous for the diversity and fast evolution of their feeding habits, body form, and sex determination ...
2015-03-18
Men and women who adapt their daily diet to meet current UK dietary guidelines could reduce their risk of a heart attack or a stroke by up to a third, according to a new study by King's College London.
The study, published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, recruited healthy middle-aged and older men and women to compare the effects on risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) of following a diet based on UK health guidelines compared with a traditional British diet. The predicted risk of CVD over the next 10 years for the participants was estimated to ...
2015-03-18
In diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the body produces too much mucus, making breathing difficult. New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provides clues to potentially counteract inappropriate mucus production.
"The new study lays the groundwork for developing treatments for diseases such as asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis and even certain cancers," said senior author Thomas J. Brett, PhD, assistant professor of medicine. "It also solves a 20-year mystery about the role of a protein that has long been ...
2015-03-18
Researchers at the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) and the Moores Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, have described for the first time the molecular mechanism of cancer development caused by well-known "resistance" mutations in the gene called epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
While these mutations were known for quite a long time, the question as to why they cause cancer or make some drugs ineffective was still not answered.
The study, called "Molecular Determinants of Drug-Specific Sensitivity for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ...
2015-03-18
Tropical Cyclone Bavi weakened to a depression and NASA's RapidScat instrument measured its waning winds from space.
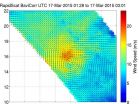
On March 17 the RapidScat instrument aboard the International Space Station (ISS) measured Bavi's surface winds from 01:28 to 3:01 UTC. RapidScat data showed surface winds were strongest winds in the northwestern quadrant. Sustained winds were near 17 m/s (38 mph/61 kph) and weaker around the rest of the storm.
On March 18 at 0000 UTC (March 17 at 8 p.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that Bavi's maximum sustained winds dropped to 25 knots ...
2015-03-18
Cambridge, Mass. - March 17, 2015 - The velvet worm is a slow-moving, unassuming creature. With its soft body, probing antennae, and stubby legs, it looks like a slug on stilts as it creeps along damp logs in tropical climates.
But it has a secret weapon. In the dark of night, when an unsuspecting cricket or termite crosses its path, the worm unleashes an instantaneous torrent of slime. Two fine jets of the gluey substance spray out of openings on its head, oscillating in all directions to cast a sticky net that entraps prey and stops it in its tracks.
Captivated, ...
2015-03-18
While unconscious race and social class biases were present in most trauma and acute-care clinicians surveyed about patient care management in a series of clinical vignettes, those biases were not associated with clinical decisions, according to a report published online by JAMA Surgery.
Disparities in the quality of care received by minority patients have been reported for decades across multiple conditions, types of care and institutions, according to the study background. Adil H. Haider, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, conducted a web-based survey ...
2015-03-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - Drugs aimed at quelling the behavior problems of dementia patients may also hasten their deaths more than previously realized, a new study finds.
The research adds more troubling evidence to the case against antipsychotic drugs as a treatment for the delusions, hallucinations, agitation and aggression that many people with Alzheimer's disease and other dementias experience.
In the new issue of the journal JAMA Psychiatry, researchers report findings from nearly 91,000 American veterans over the age of 65 with dementia.
Data from each patient who ...
2015-03-18
TORONTO (March 18, 2015) - People with a severe form of schizophrenia have major differences in their brain networks compared to others with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and healthy individuals, a new study from the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) shows.
The study, which used a novel approach to map brain networks, was led by researchers at the Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute at CAMH and published in this week's JAMA Psychiatry.
"Finding ways to help this particular group of people with schizophrenia is a priority as recovery is ...
2015-03-18
COLLEGE STATION - A ground-breaking Texas A&M AgriLife Research-led study on corn has identified useful gene variations for yield increases, drought tolerance and aflatoxin resistance that could make a real difference to Texas producers in the years to come, according to researchers.
The study, titled "Genome Wide Association Study for Drought, Aflatoxin Resistance, and Important Agronomic Traits of Maize Hybrids in the Sub-Tropics" was recently published in PLOS ONE, an international, peer-reviewed, open-access, online publication.
The study included the growing years ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA-JAXA's GPM satellite close-up of Cyclone Pam's rainfall