Spot treatment
Researchers use the latest in nanotechnology and transdermal drug delivery to take on an old problem: Acne
2015-03-19
(Press-News.org) Acne, a scourge of adolescence, may be about to meet its ultra high-tech match. By using a combination of ultrasound, gold-covered particles and lasers, researchers from UC Santa Barbara and the private medical device company Sebacia have developed a targeted therapy that could potentially lessen the frequency and intensity of breakouts, relieving acne sufferers the discomfort and stress of dealing with severe and recurring pimples.
"Through this unique collaboration, we have essentially established the foundation of a novel therapy," said Samir Mitragotri, professor of chemical engineering at UCSB.
Pimples form when follicles get blocked by sebum, an oily, waxy substance secreted by sebaceous glands located adjacent to the follicle. Excretion of sebum is a natural process and functions to lubricate and waterproof the skin. Occasionally, however, the openings of the follicles (pores) get blocked, typically by bits of hair, skin, dirt or other debris mixed in with the sebum. Overproduction of sebum is also a problem, which can be caused by hormones or medications. Changes in the skin, such as its thickening during puberty, can also contribute to follicle blockage. Whatever the cause, the accumulating sebum harbors bacteria, which results in the inflammation and local infection that we call acne.
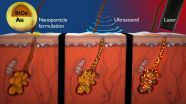
The new technology builds on Mitragotri's specialties in targeted therapy and transdermal drug delivery. Using low-frequency ultrasound, the therapy pushes gold-coated silica particles through the follicle into the sebaceous glands. Postdoctoral research associate Byeong Hee Hwang, now an assistant professor at Incheon National University, conducted research at UCSB.
"The unique thing about these particles is that when you shine a laser on them, they efficiently convert light into heat via a process called surface plasmon resonance," said Mitragotri. This also marks the first time ultrasound, which has been proved for years to deliver drugs through the skin, has been used to deliver the particles into humans.
These silica and gold particles are exceedingly tiny -- about a hundredth of the width of a human hair -- but they are key to the therapy. Once the particles are deposited in the target areas, lasers are aimed at them and, because the gold shells are designed specifically to interact with the near-infrared wavelengths of the lasers, the light becomes heat. The heated particles essentially cause deactivation of the sebaceous glands. The sebum, pore-blocking substances and particles are excreted normally.
"If you deactivate these overproducing glands, you're basically treating the root cause of the acne," said Mitragotri.
According to the research, which is published in the Journal of Controlled Release, this protocol would have several benefits over conventional treatments. Called selective photothermolysis, the method does not irritate or dry the skin's surface. In addition, it poses no risk of resistance or long-term side effects that can occur with antibiotics or other systemic treatments.
"It's highly local but highly potent as well," Mitragotri said of the treatment. "I think this would be beneficial in addressing the concerns regarding other, conventional treatments." According to Mitragotri, this photothermolysis method is particularly suited to patients with advanced, severe or difficult-to-treat acne. The research has gone from concept to clinical trials in a relatively short amount of time. However, other more long-term elements of this therapy have yet to be studied, such as the extent of follicular damage, if any; what the most effective and beneficial parameters of this treatment may be; and what contraindications exist.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-19
Our eyes are drawn to several dimensions of an object--such as color, texture, and luminance--even when we need to focus on only one of them, researchers at New York University and the University of Pennsylvania have found. The study, which appears in the journal Current Biology, points to the ability of our visual system to integrate multiple components of an item while underscoring the difficulty we have in focusing on a particular aspect of it.
"Even when we want and need to focus on one dimension of things we come across every day, such as the texture of your cat's ...
2015-03-19
For in vitro fertilization and other assisted reproductive technologies, selecting the healthiest and best swimming sperm from a sample of semen can dramatically increase success. Microfluidics--micro-scale technologies that were originally developed to enable high-throughput gene sequencing and for Point-Of-Care diagnostics--are now being adapted to enhance sperm sorting. These new methods, reviewed by engineers in the journal Trends in Biotechnology, are generating promising results in applications such as single-sperm genomics, in-home male fertility testing, and wildlife ...
