Scientists with the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE)'s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley have created a hybrid system of semiconducting nanowires and bacteria that mimics the natural photosynthetic process by which plants use the energy in sunlight to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water. However, this new artificial photosynthetic system synthesizes the combination of carbon dioxide and water into acetate, the most common building block today for biosynthesis.
"We believe our system is a revolutionary leap forward in the field of artificial photosynthesis," says Peidong Yang, a chemist with Berkeley Lab's Materials Sciences Division and one of the leaders of this study. "Our system has the potential to fundamentally change the chemical and oil industry in that we can produce chemicals and fuels in a totally renewable way, rather than extracting them from deep below the ground."
Yang, who also holds appointments with UC Berkeley and the Kavli Energy NanoSciences Institute (Kavli-ENSI) at Berkeley, is one of three corresponding authors of a paper describing this research in the journal Nano Letters. The paper is titled "Nanowire-bacteria hybrids for unassisted solar carbon dioxide fixation to value-added chemicals." The other corresponding authors and leaders of this research are chemists Christopher Chang and Michelle Chang. Both also hold joint appointments with Berkeley Lab and UC Berkeley. In addition, Chris Chang is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute (HHMI) investigator. (See below for a full list of the paper's authors.)
The more carbon dioxide that is released into the atmosphere the warmer the atmosphere becomes. Atmospheric carbon dioxide is now at its highest level in at least three million years, primarily as a result of the burning of fossil fuels. Yet fossil fuels, especially coal, will remain a significant source of energy to meet human needs for the foreseeable future. Technologies for sequestering carbon before it escapes into the atmosphere are being pursued but all require the captured carbon to be stored, a requirement that comes with its own environmental challenges.
The artificial photosynthetic technique developed by the Berkeley researchers solves the storage problem by putting the captured carbon dioxide to good use.
"In natural photosynthesis, leaves harvest solar energy and carbon dioxide is reduced and combined with water for the synthesis of molecular products that form biomass," says Chris Chang, an expert in catalysts for carbon-neutral energy conversions. "In our system, nanowires harvest solar energy and deliver electrons to bacteria, where carbon dioxide is reduced and combined with water for the synthesis of a variety of targeted, value-added chemical products."
By combining biocompatible light-capturing nanowire arrays with select bacterial populations, the new artificial photosynthesis system offers a win/win situation for the environment: solar-powered green chemistry using sequestered carbon dioxide.
"Our system represents an emerging alliance between the fields of materials sciences and biology, where opportunities to make new functional devices can mix and match components of each discipline," says Michelle Chang, an expert in biosynthesis. "For example, the morphology of the nanowire array protects the bacteria like Easter eggs buried in tall grass so that these usually-oxygen sensitive organisms can survive in environmental carbon-dioxide sources such as flue gases."
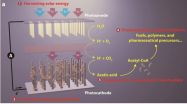
The system starts with an "artificial forest" of nanowire heterostructures, consisting of silicon and titanium oxide nanowires, developed earlier by Yang and his research group.
"Our artificial forest is similar to the chloroplasts in green plants," Yang says. "When sunlight is absorbed, photo-excited electron?hole pairs are generated in the silicon and titanium oxide nanowires, which absorb different regions of the solar spectrum. The photo-generated electrons in the silicon will be passed onto bacteria for the CO2 reduction while the photo-generated holes in the titanium oxide split water molecules to make oxygen."
Once the forest of nanowire arrays is established, it is populated with microbial populations that produce enzymes known to selectively catalyze the reduction of carbon dioxide. For this study, the Berkeley team used Sporomusa ovata, an anaerobic bacterium that readily accepts electrons directly from the surrounding environment and uses them to reduce carbon dioxide.
"S. ovata is a great carbon dioxide catalyst as it makes acetate, a versatile chemical intermediate that can be used to manufacture a diverse array of useful chemicals," says Michelle Chang. "We were able to uniformly populate our nanowire array with S. ovata using buffered brackish water with trace vitamins as the only organic component."
Once the carbon dioxide has been reduced by S. ovata to acetate (or some other biosynthetic intermediate), genetically engineered E.coli are used to synthesize targeted chemical products. To improve the yields of targeted chemical products, the S. ovata and E.coli were kept separate for this study. In the future, these two activities - catalyzing and synthesizing - could be combined into a single step process.
A key to the success of their artificial photosynthesis system is the separation of the demanding requirements for light-capture efficiency and catalytic activity that is made possible by the nanowire/bacteria hybrid technology. With this approach, the Berkeley team achieved a solar energy conversion efficiency of up to 0.38-percent for about 200 hours under simulated sunlight, which is about the same as that of a leaf.
The yields of target chemical molecules produced from the acetate were also encouraging - as high as 26-percent for butanol, a fuel comparable to gasoline, 25-percent for amorphadiene, a precursor to the antimaleria drug artemisinin, and 52-percent for the renewable and biodegradable plastic PHB. Improved performances are anticipated with further refinements of the technology.
"We are currently working on our second generation system which has a solar-to-chemical conversion efficiency of three-percent," Yang says. "Once we can reach a conversion efficiency of 10-percent in a cost effective manner, the technology should be commercially viable."
INFORMATION:
In addition to the corresponding authors, other co-authors of the Nano Letters paper describing this research were Chong Liu, Joseph Gallagher, Kelsey Sakimoto and Eva Nichols.
This research was primarily funded by the DOE Office of Science.