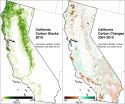
(Press-News.org) Berkeley - A new study quantifying the amount of carbon stored and released through California forests and wildlands finds that wildfires and deforestation are contributing more than expected to the state's greenhouse gas emissions.
The findings, published online today (Wednesday, April 15), in the journal Forest Ecology and Management, came from a collaborative project led by the National Park Service and the University of California, Berkeley. The results could have implications for California's efforts to meet goals mandated by the state Global Warming Solutions Act, or AB 32, to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to 1990 levels by the year 2020. The bill, which passed in 2006, assumed no net emissions for wildland ecosystems by 2020.
The researchers noted that the information available at the time the bill was passed may have underestimated the release of carbon through landmass conversions and wildfires, which are projected to increase in intensity in the western United States due to climate change. The authors pointed out that California is one of the few jurisdictions in the world to set mandatory greenhouse gas emissions targets.
"Determining the balance between carbon storage and emissions is essential for tracking the role of ecosystems in climate change. Growing vegetation naturally removes carbon from the atmosphere, reducing the magnitude of climate change," said study lead author Patrick Gonzalez, the National Park Service climate change scientist. "Conversely, burned or dead vegetation releases carbon into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change."
Gonzalez worked with forest ecologist John Battles, a professor in UC Berkeley's Department of Environmental Science, Policy and Management and the principal investigator on the project to quantify carbon storage and emissions in the state's wildlands.
The study, funded by the California Air Resources Board, used 2001-2010 data from multiple public sources, including plot-level carbon stocks from the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Forest Inventory and Assessment Program and U.S. Landfire remote sensing data of vegetation at a 30-meter spatial resolution.
The analysis confirmed that California's forests are huge carbon reservoirs for the state. Previous research has found that redwood forests near Redwood National Park contain the most carbon per hectare on the ground of any ecosystem in the world. One hectare of redwood forest can store an amount of carbon equivalent to the annual greenhouse gas emissions generated by more than 500 Americans. The giant sequoia forests of Sequoia and Kings Canyon National parks come in second.
Altogether, the forests and vegetation of state wildlands stored an estimated 850 million tons of carbon in 2010. However, those areas also accounted for approximately 69 million tons of carbon emitted between 2001 and 2010. Two-thirds of the carbon loss came from fires that burned just 6 percent of the area of wildlands in nine years. Annual carbon losses from forests and wildlands in California represent as much as 5 to 7 percent of state carbon emissions from all sectors between 2001 and 2010, according to the study.
"National parks and other protected areas clearly provide an important function in removing carbon from the atmosphere and storing it," said Battles. "But we also know from previous research that a century of fire suppression has contributed to a potentially unsustainable buildup of vegetation. This buildup provides abundant fuel for fires that contribute to carbon emissions. Projections of more wildfires in the West mean that we need to account for this source of carbon emissions. Meeting the state greenhouse gas targets for 2020 might require a reconsideration of wildland management policies."
This research is among the latest examples of the long, productive partnership between UC Berkeley and the National Park Service, highlighted in the recent "Science for Parks, Parks for Science" summit commemorating the centennial of the National Park Service.
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors of the study include researchers from the U.S. Forest Service, the Spatial Informatics Group in Pleasanton, California, and the University of San Francisco.
Researchers at the Angiocardioneurology Department of the Neuromed Scientific Institute for Research, Hospitalisation and Health Care of Pozzilli (Italy), have found, in animal models, that the absence of a certain enzyme causes a syndrome resembling the Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The study, published in the international journal EMBO Molecular Medicine, paves the way for a greater understanding of this childhood and adolescent disease, aiming at innovative therapeutic approaches.
Described for the first time in 1845, but came to the fore only in ...
HEIDELBERG, 15 April 2015 - A genetic investigation of individuals in the Framingham Heart Study may prove useful to identify novel targets for the prevention or treatment of high blood pressure. The study, which takes a close look at networks of blood pressure-related genes, is published in the journal Molecular Systems Biology.
More than one billion people worldwide suffer from high blood pressure and this contributes significantly to deaths from cardiovascular disease. It is hoped that advances in understanding the genetic basis of how blood pressure is regulated ...
Philadelphia, PA, April 16, 2015 - About 15% of patients with Lyme disease develop peripheral and central nervous system involvement, often accompanied by debilitating and painful symptoms. New research indicates that inflammation plays a causal role in the array of neurologic changes associated with Lyme disease, according to a study published in The American Journal of Pathology. The investigators at the Tulane National Primate Research Center and Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center also showed that the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone prevents many ...
New York, NY--While a large number of women quit or reduce smoking upon pregnancy recognition, many resume smoking postpartum. Previous research has estimated that approximately 70% of women who quit smoking during pregnancy relapse within the first year after childbirth, and of those who relapse, 67% resume smoking by three months, and up to 90% by six months.
A new study out in the Nicotine & Tobacco Research indicates the only significant predictor in change in smoking behaviors for women who smoked during pregnancy was in those who breastfed their infant, finding ...
Children who are taught about preventing sexual abuse at school are more likely than others to tell an adult if they had, or were actually experiencing sexual abuse. This is according to the results of a new Cochrane review published in the Cochrane Library today. However, the review's authors say that more research is needed to establish whether school-based programmes intended to prevent sexual abuse actually reduce the incidence of abuse.
It is estimated that, worldwide, at least 1 in 10 girls and 1 in 20 boys experience some form of sexual abuse in childhood. Those ...
Older adults with complex medical needs are occupying an increasing number of beds in acute care hospitals, and these patients are commonly cared for by hospitalists with limited formal geriatrics training. These clinicians are also hindered by a lack of research that addresses the needs of the older adult population. A new paper published today in the Journal of Hospital Medicine outlines a research agenda to address these issues.
To help support hospitalists in providing acute inpatient geriatric care, the Society of Hospital Medicine has developed a research agenda ...
CHICAGO --- Walking at an easy pace for about three hours every week may be just enough physical activity to help prostate cancer survivors reduce damaging side effects of their treatment, according to a new Northwestern Medicine study.
"Non-vigorous walking for three hours per week seems to improve the fatigue, depression and body weight issues that affect many men post-treatment," said Siobhan Phillips, lead author of the study. "If you walk even more briskly, for only 90 minutes a week, you could also see similar benefits in these areas."
Phillips is a kinesiologist ...
Philadelphia, PA, April 16, 2015 - With the advent of targeted lymphoma therapies on the horizon, it becomes increasingly important to differentiate the two major subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), which is the most common non-Hodgkin lymphoma. These are germinal center B-cell-like (GCB) and activated B-cell-like (ABC), which differ in management and outcomes. A report in The Journal of Molecular Diagnostics describes use of the reverse transcriptase?multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (RT-MLPA) assay for differentiating DLBCL subtypes. RT-MLPA ...
Humans may be able to communicate positive emotions like happiness through the smell of our sweat, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science. The research indicates that we produce chemical compounds, or chemosignals, when we experience happiness that are detectable by others who smell our sweat.
While previous research has shown that negative emotions related to fear and disgust are communicated via detectable regularities in the chemical composition of sweat, few studies have examined whether ...
Teachers are likely to interpret students' misbehavior differently depending on the student's race, according to new research findings published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Racial differences in school discipline are widely known, and black students across the United States are more than three times as likely as their white peers to be suspended or expelled, according to Stanford researchers.
Yet the psychological processes that contribute to those differences have not been clear -- until now.
"The fact that black ...