Ascension of marine diatoms linked to vast increase in continental weathering
2015-03-23
(Press-News.org) Troy, N.Y. - A team of researchers, including Rensselaer professor Morgan Schaller, has used mathematical modeling to show that continental erosion over the last 40 million years has contributed to the success of diatoms, a group of tiny marine algae that plays a key role in the global carbon cycle. The research was published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Diatoms consume 70 million tons of carbon from the world's oceans daily, producing organic matter, a portion of which sinks and is buried in deep ocean sediments. Diatoms account for over half of organic carbon burial in marine sediments. In a mechanism known as a the "oceanic biological pump," the diatoms absorb and bury carbon, then atmospheric carbon dioxide diffuses into the upper ocean to compensate for that loss of carbon, reducing the concentration of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
"What we really have here is a double whammy: The chemical breakdown of rocks on land efficiently consumes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, and those minerals are delivered to the ocean basins by rivers where, in this case, they fueled the massive expansion of diatoms," said Schaller, an assistant professor of earth and environmental sciences. "Diatoms are photosynthetic, so they also consume atmospheric carbon dioxide. The combination of both of these effects may help explain the drastic decrease in atmospheric carbon dioxide over the last 35 million years that has plunged us into the current condition where we have glacial ice cover at both of the poles."
Diatoms appeared in the Mesozoic about 200 million years ago as descendants of the red algal lineage. However, it was not until the last 40 million years that this group of marine microalgae rose to dominate marine primary productivity.
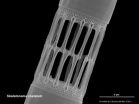
Unlike other microalgae, diatoms require silicic acid to form tiny cases of amorphous silica (glass) called frustules, which are a means of defense against predators. Therefore, understanding the sources of silicic acid in the ocean is essential to understanding the evolutionary success of diatoms, and this is where the Earth sciences come into play.
Silicate rocks such as granites and basalts comprise the majority of Earth's crust, and their chemical decomposition represents a major source of silicic acid to the world oceans. Continental erosion depends on a complex interaction of physical, chemical, and biological forces that ultimately combine to enhance the dissolution of minerals that make up the rocks. The elevation of mountain ranges such as the Himalayas over the last 40 million years favored the fracture and dissolution of continental silicate rocks facilitating the expansion of diatoms in marine ecosystems.
Previous work has associated the evolutionary expansion of diatoms with a superior competitive ability for silicic acid relative to other plankton that use silica, such as radiolarians, which evolved by reducing the weight of their silica skeleton.
But in their work, the researchers used a mathematical model in which diatoms and radiolarians compete for silicic acid to show that the observed reduction in the weight of radiolarian tests is insufficient to explain the rise of diatoms. Using the lithium isotope record of seawater as a proxy of silicate rock weathering and erosion, they calculated changes in the input flux of silicic acid to the oceans. Their results indicate that the long-term massive erosion of continental silicates was critical to the subsequent success of diatoms in marine ecosystems over the last 40 million years and suggest an increase in the strength and efficiency of the oceanic biological pump over this period.
INFORMATION:
The research team was led by Pedro Cermeño, and included Sergio M. Vallina, both of the Instituto de Ciencias del Mar in Spain, as well as Schaller, Paul G. Falkowski of Rutgers University, and Òscar E. Romero, of the University of Bremen in Germany.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-03-23
Archaeologists working in Guatemala have unearthed new information about the Maya civilization's transition from a mobile, hunter-gatherer lifestyle to a sedentary way of life.
Led by University of Arizona archaeologists Takeshi Inomata and Daniela Triadan, the team's excavations of the ancient Maya lowlands site of Ceibal suggest that as the society transitioned from a heavy reliance on foraging to farming, mobile communities and settled groups co-existed and may have come together to collaborate on construction projects and participate in public ceremonies.
The findings, ...
2015-03-23
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - March 23, 2015 - The results of a blood test done immediately after heart surgery can be a meaningful indicator of postoperative stroke risk, a study by researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center has found.
An acutely elevated level of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) - a measure of kidney function detected through blood testing - was the most powerful predictor of postoperative stroke among the study's subjects.
