LSU professor's neurological research featured in the Journal of Neuroscience
Visual objects are represented by a distributed network in the human brain
2015-04-02
(Press-News.org) BATON ROUGE - LSU Psychology Professor Megan H. Papesh was part of a research team whose study appeared in the online-first edition of the Journal of Neuroscience on Wednesday, April 1.
The research, jointly conducted by scientists from the Barrow Neurological Institute and Arizona State University, involves recording single-neuron activity in the brains of epilepsy patients who require electrodes implanted to monitor seizures. With the electrodes in place, processes such as perception and memory can be studied at the level of individual neurons.
The research focused on a hotly contested topic in cognitive neuroscience, testing the idea of "grandmother cells" in the human brain. In the past decade, several prominent studies suggested that individual brain cells are finely tuned to fire selectively to very specific concepts. For example, a neuron in the hippocampus may be quiet as the person views hundreds of images of animals, people and objects, but will fire rapidly when the person sees a photo of the actress Halle Berry. This same neuron will fire in response to various different images of Berry, and also to her name, suggesting that the neuron represents the person herself, not merely her appearance. Given such results, researchers have argued that neural representations of concepts are "sparse," a hypothesis that concepts are coded in the brain by small collections of highly selective neurons.
The new study featured in the Journal of Neuroscience used the basic same method as earlier experiments that suggested sparse coding. Patients viewed many images and names, and simply decided whether each stimulus represented a person or an animal/landmark. For every concept, there were four different representations shown six times each. Despite using nearly the same method as prior studies, the new results provide strong evidence for distributed coding, with different objects creating firing-rate changes across many neurons. Of the recorded neurons that were active, most responded to multiple, often unrelated, concepts. Only one recorded neuron out of 1,532 behaved like the grandmother cells from previous studies.
What accounts for this dramatic difference across experiments? Papesh and her colleagues suggest that new memories for specific stimuli might be the key. Whereas patients in the new experiment saw particular images only six times, the volunteers in previous studies saw individual images up to 50 times. Taking the old and new studies together, the results suggest that episodic memory for particular images can tune individual neurons to behave in a highly selective fashion. But, as a general rule, people rarely encounter identical images of people or places dozens of times, and the human brain presumably evolved its coding schemes long before photography existed. The brain is adapted to robustly recognize new images as examples of known categories, despite changes in appearance.
The new results suggest that classification is achieved by sharing the computational load across large sets of neurons. In a broadly distributed system, small responses from thousands of neurons represent knowledge; losing cells would have essentially no impact on the ability to recognize objects or people. The combined results of these studies testify to the incredible flexibility of the human brain, which can classify newly encountered objects while also forming stable episodic memories for specific images.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the Barrow Neurological Foundation, Arizona Biomedical Research Council and the National Institute for Deafness and other Communication Disorders.
To view the April 1 edition of the Journal of Neuroscience, visit http://www.jneurosci.org/.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-02
As man-made threats to coral reefs mount and interest in conserving reef ecosystems grows, scientists have turned to studying extremely remote and uninhabited reefs in an effort to understand what coral reefs would be like in the absence of humans. A number of islands and atolls in the Pacific Ocean remain virtually untouched by human influence, situated hundreds of kilometers from the nearest human populations.
A study published today by scientists at the University of Hawai'i at Mānoa (UHM) School of Ocean and Earth Science and Technology (SOEST), the National ...
2015-04-02
MADISON, Wis. - Clearing grasslands to make way for biofuels may seem counterproductive, but University of Wisconsin-Madison researchers show in a study today (April 2, 2015) that crops, including the corn and soy commonly used for biofuels, expanded onto 7 million acres of new land in the U.S. over a recent four-year period, replacing millions of acres of grasslands.
The study -- from UW-Madison graduate student Tyler Lark, geography Professor Holly Gibbs, and postdoctoral researcher Meghan Salmon -- is published in the journal Environmental Research Letters and addresses ...
