Ocean myth busted: 'Toddler' sea turtles are very active swimmers
2015-04-09
(Press-News.org) It turns out sea turtles, even at a tender 6-18 months of age, are very active swimmers. They don't just passively drift in ocean currents as researchers once thought. NOAA and University of Central Florida researchers say it's an important new clue in the sea turtle "lost years" mystery. Where exactly turtles travel in their first years of life, before returning to coastal areas as adults to forage and reproduce, has puzzled scientists for decades.
"All species of sea turtles are endangered or threatened under the Endangered Species Act; knowing their distribution is an essential part of protecting them. With a better understanding of swimming behavior in these yearlings we can make better predictions about where they go and what risks they might encounter," said Dr. Nathan Putman, lead author of this new study and sea turtle biologist with NOAA's Southeast Fisheries Science Center in Miami.
Upon hatching, young sea turtles swim offshore and disperse with the help of ocean currents. The turtles are rarely observed during the next two to ten years or so, but prior studies suggest that at least some reside among mats of seaweed, such as Sargassum, that provide shelter and habitat in the open sea. Not much is known about these juveniles' movements during this time (researchers dub it the "lost years"), but it has been widely assumed that turtles simply drift with ocean currents.
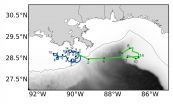
Putman worked with Dr. Kate Mansfield, director of the University of Central Florida's Marine Turtle Research Group, to challenge this long-existing hypothesis. Mansfield placed specially designed solar-powered tags on 24 green & 20 Kemp's ridley wild-caught sea turtle toddlers in the Gulf of Mexico. The tags were tracked by satellite for a short period of time before shedding cleanly from the turtle shells (max. 2-3 months). Next to the turtles, Mansfield deployed small, carefully-weighted/passively-drifting surface buoys that were also tracked by satellite.
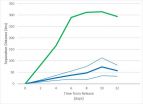
When the drifter tracks were compared to the sea turtles' movements, the researchers found that the turtles' paths differed significantly from the passive drifters. Using observed and modeled ocean current conditions, they found a difference of distance between the turtles and drifters to be as much as 125 miles in the first few days. In nearly every instance, the toddlers' swimming behavior appears to help them reach or remain in favorable ocean habitats.
"The results of our study have huge implications for better understanding early sea turtle survival and behavior, which may ultimately lead to new and innovative ways to further protect these imperiled animals," said Mansfield.
She added, "What is exciting is that this is the first study to release drifters with small, wild-caught yearling or neonate sea turtles in order to directly test the 'passive drifter' hypothesis in these young turtles. Our data show that one hypothesis doesn't, and shouldn't, fit all, and that even a small degree of swimming or active orientation can make a huge difference in the dispersal of these young animals."
INFORMATION:
The study was published in the journal Current Biology. To learn more about sea turtles, visit NOAA Fisheries and the UCF Marine Turtle Research Group webpages.
NOAA's mission is to understand and predict changes in the Earth's environment, from the depths of the ocean to the surface of the sun, and to conserve and manage our coastal and marine resources. Join us on Twitter, Facebook, Instagram and our other social media channels.
America's Partnership University: The University of Central Florida, the nation's second-largest university with more than 60,000 students, has grown in size, quality, diversity and reputation in its first 50 years. Today, the university offers more than 200 degree programs at its main campus in Orlando and more than a dozen other locations. UCF is an economic engine attracting and supporting industries vital to the region's future while providing students with real-world experiences that help them succeed after graduation. For more information, visit http://today.ucf.edu and join the UCF Marine Turtle Research Group on Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram.
On the Web:
Study, "Direct Evidence of Swimming Demonstrates Active Dispersal in the Sea Turtle 'Lost Years'"
NOAA Fisheries' Sea Turtles Page:
http://www.nmfs.noaa.gov/pr/species/turtles/
UCF Marine Turtle Research Group:
http://biology.cos.ucf.edu/marineturtleresearchgroup/
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-09
Building on their discovery of a gene linked to eating disorders in humans, a team of researchers at the University of Iowa has now shown that loss of the gene in mice leads to several behavioral abnormalities that resemble behaviors seen in people with anorexia nervosa.
