Quantum model reveals surface structure of water
National Physical Laboratory, IBM and Edinburgh University have used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface
2015-04-20
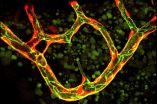
(Press-News.org) The National Physical Laboratory (NPL), the UK's National Measurement Institute in collaboration with IBM and the University of Edinburgh, has used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface.
The liquid-vapour interface of water is one of the most common of all heterogeneous (or non-uniform) environments. Understanding its molecular structure will provide insight into complex biochemical interactions underpinning many biological processes. But experimental measurements of the molecular structure of water's surface are challenging, and currently competing models predict various different arrangements.
NPL has been working with IBM and the University of Edinburgh to make materials simulation more predictive and intuitive, by developing a new class of materials model based on quantum mechanical effects.
The model is based on a single charged particle, the quantum Drude oscillator (QDO), which mimics the way the electrons of a real water molecule fluctuate and respond to their environment. This simplified representation retains interactions not normally accessible in classical models and accurately captures the properties of liquid water.
In new research, published in a featured article in the journal Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, the team used the QDO model to determine the molecular structure of water's liquid surface. The results provide new insight into the hydrogen-bonding topology at the interface, which is responsible for the unusually high surface tension of water.
This is the first time the QDO model of water has been applied to the liquid-vapour interface. The results enabled the researchers to identify the intrinsic asymmetry of hydrogen bonds as the mechanism responsible for the surface's molecular orientation. The model was also capable of predicting the temperature dependence of the surface tension with remarkable accuracy - to within 1 % of experimental values.
Coupled with earlier work on bulk water, this result demonstrates the exceptional transferability of the QDO approach and offers a promising new platform for molecular exploration of condensed matter.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-20
The discovery of a gene involved in determining the melting point of cocoa butter -- a critical attribute of the substance widely used in foods and pharmaceuticals -- will likely lead to new and improved products, according to researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
The finding by plant geneticists also should lead to new varieties of the cocoa plant that could extend the climate and soil-nutrient range for growing the crop and increase the value of its yield, they said, providing a boost to farmers' incomes in the cocoa-growing regions of the world.
Cacao, ...
2015-04-20
Singapore, 20 April 2015 - Since the discovery of graphene about a decade ago, scientists have been studying ways to engineer electronic band gaps in the material to produce semiconductors which can create new electronic devices. A team of researchers from Yale-NUS College, the Center for Advanced 2D Materials and Department of Physics at the National University of Singapore (NUS) and the University of Texas at Austin, USA (UT Austin) have established a theoretical framework to understand the elastic and electronic properties of graphene. The findings were published in ...
2015-04-20
As two galaxies enter the final stages of merging, scientists have theorized that the galaxies' supermassive black holes will form a "binary," or two black holes in such close orbit they are gravitationally bound to one another. In a new study, astronomers at the University of Maryland present direct evidence of a pulsing quasar, which may substantiate the existence of black hole binaries.
"We believe we have observed two supermassive black holes in closer proximity than ever before," said Suvi Gezari, assistant professor of astronomy at the University of Maryland and ...
2015-04-20
Research by scientists at The University of Manchester has revealed that the colour of light has a major impact on how our body clock measures the time of day.
It's the first time the impact of colour has been tested and demonstrates that colour provides a more reliable way of telling the time than measuring brightness.
In research being published on April 17th in the Open Access journal PLOS Biology, the researchers looked at the change in light around dawn and dusk to analyse whether colour could be used to determine time of day. Besides the well-known changes in ...
2015-04-20
Cells of the vascular system of vertebrates can fuse with themselves. This process, which occurs when a blood vessel is no longer necessary and pruned, has now been described on the cellular level by Prof. Markus Affolter from the Biozentrum of the University of Basel. The findings of this study have been published in the journal PLOS Biology.
The vascular system is the supply network of the human organism and delivers oxygen and nutrients to the last corners of the body. So far, research on the vascular system has focused primarily on the formation of such vascular networks. ...
2015-04-20
The horticulturist who came up with the concept of 'evolution by natural selection' 27 years before Charles Darwin did should be more widely acknowledged for his contribution, states a new paper by a King's College London geneticist.
The paper, published in the Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, argues that Patrick Matthew deserves to be considered alongside Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace as one of the three originators of the idea of large-scale evolution by natural selection.
Furthermore, Matthew's version of evolution by natural section captures ...
2015-04-20
Human emotion can be transferred by technology that stimulates different parts of the hand without making physical contact with your body, a University of Sussex-led study has shown.
Sussex scientist Dr Marianna Obrist, Lecturer at the Department of Informatics, has pinpointed how next-generation technologies can stimulate different areas of the hand to convey feelings of, for example, happiness, sadness, excitement or fear.
For example, short, sharp bursts of air to the area around the thumb, index finger and middle part of the palm generate excitement, whereas sad ...
2015-04-20
Philadelphia, PA, April 20, 2015 - The search for genes that contribute to the risk for autism has made tremendous strides over the past 3 years. As this field has advanced, investigators have wondered whether the diversity of clinical features across patients with autism reflects heterogeneous sources of genetic risk.
If so, it was reasoned, then selecting a group of patients with very similar clinical features might result in a "purer", i.e., more genetically homogenous, group of patients, making it easier to find autism-related genes.
Results from a new study published ...
2015-04-20
Research has shown that, for a number of reasons, lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people are significantly more likely than heterosexuals to avoid or delay medical care.
For instance, LGBT individuals who are between the ages of 18 and 44 and single are less likely than heterosexuals to have the money or insurance for care, and even partnered gays and lesbians are twice as likely to be uninsured. The fear of stigma and homophobia can also keep LGBT people from seeking care. And many are afraid to disclose their sexual or gender identity to their physicians, which ...
2015-04-20
PHILADELPHIA - A protein produced by nerve cells appears to be elevated in the blood of those with an aggressive form of neuroblastoma. The finding, presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research 2015 Annual Meeting in Philadelphia, could potentially lead to a prognostic test for the disease or be used to monitor its progress.
Neuroblastoma is a pediatric cancer with varying types, ranging from spontaneously regressing to untreatable fatal tumors. Consequently, treatment strategies vary significantly between patients, encompassing different approaches ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Quantum model reveals surface structure of water
National Physical Laboratory, IBM and Edinburgh University have used a new quantum model to reveal the molecular structure of water's liquid surface