Up to 9 percent of cardiac surgery patients suffer post-operative stroke, and these events are significantly more serious and more frequently ...
2015-03-23
The concept was simple: If two compounds each individually show promise in preventing colon cancer, surely it's worth trying the two together to see if even greater impact is possible.
In this instance, Case Western Reserve cancer researcher Li Li, MD, PhD, could not have been more prescient.
Not only did the combination of the two improve outcomes in animal studies, but the dual-compound effect was dramatically better than either option alone. Even better, these impressive results required only modest amounts of metformin and Vitamin D3, making concerns about side ...
2015-03-23
DURHAM, N.C. - Scientists have known for some time that people who carry a lot of weight around their bellies are more likely to develop diabetes and heart disease than those who have bigger hips and thighs. But what hasn't been clear is why fat accumulates in different places to produce these classic "apple" and "pear" shapes.
Now, researchers have discovered that a gene called Plexin D1 appears to control both where fat is stored and how fat cells are shaped, known factors in health and the risk of future disease.
Acting on a pattern that emerged in an earlier study ...
2015-03-23
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. -- MARCH 23, 2015) Research led by scientists at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital has identified key molecules that trigger the immune system to launch an attack on the bacterium that causes tularemia. The research was published online March 16 in Nature Immunology.
The team, led by Thirumala-Devi Kanneganti, Ph.D., a member of the St. Jude Department of Immunology, found key receptors responsible for sensing DNA in cells infected by the tularemia-causing bacterium, Francisella. Tularemia is a highly infectious disease that kills more than 30 percent ...
2015-03-23
MAYWOOD, Ill. - No cures are possible for most patients who suffer debilitating movement disorders called cerebellar ataxias.
But in a few of these disorders, patients can be effectively treated with regimens such as prescription drugs, high doses of vitamin E and gluten-free diets, according to a study in the journal Movement Disorders.
"Clinicians must become familiar with these disorders, because maximal therapeutic benefit is only possible when done early. These uncommon conditions represent a unique opportunity to treat incurable and progressive diseases," first ...
2015-03-23
Contrary to the statistician's slogan, in the quantum world, certain kinds of correlations do imply causation.
Research from the Institute for Quantum Computing (IQC) at the University of Waterloo and the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics shows that in quantum mechanics, certain kinds of observations will let you distinguish whether there is a common cause or a cause-effect relation between two variables. The same is not true in classical physics.
Explaining the observed correlations among a number of variables in terms of underlying causal mechanisms, known ...
2015-03-23
A surgical sedative may hold the key to reversing the devastating symptoms of a neurodevelopmental disorder found almost exclusively in females. Ketamine, used primarily for operative procedures, has shown such promise in mouse models that Case Western Reserve and Cleveland Clinic researchers soon will launch a two-year clinical trial using low doses of the medication in up to 35 individuals with Rett Syndrome.
The $1.3 million grant from Rett Syndrome Research Trust (RSRT) represents a landmark step in area researchers' efforts to create a true regional collaborative ...
2015-03-23
When an earthquake hits, the faster first responders can get to an impacted area, the more likely infrastructure--and lives--can be saved.
New research from the University of Iowa, along with the United States Geological Survey (USGS), shows that GPS and satellite data can be used in a real-time, coordinated effort to fully characterize a fault line within 24 hours of an earthquake, ensuring that aid is delivered faster and more accurately than ever before.
Earth and Environmental Sciences assistant professor William Barnhart used GPS and satellite measurements from ...
2015-03-23
In addition to antiretroviral medications, people with HIV may soon begin receiving a home exercise plan from their doctors, according to a researcher at Case Western Reserve University's Frances Payne Bolton School of Nursing.
"People with HIV are developing secondary chronic illnesses earlier and more frequently than their non-HIV counterparts," said Allison Webel, PhD, RN, assistant professor of nursing. "And heart disease is one for which they are especially at risk."
An estimated 1.2 million people nationally live with HIV, according to the Centers for Disease ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ascension of marine diatoms linked to vast increase in continental weathering