Meteorites key to the story of Earth's layers: ANU media release
A new analysis of the chemical make-up of meteorites has helped scientists work out when the Earth formed its layers, confirming the Earth's first crust had formed around 4.5 billion years ago
2015-04-13
(Press-News.org) A new analysis of the chemical make-up of meteorites has helped scientists work out when the Earth formed its layers.
The research by an international team of scientists confirmed the Earth's first crust had formed around 4.5 billion years ago.
The team measured the amount of the rare elements hafnium and lutetium in the mineral zircon in a meteorite that originated early in the solar system.
"Meteorites that contain zircons are rare. We had been looking for an old meteorite with large zircons, about 50 microns long, that contained enough hafnium for precise analysis," said Dr Yuri Amelin, from The Australian National University (ANU) Research School of Earth Sciences.
"By chance we found one for sale from a dealer. It was just what we wanted. We believe it originated from the asteroid Vesta, following a large impact that sent rock fragments on a course to Earth."
The heat and pressure in the Earth's interior mixes the chemical composition of its layers over billions of years, as denser rocks sink and less dense minerals rise towards the surface, a process known as differentiation.
Determining how and when the layers formed relies on knowing the composition of the original material that formed into the Earth, before differentiation, said Dr Amelin.
"Meteorites are remnants of the original pool of material that formed all the planets," he said.
"But they have not had planetary-scale forces changing their composition throughout their five billion years orbiting the sun."
The team accurately measured the ratio of the isotopes hafnium-176 and hafnium-177 in the meteorite, to give a starting point for the Earth's composition.
The team were then able to compare the results with the oldest rocks on Earth, and found that the chemical composition had already been altered, proving that a crust had already formed on the surface of the Earth around 4.5 billion years ago.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-13
Diversity of life abounds on Earth, and there's no need to look any farther than the ocean's surface for proof. There are over 200,000 species of phytoplankton alone, and all of those species of microscopic marine plants that form the base of the marine food web need the same basic resources to grow--light and nutrients.
A study by a team of scientists from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI), University of Rhode Island (URI), and Columbia University, published April 13 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences reveals how species of diatoms--one ...
2015-04-13
ANN ARBOR, Mich. - One of the brain's main jobs is information processing - what is critical, however, is that information in the brain gets transferred to the right places at the right times.
Research on large-scale brain networks by the University of Michigan Medical School reveals that "hubs" in the brain - highly connected regions that like hubs of the airport system - tend to consistently attract information flow.
"Understanding how information transfer occurs in the brain is critical, especially if network hubs are taken off line by anesthesia, tumor or stroke," ...
2015-04-13
This news release is available in German.
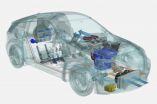
How can a pleasant vehicle climate be achieved efficiently? Researchers at the Technische Universität München (TUM) pursued this question in the context of the research project Visio.M funded by the German Federal Ministry for Education and Research (BMBF) with a total of 7.1 million euro. The results of their research show that the potential of energy efficient air conditioning is all but exhausted. And this applies also to gasoline powered cars.
Inefficiency has its advantages, too: In the past, waste heat ...
2015-04-13
Researchers are beginning to explore whether the genetics of patients who experience a placebo effect are different from those of patients who don't. It's well known that people can feel better if they believe they are receiving treatment, but the biological pathways involved are relatively unexplored. In a new review, publishing April 13 in Trends in Molecular Medicine, scientists at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center discuss what we know as well as possible ethical issues related to conducting genetic tests to determine whether a patient is a placebo responder.
"Understanding ...
2015-04-13
A new strategy to rule-out and rule-in heart attacks in emergency departments will help physicians treat patients faster, found a clinical trial published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is a common cause of death and disability around the world. Early diagnosis is critical for treatment and survival.
Swiss and Spanish researchers conducted a clinical trial to determine whether a new technique, previously tested in a small pilot study, would be effective in determining whether a patient has had a heart attack. They enrolled ...
2015-04-13
Family physicians have an important role in advising women about the benefits and risks of egg freezing, argues an analysis in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"With growing public awareness of social egg freezing, Canadian women may increasingly approach physicians in search of information and advice about the procedure," writes Dr. Angel Petropanagos, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, with coauthors Alana Cattapan, Françoise Baylis and Arthur Leader. "Family physicians are uniquely positioned at the front lines of medical ...
2015-04-13
Melanoma cells become drug resistant by using surrounding healthy cells to provide a 'safe haven' from treatment, according to new research* published in Cancer Cell today (Monday).
Around half of melanomas are caused by a mutation in a gene called BRAF. Drugs called BRAF inhibitors treat these melanomas by targeting the faulty gene. But these cancers can quickly develop resistance to these targeted treatments.
Scientists at the Francis Crick Institute, funded by Cancer Research UK, and at the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute have discovered that a side effect ...
2015-04-13
A drug with the potential to reverse resistance to immunotherapy has been developed by scientists at the University of Southampton. It has shown great promise in pre-clinical models and will be available to patients with certain leukaemias and non-Hodgkin lymphomas in clinical trials later this year.
Targeted drugs made from engineered immune proteins - called monoclonal antibodies - have revolutionised treatment for several types of cancer in recent years. They work by sticking to specific proteins found on the surface of cancer cells, flagging them up to be killed by ...
2015-04-13
BOSTON -Placebos have helped to ease symptoms of illness for centuries and have been a fundamental component of clinical research to test new drug therapies for more than 70 years. But why some people respond to placebos and others do not remains under debate.
With the advent of genomics, researchers are learning that placebo responses are modified by a person's genetics, a discovery that raises important new questions regarding the role of the placebo in patient care and in drug development: How many genetic biomarkers exist? Can the medical field harness the placebo ...
2015-04-13
This news release is available in Spanish. Through his latest research, Javier Polavieja, a professor Sociology in the Social Sciences Department who holds a UC3M- Santander Named Chair of (Cátedra de Excelencia), has shown how European women who emigrate to other countries within the same continent take the cultural norms of their home countries with them. Those norms are decisive when it comes to determining their work behavior.
To reach this conclusion, the researcher compared the attitudes of over three thousand immigrant women from some twenty European countries ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Meteorites key to the story of Earth's layers: ANU media release
A new analysis of the chemical make-up of meteorites has helped scientists work out when the Earth formed its layers, confirming the Earth's first crust had formed around 4.5 billion years ago