2015-04-02
Use of a class of insecticides, called neonicotinoids, increased dramatically in the mid-2000s and was driven almost entirely by the use of corn and soybean seeds treated with the pesticides, according to researchers at Penn State.
"Previous studies suggested that the percentage of corn acres treated with insecticides decreased during the 2000s, but once we took seed treatments into account we found the opposite pattern," said Margaret Douglas, graduate student in entomology. "Our results show that application of neonicotinoids to seed of corn and soybeans has driven ...
2015-04-02
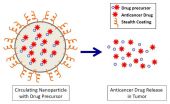
Delving into the world of the extremely small, researchers are exploring how biodegradable nanoparticles can precisely deliver anticancer drugs to attack neuroblastoma, an often-deadly children's cancer.
By bringing together experts in pediatric oncology with experts in nanotechnology, researchers at The Children's Hospital of Philadelphia aim to thread the needle of delivering effective doses of cancer-killing agents while avoiding toxicity in healthy tissues. The team's new research shows that this approach inhibits tumor growth and markedly prolongs survival in animal ...
2015-04-02
DENVER - Exercise and physical activity should be considered as therapeutic options for lung cancer as they have been shown to reduce symptoms, increase exercise tolerance, improve quality of life, and potentially reduce length of hospital stay and complications following surgery for lung cancer.
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States with an estimated 160,000 deaths each year and worldwide there are 1.4 million deaths. In the last two decades lung cancer therapy has improved, but the overall 5-year survival rate is still quite low at 17%. ...
2015-04-02
A particular molecular pathway permits stem cells in pediatric bone cancers to grow rapidly and aggressively, according to researchers at NYU Langone Medical Center and its Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center.
In normal cell growth, the Hippo pathway, which controls organ size in animals, works as a dam, regulating cell proliferation. What the researchers found is that the transcription factor of a DNA binding protein called sex determining region Y box 2, or Sox2 for short, which normally maintains cell self-renewal, actually releases the floodgates in the Hippo ...
2015-04-02
ARLINGTON HEIGHTS, Ill. (April 2, 2015) - No home is perfect, but dysfunction in the home is now revealed to be especially dangerous for children at risk for asthma. A new study shows that children exposed to just one adverse childhood experience (ACE) had a 28 percent increased chance of developing asthma than those with no ACEs.
The study, published in the Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, the scientific publication of the American College of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology (ACAAI), used data from the National Survey of Children's Health. The survey drew from ...
2015-04-02
Globally, residential development is a leading driver of natural resource consumption, native species decline and fossil fuel emissions.
Today, residential development covers one out of every four acres of the land in the United States, and is predicted to more than double by 2100.
In many communities, local governments and planners are adopting sustainable development practices to address residential development impacts on human well-being and the environment. These sustainable development practices include considerations of a healthy environment, a robust economy, ...
2015-04-02
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Unlike some conditions, heart failure must be managed by patients taking prescriptions for the rest of their lives. Individuals who do not take their heart medication as prescribed have increased risks of mortality and hospitalization and higher health care costs. Numerous interventions have been designed to increase patients' adherence to medications; yet, no research has determined what intervention techniques are most effective. Now, a University of Missouri researcher found that interventions to encourage patients to take their medications as prescribed ...
2015-04-01
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Purdue researchers have identified a new class of chemical insecticides that could provide a safer, more selective means of controlling mosquitoes that transmit key infectious diseases such as dengue, yellow fever and elephantiasis.
Known as dopamine receptor antagonists, the chemicals beat out the neurotransmitter dopamine to lock into protein receptors that span the mosquito cell membrane. Disrupting the mechanics of dopamine - which plays important roles in cell signaling, movement, development and complex behaviors - eventually leads to the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] LSU professor's neurological research featured in the Journal of Neuroscience
Visual objects are represented by a distributed network in the human brain