2015-03-19
A combination of human stem cell transplantation and antidiabetic drugs proved to be highly effective at improving body weight and glucose metabolism in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. The findings, published March 19th by Stem Cell Reports, could set the stage for clinical trials to test the first stem cell-based approach for insulin replacement in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes, which accounts for 90%-95% of the now approaching 400 million cases of diabetes worldwide, is currently treated by oral medication, insulin injections, or both to control blood ...
2015-03-19
Altered signaling through the vitamin D receptor on certain immune cells may play a role in causing the chronic inflammation that leads to cardiometabolic disease, the combination of type 2 diabetes and heart disease that is the most common cause of illness and death in Western populations. The research appears March 19 in the journal Cell Reports.
"Because low vitamin D levels are associated with diabetes and heart disease, we looked at the connections between vitamin D, immune function, and these disease states," says senior author Carlos Bernal-Mizrachi, of the Washington ...
2015-03-19
Scientists at the University of British Columbia and BetaLogics, part of Janssen Research & Development, LLC have shown for the first time that Type 2 diabetes can be effectively treated with a combination of specially-cultured stem cells and conventional diabetes drugs.
Stem cells - generic cells that haven't yet taken on specialized form and function - have recently been used by scientists at UBC and elsewhere to reverse Type 1 diabetes in mice. In Type 1 diabetes, which usually begins in childhood, the pancreas produces little or no insulin, the hormone that enables ...
2015-03-19
A research team at UC San Francisco has discovered an RNA molecule called Pnky that can be manipulated to increase the production of neurons from neural stem cells.
The research, led by neurosurgeon Daniel A. Lim, MD, PhD, and published on March 19, 2015 in Cell Stem Cell, has possible applications in regenerative medicine, including treatments of such disorders as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and traumatic brain injury, and in cancer treatment.
Pnky is one of a number of newly discovered long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), which are stretches of 200 or more ...
2015-03-19
A new study has shown that the dottyback, a small predatory reef fish, can change the colour of its body to imitate a variety of other reef fish species, allowing the dottyback to sneak up undetected and eat their young.
The dottyback also uses its colour-changing abilities to hide from larger predators by colour-matching to the background of its habitat - disappearing into the scenery.
The research, published today in the journal Current Biology, reveals a sophisticated new example of 'mimicry': disguising as a different species to gain evolutionary advantage. ...
2015-03-19
Stem cells can have a strong sense of identity. Taken out of their home in the hair follicle, for example, and grown in culture, these cells remain true to themselves. After waiting in limbo, these cultured cells become capable of regenerating follicles and other skin structures once transplanted back into skin. It's not clear just how these stem cells -- and others elsewhere in the body -- retain their ability to produce new tissue and heal wounds, even under extraordinary conditions.
New research at Rockefeller University has identified a protein, Sox9, that takes the ...
2015-03-19
There is no doubt that teenage boys and girls are swayed and shaped by music TV. For example, sexually active youth of both genders, after watching music TV, think their peers are sexually active, too. Moreover, when girls and boys perceive males in music videos as being sexually active, it makes boys watch more music TV, and girls watch less. These are some of the surprising findings from a study conducted at the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium, published in Springer's journal Sex Roles. The results question the frequently reported blanket influence of the mass ...
2015-03-19
A tiny new millipede has been found which is only known to occur within the city of Launceston, Tasmania, Australia.
The 1 cm-long species was discovered in a city park by two local naturalists, Wade and Lisa Clarkson. Working with millipede specialist Dr Bob Mesibov of Launceston's Queen Victoria Museum and Art Gallery, the Clarksons carefully mapped the range of the new species over several years.
To their surprise, the millipede was easy to find in eucalypt woodland in city parks and reserves, but apparently absent from eucalypt woodland just outside the city, or ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Spot treatment
Researchers use the latest in nanotechnology and transdermal drug delivery to take on an old problem: Acne