INFORMATION:
Kuebler earned the Ph.D. in chemistry from the University of Oxford. He joined UCF in 2003 through an appointment in Chemistry and CREOL, The College of Optics & Photonics. His research has been continuously funded by the National Science Foundation (NSF) and industry. In 2007 he received the NSF CAREER Award. His teaching has been recognized with Teaching Incentive Program awards (2008, 2014) and Excellence in Undergraduate Teaching awards (2008, 2015) from the UCF College of Sciences.
Scientists invent new way to control light, critical for next gen of super fast computing
2015-03-19
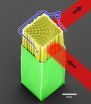
(Press-News.org) A device resembling a plastic honeycomb yet infinitely smaller than a bee's stinger can steer light beams around tighter curves than ever before possible, while keeping the integrity and intensity of the beam intact.
The work, conducted by researchers at the University of Texas El Paso (UTEP) and at the University of Central Florida (UCF) and published in the journal Optics Express, introduces a more effective way to transmit data rapidly on electronic circuit boards by using light.
Sending information on light beams, instead of electrical signals, allows data to be transmitted thousands of times more quickly. But controlling the light beams without losing their energy has been the challenge. Microchip and computer manufacturers however, are increasingly looking to light as the best way to overcome speed bottlenecks associated with today's electronics.
"Computer chips and circuit boards have metal wire connections within them that transport data signals," said Raymond Rumpf, professor of electrical and computer engineering at UTEP. "One of challenges when using light is figuring out a way to make tight bends so we can replace the metal wiring more effectively."
That's where UCF comes in.
"Direct laser writing has the potential to become a flexible means for manufacturing next-generation computer devices," said Stephen Kuebler, associate professor of chemistry at UCF.
Kuebler and his students used direct laser writing, a kind of nanoscale 3D printing, to create the miniature lattices. The team then ran light beams through the lattices and confirmed that they could flow light without loss through turns that are twice as tight as any done previously.
The finding is significant because with the demand for ever-smaller and faster computers and hand-held devices, engineers need ways to pack ultra-fast data-transmission devices into smaller spaces.
Conventional light waveguides, like optical fibers, can be used to steer light through turns. But the turns must be gradual. If the turn is too quick, the light beams escape and energy is lost.
To make ultra-sharp turns, the team designed the plastic devices so that its lattice steers the beam around corners without losing energy.
The UTEP-UCF team's technology creates a new record in the field of optics for its ability to bend light beams. Kuebler said the team is now working to double that record, creating a lattice that will turn the light through an even tighter turn.
Rumpf, who runs UTEP's Electromagnetic Lab, envisions this groundbreaking technology will first appear in high-performance super computers before it can be found in people's everyday laptops.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Racial, ethnic differences in picking surgeons, hospitals for breast cancer care
2015-03-19
Black and Hispanic women with breast cancer were less likely to pick their surgeon and the hospital for treatment based on reputation compared with white women, suggesting minority patients may rely more on physician referrals and health plans in those decisions, according to a study published online by JAMA Oncology.
Racial and ethnic disparities in the use, quality and delivery of medical care have been well described. However, data are limited with regard to how women select surgeons and hospitals for cancer treatment and whether there are racial and ethnic differences ...
Effect of smoking, alcohol on feeding tube duration in head/neck cancer patients
2015-03-19
Current smoking and heavy alcohol consumption appear to be risk factors for prolonged use of a gastrostomy tube (GT, feeding tube) in patients with head and neck cancer undergoing radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy, according to a report published online by JAMA Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery.
Chemoradiotherapy is a well-established treatment for advanced cancer of the head and neck. But its toxic effects can compromise eating and result in weight loss and malnutrition. Consequently, many institutions recommend prophylactic GT insertion before starting treatment, according ...
Miriam Hospital researchers find topical TXA in total joint replacement lowers blood transfusion use
2015-03-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. - Orthopedic surgeons from The Miriam Hospital have conducted a cost-benefit analysis of topical tranexamic acid (TXA) in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty patients that revealed a 12 percent transfusion rate reduction - from 17.5 percent to 5.5 percent - with no significant difference in complication rates. In addition to reducing the risk for postoperative bleeding and transfusion following total joint replacement, use of topical TXA enabled approximately 9.3 percent more patients to be discharged to home rather than to a skilled nursing facility. ...
Educated women choosing to be mothers without marrying their spouses
2015-03-19
This news release is available in French. In Latin America, consensual (common-law) unions are traditionally associated with poorer or indigenous populations. But recent research is turning this conventional wisdom on its head, finding that that in the past 30 years or so consensual unions have become increasingly popular throughout Latin America, including in higher-income groups. In certain countries, such as Panama, common-law partnerships are now as widespread as in Quebec.
Another widely held belief was that only low-income, uneducated women bore children in ...
Kindergarten and crime: What's the Link?
2015-03-19
DURHAM, N.C.-- Children who are older when they start kindergarten do well in the short term, academically and socially. But as teenagers, these old-for-grade students are more likely to drop out and commit serious crimes, says new research from Duke University.
The negative outcomes are significantly more likely for children from disadvantaged backgrounds.
"This research provides the first compelling evidence of a causal link between dropout and crime. It supports the view that crime outcomes should be considered in evaluating school reforms," said lead author Philip ...
Citizen scientists discover new plant species in the Cape Floral Kingdom
2015-03-19
Amateur botanists in the Western Cape Province of South Africa have discovered two new species of beautiful blue-flowered legumes. The study was published in the open access journal PhytoKeys.
Few people take the chance to tramp the empty rolling ranges of mountains and the fragmented and jagged coastline of the Southern Cape in South Africa. Most avoid it because of how wild and tough-going it can be.
This region is part of a unique and species rich global flora called the Cape Floral Kingdom. Yet there are a band of intrepid walkers and climbers who traverse these ...
Medical expansion has led people worldwide to feel less healthy
2015-03-19
COLUMBUS, Ohio - Across much of the Western world, 25 years of expansion of the medical system has actually led to people feeling less healthy over time, a new study has found.
A researcher at The Ohio State University used several large multinational datasets to examine changes in how people rated their health between 1981 and 2007 and compared that to medical expansion in 28 countries that are members of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development.
During that time, the medical industry expanded dramatically in many of those countries, which you might ...
Pregnant women with asthma need to curb urge to ask for antibiotics
2015-03-19
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (March 3, 2015) - Getting sick when you're pregnant is especially difficult, but women whose children are at risk for developing asthma should avoid antibiotics, according to a new study.
The study, published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), followed 298 mother-child pairs through the child's third year of life. The study found that 22 percent of the 103 children born to mothers who took antibiotics during pregnancy were diagnosed with ...
Immigrants are usually in better health than native Canadians... at least when they arrive
2015-03-19
This news release is available in French. Research has shown that the health of immigrants is generally better than that of citizens of their host country, at least on their arrival and for some time afterwards. But a team of researchers in Montreal has found that this is not true of all groups of immigrants; children and older people, for example, may be exceptions. "Our analysis suggests that immigrant health policies should not be 'one size fits all' in type, and that they need to take account of immigrants' ages and the indicators of the health problems they are ...
Physician practices need help to adopt new payment models, study finds
2015-03-19
Physician practices are engaging in new health care payment models intended to improve quality and reduce costs, but are finding that they need help with successfully managing increasing amounts of data and figuring out how to respond to the diversity of programs and quality metrics from different payers, according to a new joint study by the RAND Corporation and the American Medical Association.
Both the federal government and private payers are changing the way they pay physicians and other health professionals, moving to innovative models intended to improve quality ...