(Press-News.org) The use of technology in daily life is getting easier all the time as people accumulate knowledge and skills in information and communications technology. However, the most important thing in developing health care services, for example, is to take into account people's day to day lives and their subjective experience of the utility of using services. For example, people's previous bad experience of using a service is reflected for a long time in their use of the service in the future, and thus the dissemination of new service models is a lot slower than might be imagined. This data was the result of research carried out at Lappeenranta University of Technology, LUT.
"We should provide services that are rapidly accepted among large groups of people. On the basis of our observations, people's use of health care services could change through unofficial networks, for example pioneering village associations", observes Mika Immonen, a post-doctoral researcher.
LUT's production management researchers are examining users' experience of the utility and availability of health care services. In addition they have investigated the importance of users' attitudes, familiarity and routines in the use of electronic and physical health care services. The results show clearly that an understanding of the user's daily life needs to be added when planning new service models. The research findings were published in the International Journal of Public Sector Management in January 2015.
According to Mika Immonen, what is known as "experienced utility" is a problematic issue as all of us construct it ourselves. What is also problematic is that engineers have designed electronic services without behavioural scientists even though the development of new service models requires specific knowledge about people's behaviour and attitudes.
Older people from South Karelia subjects of the study
Immonen and his team have carried out two major surveys on health care services in the South Karelia region among the population of the over-60s in 2004 and 2012. There were over a thousand respondents to the latest questionnaire. On the basis of the questionnaires we can conclude that the future use of services is largely directed by preconceptions regarding the service that are the product of the individual's experiential history.
"People's attitudes change extremely slowly, but the operating environment for services is subject to continuous change. The danger is that when the availability of health care services is reduced and at the same time they are replaced by new electronic services, for example, people do not necessarily start to use them. Thus the change results in the risk of them being totally excluded from the services", explains Mika Immonen.
According to him, political decision makers should consider that if there are no replacement services and people decide that they will not use the scaled-down services, then in a few years' time this same group will require acute treatment in specialist hospital care.
"And that if anything, will be a cost to society. What is essential is to get precisely the people who are not active users of the new health care services to start to use them. The healthy citizens of the future will be the group who are the more active users of the new social and health care services. Change made today will only be seen in a few years, and this also applies to the total costs of health care", comments Mika Immonen.
He believes that replacement health care services should be such that people will really start to use them and replacement services must also, of course, be available, including in remote areas.
"If we consider sparsely populated areas, then the whole village has to approve the new kinds of services so that the community starts to use them. Once development idea would be for a community to get a few active people to commit to being involved in the design of the new service models. Their example would probably get the others to use the new health care services too."
The research is part of the HEA project which was carried out during the period 2011?2014. The abbreviation comes from the Finnish for "well-being and energy efficiency in housing": operating models for mobile services and services provided at home. The project generated data for the development of new service models for the public, private and third sectors. Funding was provided by the European Regional Development Fund, i.e. ERDF Päijät-Häme, and the budget for LUT's part of the project was about EUR 200 000.
INFORMATION:
Further information:
Mika Immonen, tel. +358 40 483 5793, mika.immonen@lut.fi
Link to the research web pages: http://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/abs/10.1108/IJPSM-03-2014-0035
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that symptoms of depression and insomnia are the strongest predictors of having frequent nightmares.
Results show that 3.9 percent of participants reported having frequent nightmares during the previous 30 days, including 4.8 percent of women and 2.9 percent of men. Frequent nightmares were reported by 28.4 percent of participants with severe depressive symptoms and 17.1 percent of those with frequent insomnia. Further analysis that adjusted for potential confounders found that the strongest independent risk factors for nightmares were ...
Bethesda, MD (April 2, 2015) -- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), the more severe form of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) that can progress to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, is associated with leakiness of the intestinal wall, which in turn may worsen liver disease, according to research1 published in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology, the new basic science journal of the American Gastroenterological Association.
"Our study strengthens the clinical association between intestinal permeability and NASH, although we were unable to identify ...
Accurate blood pressure measurement (BP) is fundamental to the early diagnosis of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, says a review published 1 April, 2015, in The Obstetrician & Gynaecologist (TOG).
The diagnosis and management of hypertensive disorders in pregnancy, as well as obstetric haemorrhage, sepsis and safe abortion, are guided in part by the measurement of BP. These conditions contribute to more than half of all maternal deaths globally, so the accuracy of BP measurement is vital, the review concludes.
The review explains that BP monitoring is the most ...
BATON ROUGE - LSU Psychology Professor Megan H. Papesh was part of a research team whose study appeared in the online-first edition of the Journal of Neuroscience on Wednesday, April 1.
The research, jointly conducted by scientists from the Barrow Neurological Institute and Arizona State University, involves recording single-neuron activity in the brains of epilepsy patients who require electrodes implanted to monitor seizures. With the electrodes in place, processes such as perception and memory can be studied at the level of individual neurons.
The research focused ...
As man-made threats to coral reefs mount and interest in conserving reef ecosystems grows, scientists have turned to studying extremely remote and uninhabited reefs in an effort to understand what coral reefs would be like in the absence of humans. A number of islands and atolls in the Pacific Ocean remain virtually untouched by human influence, situated hundreds of kilometers from the nearest human populations.
A study published today by scientists at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa (UHM) School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), the National ...
MADISON, Wis. - Clearing grasslands to make way for biofuels may seem counterproductive, but University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers show in a study today (April 2, 2015) that crops, including the corn and soy commonly used for biofuels, expanded onto 7 million acres of new land in the U.S. over a recent four-year period, replacing millions of acres of grasslands.
The study -- from UW-Madison graduate student Tyler Lark, geography Professor Holly Gibbs, and postdoctoral researcher Meghan Salmon -- is published in the journal Environmental Research Letters and addresses ...
Use of a class of insecticides, called neonicotinoids, increased dramatically in the mid-2000s and was driven almost entirely by the use of corn and soybean seeds treated with the pesticides, according to researchers at Penn State.
"Previous studies suggested that the percentage of corn acres treated with insecticides decreased during the 2000s, but once we took seed treatments into account we found the opposite pattern," said Margaret Douglas, graduate student in entomology. "Our results show that application of neonicotinoids to seed of corn and soybeans has driven ...
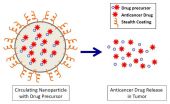
Delving into the world of the extremely small, researchers are exploring how biodegradable nanoparticles can precisely deliver anticancer drugs to attack neuroblastoma, an often-deadly children's cancer.
By bringing together experts in pediatric oncology with experts in nanotechnology, researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia aim to thread the needle of delivering effective doses of cancer-killing agents while avoiding toxicity in healthy tissues. The team's new research shows that this approach inhibits tumor growth and markedly prolongs survival in animal ...
DENVER - Exercise and physical activity should be considered as therapeutic options for lung cancer as they have been shown to reduce symptoms, increase exercise tolerance, improve quality of life, and potentially reduce length of hospital stay and complications following surgery for lung cancer.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States with an estimated 160,000 deaths each year and worldwide there are 1.4 million deaths. In the last two decades lung cancer therapy has improved, but the overall 5-year survival rate is still quite low at 17%. ...
A particular molecular pathway permits stem cells in pediatric bone cancers to grow rapidly and aggressively, according to researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center and its Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center.
In normal cell growth, the Hippo pathway, which controls organ size in animals, works as a dam, regulating cell proliferation. What the researchers found is that the transcription factor of a DNA binding protein called sex determining region Y box 2, or Sox2 for short, which normally maintains cell self-renewal, actually releases the floodgates in the Hippo ...