INFORMATION:
[P5.192] 'Doctor, can I stop my medicine?' Analysis of disease course after stopping disease-modifying therapy in stable MS patients
Date/Time: Wednesday, April 22, 2015 - 2:00 pm
Session: P5: Poster Session V: MS and CNS Inflammatory Diseases: MS Disease Course, Activity, Progression, Cognition, and Quality of Life (2:00 PM-6:30 PM)
Media Inquiries:
Ryan Jaslow
Cell: 347-638-4534
ryan.jaslow@nyumc.org
What happens when multiple sclerosis patients stop taking their medication?
2015-04-21
(Press-News.org) New research led by NYU Langone Medical Center examines what happens when a patient with multiple sclerosis (MS) who is clinically stable stops taking their medication.
The international, multi-site study found almost 40 percent of patients had some disease activity return when they stopped taking their meds.
The findings were presented at the American Academy of Neurology Annual Meeting held April 18-25, in Washington, D.C.
"Despite long periods of disease stability while taking medication, we found a large minority of patients who stopped experienced relapses or disability progression," says lead study author Ilya Kister, MD, an assistant professor of neurology at the NYU Langone Multiple Sclerosis Comprehensive Care Center. "We need to identify situations when it is safe for patients with MS to stop taking these medications."
Little is known about MS disease progression after first-line, disease-modifying therapies are discontinued in clinically-stable patients.
For the study, Dr. Kister and colleagues prospectively studied 181 patients from the global observational MSBase Registry, examining MS relapse rates and disability progression rates in patients who stopped taking disease-modifying therapy.
Patients in the study were ages 40 and older, had experienced no relapses and reported stable disability progression (measured by EDSS scores) for at least 5 years, and had been taking medication for at least three years. Once medications were ceased, patients were followed for at least three years.
After discontinuing medication, 24 percent of patients experienced a clinician-reported relapse, 32 percent sustained three-month disability progression, and 10.6 percent of patients recorded both relapses and disability progression.
Researchers found 77 patients - or 42 percent - restarted medication after a median of 22 months. Restarting medication was associated with a 59-percent risk reduction of disability progression.
More than 2.3 million people worldwide are affected by MS, according to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS). The unpredictable disease affects the central nervous system, causing disability that can range in severity, with symptoms including muscle weakness, pain, difficulty with coordination and balance, partial or complete paralysis, tremors and hearing and vision loss.
Medication can help to manage attacks, reduce symptoms, and slow the progression of multiple sclerosis. According to the NMSS, some people stop taking disease-modifying medication for reasons including side effects, perceptions they're not feeling better or because they still experience exacerbations, or insurance purposes.
"Decisions regarding stopping disease-modifying therapy may have implications for short and long-term prognosis. We know a lot about what happens when therapy is started, but we know very little about what happens when therapy is stopped", says Dr Kister
Dr. Kister and colleagues call for a randomized trial of discontinuation of disease-modifying therapy to provide more evidence of when exactly it might be safe for patients to stop taking their medications.
In addition to Dr. Kister, the authors on this study were: Tim Spelman, Raed Alroughani, Jeannette Lechner-Scott, Helmut Butzkueven, Pierre Duquette, Francois Grand'Maison, Mark Slee, Alessandra Lugaresi, Michael Barnett, Pierre Grammond, Gerardo Iuliano, Raymond Hupperts, Maria Trojano & Joseph Herbert on behalf of the MSBase Study Group.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Messenger RNA-associated protein drives multiple paths in T-cell development
2015-04-21
PHILADELPHIA - RNA is both the bridge between DNA and the production of proteins that carry out the functions of life and what guides which and how much protein gets made. As messenger RNA (mRNA) is transcribed from DNA to carry genetic information out of the nucleus, segments that don't code for actual proteins need to be removed from the RNA strand and the remaining pieces spliced together. Different pieces of the expressed gene (exons) are cut out, and these sections are joined together to form the final mRNA strand. Cells gain their ability to produce proteins with ...
Reflections on current state of situation awareness topic of JCEDM special issue
2015-04-21
Over the past 25 years, the construct of situation awareness (SA), or the perception and interpretation of what is happening around you, has been a catalyst for new advances in the human factors/ergonomics field, particularly in the areas of information display, automation, and training.
