(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES (EMBARGOED UNTIL 7 A.M. EDT on APRIL 14, 2015) - An injection of stem cells into the eye may soon slow or reverse the effects of early-stage age-related macular degeneration, according to new research from scientists at Cedars-Sinai. Currently, there is no treatment that slows the progression of the disease, which is the leading cause of vision loss in people over 65.
"This is the first study to show preservation of vision after a single injection of adult-derived human cells into a rat model with age-related macular degeneration," said Shaomei Wang, MD, PhD, lead author of the study published in the journal STEM CELLS and a research scientist in the Eye Program at the Cedars-Sinai Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute.
The stem cell injection resulted in 130 days of preserved vision in laboratory rats, which roughly equates to 16 years in humans.
Age-related macular degeneration affects upward of 15 million Americans. It occurs when the small central portion of the retina, known as the macula, deteriorates. The retina is the light-sensing nerve tissue at the back of the eye. Macular degeneration may also be caused by environmental factors, aging and a genetic predisposition.
When animal models with macular degeneration were injected with induced neural progenitor stem cells, which derive from the more commonly known induced pluripotent stem cells, healthy cells began to migrate around the retina and formed a protective layer. This protective layer prevented ongoing degeneration of the vital retinal cells responsible for vision.
Cedars-Sinai researchers in the Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell (iPSC) Core, directed by Dhruv Sareen, PhD, with support from the David and Janet Polak Foundation Stem Cell Core Laboratory, first converted adult human skin cells into powerful induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), which can be expanded indefinitely and then made into any cell of the human body. In this study, these induced pluripotent stem cells were then directed toward a neural progenitor cell fate, known as induced neural progenitor stem cells, or iNPCs.
"These induced neural progenitor stem cells are a novel source of adult-derived cells which should have powerful effects on slowing down vision loss associated with macular degeneration," said Clive Svendsen, PhD, director of the Board of Governors Regenerative Medicine Institute and contributing author to the study. "Though additional pre-clinical data is needed, our institute is close to a time when we can offer adult stem cells as a promising source for personalized therapies for this and other human diseases."
Next steps include testing the efficacy and safety of the stem cell injection in preclinical animal studies to provide information for applying for an investigational new drug. From there, clinical trials will be designed to test potential benefit in patients with later-stage age-related macular degeneration.
INFORMATION:
Additional Cedars-Sinai authors include Dhruv Sareen, PhD; Yuchun Tsai, PhD; Bin Lu, MD, PhD; Benjamin Bakondi, PhD; Sergey Girman, PhD; and Anais Sahabian, PhD.
This work was supported by the Simon and Beathrice Apple Stem Cell Fund for Eye Research, the David and Janet Polak Foundation Stem Cell Core Laboratory; National Institutes of Health (R01 EY020488), Department of Defense (W81XWH-12-1-0617), Foundation Fighting Blindness and the Knights Templar Eye Foundation Inc.
Citation: STEM CELLS. 2015 April: Human iPSC-derived neural progenitors preserve vision in an AMD-like model.
Scientists at the University of Southampton have shown that higher muscle mass is strongly linked with healthier bone development in children.
Researchers also found no relationship between fat mass and bone development, indicating it is not an important factor in childhood skeletal strength.
A new study, published in the journal Bone, by researchers from the University's Medical Research Council Lifecourse Epidemiology Unit shows a link between the amount of lean muscle and healthy bone development, indicated by the size, shape and density of limb bones, in children ...
Methane, a highly effective greenhouse gas, is usually produced by decomposition of organic material, a complex process involving bacteria and microbes.
But there is another type of methane that can appear under specific circumstances: Abiotic methane is formed by chemical reactions in the oceanic crust beneath the seafloor.
New findings show that deep water gas hydrates, icy substances in the sediments that trap huge amounts of the methane, can be a reservoir for abiotic methane. One such reservoir was recently discovered on the ultraslow spreading Knipovich ridge, ...
Researchers at Uppsala University have, together with researchers from Turku and Bergen, discovered a new biomarker which makes it possible to identify women with uterine cancer who have a high risk of recurrence. The findings were recently published in the journal Gynecologic Oncology.
Endometrial cancer of the uterus is the most common form of gynecologic cancer in Europe and North America. The treatment primarily consists of removing the uterus and in some cases offering chemotherapy if the risk of recurrence is deemed high.
The current study looks at the amount ...
Researchers at the University of Manchester and Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust have published data for the first time about public knowledge of and interest in the process of medicines research and development.
The study, which is part of the wider European Patients' Academy on Therapeutic Innovation (EUPATI) project, is believed to be the largest peer-reviewed survey of its kind and was published today in the BMJ Open.
Medicines R&D describes the entire process of bringing a new medicine to patients - from laboratory studies to clinical ...
The seabed is inhabited by vast numbers of small animals with hidden lives in the sandy sediments. Here they play an important role in keeping the oceans healthy. But how these animals behave and interact with each other is unclear, as it is not possible to see them without disturbing the sediment.
Researchers like Ph.D. Matthieu Delefosse would enjoy putting on a pair of X-ray glasses and study the sediment living animals without disturbing them.
"We know bits and pieces of what these animals do through different measurements/experiments, but we do not have an integrated ...
Researchers at Genes and Cancer group at Bellvitge Biomedical Research Institute (IDIBELL), led by Montse Sanchez-Cespedes, have identified the PARD3 gene as a tumor suppressor that is inactivated in lung cancer squamous type. The results of the study have been published in Cancer Research.
Correct polarization (orientation in space) of bronchial epithelial cells is essential for the maintenance and proper development of this tissue under normal conditions.
PARD3 gene encodes a protein that regulates cell polarization and cell junctions. When the gene is inactivated, ...
Scientists at the University of Sheffield calculate that all of the UK's high level nuclear waste from spent fuel reprocessing could be disposed of in just six boreholes 5km deep, fitting within a site no larger than a football pitch.
The concept - called deep borehole disposal - has been developed primarily in the UK but is likely to see its first field trials in the USA next year. If the trials are successful, the USA hopes to dispose of its 'hottest' and most radioactive waste - left over from plutonium production and currently stored at Hanford in Washington State ...
Simply declaring a region as a nature protection area is not enough, regular monitoring of its ecological condition is also necessary. Since Nature protection areas already cover almost one fifth of the surface of the European Union, it is impossible to inspect such a vast area in the traditional way on foot. Therefore, new methods are being developed to monitor Europe's nature protection areas from the air. Short laser pulses are sent to the ground, and information on the status of the habitat can be deduced from the reflected light signals using elaborate computer algorithms.
Laser ...
Cancer Mortality Reductions Were Greatest Among Countries Where Cancer Care Spending Rose The Most, 1995-2007.
Warren Stevens of Precision Health Economics, Dana P. Goldman of the Schaeffer Center for Health Policy and Economics at the University of Southern California, and coauthors compared cancer care across sixteen countries over time, examining changes in cancer spending and two measures of cancer mortality (amenable and excess mortality). They found that, compared to low-spending health systems, high-spending systems had consistently lower cancer mortality in the ...
Fast Facts:
More than 30,000 people in the U.S. are diagnosed with Lou Gehrig's disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
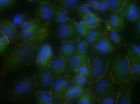
Johns Hopkins researchers have transformed skin cells donated by ALS patients into brain cells affected by the progressive, fatal disease.
The resulting cell library is being used by researchers worldwide in the quest for better ALS treatments.
Researchers at Johns Hopkins Medicine have transformed skin cells from patients with Lou Gehrig's disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), into brain cells affected by the progressive, ...