The team, led by Michael Lutter, MD, PhD, assistant professor of psychiatry in the UI Carver College of Medicine, found that mice that lack the estrogen-related receptor alpha (ESRRA) gene are less motivated to seek out high-fat food when they are hungry and have abnormal social interactions. The effect ...
2015-04-09
WASHINGTON -- Facial plastic surgery may do more than make you look youthful. It could change -- for the better -- how people perceive you. The first study of its kind to examine perception after plastic surgery finds that women who have certain procedures are perceived as having greater social skills and are more likeable, attractive and feminine.
The study is not superficial -- the importance of facial appearance is rooted in evolution and studies suggest that judging a person based on his or her appearance boils down to survival. The results were published online ...
2015-04-09
Facial rejuvenation surgery may not only make you look younger, it may improve perceptions of you with regard to likeability, social skills, attractiveness and femininity, according to a report published online by JAMA Facial Plastic Surgery.
The relationship between facial features and personality traits has been studied in other science fields, but it is lacking in the surgical literature, according to the study background.
Michael J. Reilly, M.D., of the MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, and coauthors measured the changes in personality perception ...
2015-04-09
Axillary lymph node evaluation is performed frequently in women with ductal carcinoma in situ breast cancer, despite recommendations generally against such an assessment procedure in women with localized cancer undergoing breast-conserving surgery, according to a study published online by JAMA Oncology.
While axillary lymph node evaluation is the standard of care in the surgical management of invasive breast cancer, a benefit has not been demonstrated in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS). For women with invasive breast cancer, sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) replaced ...
2015-04-09
LAWRENCE -- A team of scientists at the University of Kansas has pinpointed six chemical compounds that thwart HuR, an "oncoprotein" that binds to RNA and promotes tumor growth.
The findings, which could lead to a new class of cancer drugs, appear in the current issue of ACS Chemical Biology.
"These are the first reported small-molecule HuR inhibitors that competitively disrupt HuR-RNA binding and release the RNA, thus blocking HuR function as a tumor-promoting protein," said Liang Xu, associate professor of molecular biosciences and corresponding author of the paper.
The ...
2015-04-09
As we age, the physical make up of our brains changes. This includes changes in neural processing in grey matter, but also in the deterioration of structural connections in the brain, which allow communication between distinct brain regions, so the brain is able to work as a well-wired network system.
Researchers at the Lifelong Brain and Cognition Lab at the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the University of Illinois have utilized the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) facilities available in Beckman's Biomedical Imaging Center to measure the moment-to-moment ...
2015-04-09
Every year, 300,000 pregnant women and 2,600,000 newborn babies are estimated to die worldwide, and more than 99% of these deaths occur in developing countries. Effective interventions to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality are critically needed, and an ongoing challenge for researchers and health professionals is finding the best way to deliver these interventions in resource-limited settings such as Mongolia. Antenatal visits can provide the first opportunity to deliver these interventions. Now, a new study has shown that Japan's flagship intervention, the Maternal ...
2015-04-09
The question if humans can communicate via pheromones in the same way as animals is under debate. Cell physiologists at the Ruhr-Universität Bochum have demonstrated that the odorous substance Hedione activates the putative pheromone receptor VN1R1, which occurs in the human olfactory epithelium. Together with colleagues from Dresden, the Bochum-based researchers showed that the scent of Hedione generates sex-specific activation patters in the brain, which do not occur with traditional fragrances. "These results constitute compelling evidence that a pheromone effect ...
2015-04-09
Well intentioned, but costly and potentially problematic. That's how researchers describe the end result of a decision by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to regulate colchicine, a drug used to treat gout, among other ailments. Fewer patients are actually now taking it, and it has come at a cost to their wallets, says study leader Aaron Kesselheim of Brigham and Women's Hospital and the Harvard Medical School in the US. The findings¹ appear in the Journal of General Internal Medicine,² published by Springer.
Colchicine had been sold at low cost for many ...
2015-04-09
Shakespeare is such a towering literary figure that any new insight into the man, or his work, tends to generate a jolt of excitement in academic and non-academic communities of Shakespeare aficionados. Applying psychological theory and text-analyzing software, researchers at the University of Texas at Austin have discovered a unique psychological profile that characterizes Shakespeare's established works, and this profile strongly identifies Shakespeare as an author of the long-contested play Double Falsehood.
The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ocean myth busted: 'Toddler' sea turtles are very active swimmers