But recent advances also raise new questions, such as these: To what extent is SA about "awareness in the head" versus "awareness of where to look around you"? How is the process of maintaining SA affected by workload? Is it possible to have high-level SA about, for example, the progress ...
Trial shows benefit of 'BRCA-targeting' drug in prostate cancer
2015-04-21
Men with prostate cancer benefit from treatment with the pioneering drug olaparib - the first cancer drug to target inherited mutations - according to the results of a major trial presented today (Tuesday).
Olaparib was licensed in December for women with ovarian cancer and inherited BRCA mutations, but the new research suggests it could also benefit men with genomic faults within their tumours.
Researchers told the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) conference in Philadelphia that up to 30 per cent of men with advanced prostate cancer had tumours with defects ...
Amazon rainforest losses impact on climate change, study shows
2015-04-21
Human activity has removed more than one-tenth of trees and plants from the Amazon rainforest since the 1960s, a study shows.
Widespread removal of trees has contributed to a rise in the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, increasing the potential impact of climate change, researchers say.
Deforestation of the Amazon accounted for 1.5 per cent of the increase in carbon dioxide levels seen since the mid-nineteenth century, the team says.
However, this increased the total amount of carbon found in the atmosphere only very slightly compared with fossil fuel ...
Fishing impacts on the Great Barrier Reef
2015-04-21
New research shows that fishing is having a significant impact on the make-up of fish populations of the Great Barrier Reef.
It's long been known that environmental impacts such as climate change and pollution are amongst the drivers of change on the Great Barrier Reef.
Now researchers from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies (Coral CoE) at James Cook University have found that removing predatory fish such as coral trout and snapper, through fishing, causes significant changes to the make-up of the reef's fish populations.
"A stable and healthy reef ...
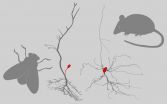
Why some neurons 'outsource' their cell body
2015-04-21
Nerve cells come in very different shapes. Researchers at the Bernstein Center Berlin now reveal why, in insects, the cell body is usually located at the end of a separate extension. Using mathematical models, they show that this increases the strength of electrical signal transmission at no additional energetic cost.
Nerve cells follow a functional design: They receive input signals over more or less ramified cell branches (dendrites), which they forward to other nerve cells along an elongated, thin cell process (axon). The cell body contains the nucleus with genetic ...
Online discussion forums good for well-being, study shows
2015-04-21
A new study has found that internet discussion forums have positive links to well-being and are even associated with increased community engagement offline, contrary to a common perception of them being outdated and prone to trolling.
Research just published in the journal Computers in Human Behavior found that online forums have benefits for both individuals and wider society and are of greater importance than previously realised.
Although seemingly eclipsed in the past decade by social networking sites such as Facebook and Twitter, forums are still regularly used ...
Hurdles to US climate change action are in economics and politics, not divided science
2015-04-21
The U.S. Congress successfully hears the "supermajority" consensus on the reality and causes of climate change, according to scientists from Texas A&M University, Idaho State University, and University of Oklahoma. In a paper published in Climatic Change, the scientists suggest looking at business interests, partisan predispositions and political ideology for the hurdles to policy action.
"Different perceptions and claims among lawmakers are a major hurdle to agreeing on action to address global warming and these were thought to simply reflect scientific uncertainty," ...
More detailed findings confirm that coffee protects against breast cancer recurrence
2015-04-21
A number of research studies have shown that coffee helps to protect against breast cancer. A new study led by Lund University, has confirmed that coffee inhibits the growth of tumours and reduces the risk of recurrence in women who have been diagnosed with breast cancer and treated with the drug tamoxifen.
The study, which is a follow-up of the results the researchers obtained two years ago, was carried out at Lund University and Skåne University Hospital, in collaboration with researchers in the UK.
"Now, unlike in the previous study, we have combined information ...
Regular consumption of yogurt does not improve health
2015-04-21
Dietary recommendations support the consumption of dairy products as part of a healthy diet. However, after a Spanish study involving more than 4,000 people analysed the relationship between the regular intake of yogurt and health-related quality of life, it declared that there was no link with the improvement of the physical and mental parameters analysed.
For years various researchers have stated the benefits of eating yogurt on a regular basis although its effectiveness has never been proven. In fact, until now, few studies have specifically examined the effect of ...