Finding support for surgery on Facebook
2015-03-18
(Press-News.org) For many, Facebook connects friends, family, and others with common interests. Despite the popularity of social networking sites like Facebook, scientists are only beginning to learn how they affect human interaction.
In a recent study published by the journal Social Science & Medicine, Dartmouth researchers examined nearly 9,000 Facebook conversations to better understand how people seek and receive support on social networking sites.
"Among the many Facebook conversations that were mostly casual, we noticed more serious exchanges among people who mentioned a major medical event, such as surgery," says Denise Anthony, professor of sociology at Dartmouth.
The study examined Facebook conversations among approximately 33,000 people who gave permission to be monitored for a six-month period. During this period, nearly four thousand people posted something about surgery. When the researchers examined the conversations where the initial posts mentioned surgery, they discovered that posts referencing a family member triggered much greater response via comments on that post. The researchers also reported a common pattern of call-and-response in asking for and offering prayers.
"In our data, many individuals talking about surgery would ask for prayers in their initial post. These posts received more responses in the form of digital prayers in reply," says Anthony.
While the study is just the first step in directly observing social support on Facebook, the researchers say that future studies are needed to understand how support garnered on social networking sites translates to the real world.
"Our research suggests that resources in the offline world that are associated with greater social support and better health outcomes, like income, appear to translate into greater social support online as well," says Anthony. "It is important to understand such patterns, because if inequality in the offline world translates into differential resources online, especially those that affect health over time, then new technologies like social network sites could exacerbate rather than reduce health disparities."
The interdisciplinary research team consisted of Anthony and her colleagues Matthew Davis, an epidemiologist now at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and Scott Pauls, professor of mathematics at Dartmouth.
INFORMATION:
Professor Denise Anthony is available for media comment, and she can be reached directly at denise.l.anthony@dartmouth.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-18
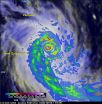
As one of the strongest cyclones every recorded in the South Pacific Ocean, Cyclone Pam devastated the island archipelago of Vanuatu. The Global Precipitation Measurement or GPM core observatory provided data on rain rates throughout the storm. At the end of Pam's life on March 17, NASA's RapidScat provided a look at the winds of the waning storm.
As the cyclone bore down on Vanuatu's central islands on the afternoon (local time) of March 13, 2015, Pam's maximum sustained winds were estimated to have increased to 270 kph (~167 mph) by the U.S. Joint Typhoon Warning Center ...
2015-03-18
New research shows that courtship rituals evolve very fast in cichlid fish in Lake Malawi. Whenever species evolve to feed at different depths, their courtship evolves as well. In the shallows where the light is good, males build sand castles to attract females. Males of deep-dwelling species dig less elaborate pits and compensate with longer swimming displays. The results are published in the open-access journal Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution.
"Lake Malawi cichlids are famous for the diversity and fast evolution of their feeding habits, body form, and sex determination ...
2015-03-18
Men and women who adapt their daily diet to meet current UK dietary guidelines could reduce their risk of a heart attack or a stroke by up to a third, according to a new study by King's College London.
The study, published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, recruited healthy middle-aged and older men and women to compare the effects on risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) of following a diet based on UK health guidelines compared with a traditional British diet. The predicted risk of CVD over the next 10 years for the participants was estimated to ...
2015-03-18
In diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), the body produces too much mucus, making breathing difficult. New research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis provides clues to potentially counteract inappropriate mucus production.
"The new study lays the groundwork for developing treatments for diseases such as asthma, COPD, cystic fibrosis and even certain cancers," said senior author Thomas J. Brett, PhD, assistant professor of medicine. "It also solves a 20-year mystery about the role of a protein that has long been ...
2015-03-18
Researchers at the San Diego Supercomputer Center (SDSC) and the Moores Cancer Center at the University of California, San Diego, have described for the first time the molecular mechanism of cancer development caused by well-known "resistance" mutations in the gene called epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).
While these mutations were known for quite a long time, the question as to why they cause cancer or make some drugs ineffective was still not answered.
The study, called "Molecular Determinants of Drug-Specific Sensitivity for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor ...
2015-03-18
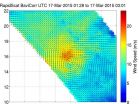
Tropical Cyclone Bavi weakened to a depression and NASA's RapidScat instrument measured its waning winds from space.
On March 17 the RapidScat instrument aboard the International Space Station (ISS) measured Bavi's surface winds from 01:28 to 3:01 UTC. RapidScat data showed surface winds were strongest winds in the northwestern quadrant. Sustained winds were near 17 m/s (38 mph/61 kph) and weaker around the rest of the storm.
On March 18 at 0000 UTC (March 17 at 8 p.m. EDT), the Joint Typhoon Warning Center noted that Bavi's maximum sustained winds dropped to 25 knots ...
2015-03-18
Cambridge, Mass. - March 17, 2015 - The velvet worm is a slow-moving, unassuming creature. With its soft body, probing antennae, and stubby legs, it looks like a slug on stilts as it creeps along damp logs in tropical climates.
But it has a secret weapon. In the dark of night, when an unsuspecting cricket or termite crosses its path, the worm unleashes an instantaneous torrent of slime. Two fine jets of the gluey substance spray out of openings on its head, oscillating in all directions to cast a sticky net that entraps prey and stops it in its tracks.
Captivated, ...
2015-03-18
While unconscious race and social class biases were present in most trauma and acute-care clinicians surveyed about patient care management in a series of clinical vignettes, those biases were not associated with clinical decisions, according to a report published online by JAMA Surgery.
Disparities in the quality of care received by minority patients have been reported for decades across multiple conditions, types of care and institutions, according to the study background. Adil H. Haider, M.D., M.P.H., of Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, conducted a web-based survey ...
2015-03-18
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - Drugs aimed at quelling the behavior problems of dementia patients may also hasten their deaths more than previously realized, a new study finds.
The research adds more troubling evidence to the case against antipsychotic drugs as a treatment for the delusions, hallucinations, agitation and aggression that many people with Alzheimer's disease and other dementias experience.
In the new issue of the journal JAMA Psychiatry, researchers report findings from nearly 91,000 American veterans over the age of 65 with dementia.
Data from each patient who ...
2015-03-18
TORONTO (March 18, 2015) - People with a severe form of schizophrenia have major differences in their brain networks compared to others with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and healthy individuals, a new study from the Centre for Addiction and Mental Health (CAMH) shows.
The study, which used a novel approach to map brain networks, was led by researchers at the Campbell Family Mental Health Research Institute at CAMH and published in this week's JAMA Psychiatry.
"Finding ways to help this particular group of people with schizophrenia is a priority as recovery is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Finding support for surgery on Facebook