User creativity made YouTube the world's biggest music service
Alternative variations from popular artists' videos may reach an audience of millions, shows the new study from Finland's Aalto University
2015-04-22
(Press-News.org) Alternative variations from popular artists' videos may reach an audience of millions, shows the new study from Finland's Aalto University.
Music is the most popular YouTube content by several measures, including video views and search activity. The world's first academic study on YouTube music consumption by Aalto University in Finland shows that one reason for its popularity lies in users' own video. People re-use original music by popular artists to create their own alternative video variations, which may reach an audience of millions and can be found alongside any popular music title.
- These variations that we call user-appropriated videos are readily available and well promoted on YouTube. This is what makes YouTube an interesting music service, says Dr of Technology Lassi A. Liikkanen from Aalto University.
Lyrics and still videos, which only include music, rank highly in YouTube search results. A popular video, say a new Beyoncé song, may share its audience collaterally with similar user-generated videos because they appear next to one another in the search results and suggested content. The researchers named this the halo effect.
Three types of videos
In this study the researchers created a typology of YouTube music videos.
- Our analysis found three primary music video types: traditional, user-appropriated, and derivative music videos, post-doctoral researcher Antti Salovaara explains.
Through a series of qualitative and quantitative studies of YouTube content, researchers studied both the popularity of music videos and the attention they get from the audience.
The study shows that users are willing to listen to music from Youtube even without video content. They are also happy with music with rolling lyrics over a still photo, cover versions, and even parodies of the authentic music content.
- YouTube transformed the digital media world. It changed music listening practices. Finally, we have a scientific record of this wonderfully rich cultural phenomenon,' the primary author, Lassi A. Liikkanen, explains.
- Earlier studies ignored music's tremendous pull, even though it must have been obvious to everyone using YouTube. We only have a single academic reference point from six years back. In this time, the artists have changed, but music has remained on top of the charts.
INFORMATION:
Publication information:
Liikkanen L. & Salovaara A. Music on YouTube: User engagement with Traditional, User-Appropriated and Derivative Videos.
Computers in Human Behavior. Elsevier. DOI: 10.1016/j.chb.2015.01.067
Read the full article: http://authors.elsevier.com/a/1Qtbq2f~UVu9Lv
Experience the video subtypes:
http://tinyurl.com/youtubemusicstudy
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-04-22
TORONTO, April 22, 2015--In a study to ascertain whether breast arterial calcification (BAC) detected with digital mammography correlates to chest CT findings of coronary artery calcification (CAC), researchers have discovered a striking relationship between the two factors. In 76% of the study cohort, women who had a BAC score of 0 also had a CAC score of 0. As the BAC score increases, there is a concomitant increase in the CAC score.
The findings indicate that the presence of BAC could play a significant role in identifying women who may benefit from coronary artery ...
2015-04-22
The exoplanet 51 Pegasi b [1] lies some 50 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered in 1995 and will forever be remembered as the first confirmed exoplanet to be found orbiting an ordinary star like the Sun [2]. It is also regarded as the archetypal hot Jupiter -- a class of planets now known to be relatively commonplace, which are similar in size and mass to Jupiter, but orbit much closer to their parent stars.
Since that landmark discovery, more than 1900 exoplanets in 1200 planetary systems have been confirmed, but, in the year of the ...
2015-04-22
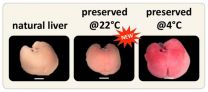
People waiting for organ transplants may soon have higher hopes of getting the help that they need in time. Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology have developed a new technique that extends the time that donor organs last and can also resuscitate organs obtained after cardiac arrest. The work published in Scientific Reports details a procedure that cools organs down to 22 °C (71.6 °F) and slows down organ function while still supplying oxygen, resulting in more successful transplants than the current standard methods. Team leader Takashi Tsuji ...
2015-04-22
Real or counterfeit? Northwestern University scientists have invented sophisticated fluorescent inks that one day could be used as multicolored barcodes for consumers to authenticate products that are often counterfeited. Snap a photo with your smartphone, and it will tell you if the item is real and worth your money.
Counterfeiting is very big business worldwide, with $650 billion per year lost globally, according to the International Chamber of Commerce. The new fluorescent inks give manufacturers and consumers an authentication tool that would be very difficult for ...
2015-04-22
Overall, an estimated 211,514 people attended Emergency Departments (EDs), Minor Injury Units (MIUs) and Walk-in Centres in England and Wales for treatment following violence in 2014 - 22,995 fewer than in 2013.
Serious violence affecting all age groups decreased in 2014 compared to 2013. Most notably, recorded acts of violence against children (0-10 year olds) and adolescents (11-17 year olds) were marked by an 18% decline.
The data was gathered from a scientific sample of 117 EDs, MIUs and Walk-in Centres in England and Wales. All are certified members of the National ...
2015-04-22
Research suggests health and social care professionals put a different emphasis on the meaning of dignity than their patients do.
Although the UK has well-established local and national policies that champion the need to provide dignified care, breaches in dignity are still a problem with the NHS - and the study by Brunel University London has uncovered a potential gap between what patients expect and the focus of care professionals.
When asked what dignified care meant to them, health care professionals referred to 'what dignity is', often as a conceptual idea, ...
2015-04-22
SALT LAKE CITY, April 22, 2015 - Using statistics that describe how an infectious disease spreads, a University of Utah anthropologist analyzed different theories of how people first settled islands of the vast Pacific between 3,500 and 900 years ago. Adrian Bell found the two most likely strategies were to travel mostly against prevailing winds and seek easily seen islands, not necessarily the nearest islands.
The study - published in this month's issue of the journal American Antiquity - suggests early Pacific seafarers "weren't just drifting around," says Bell, the ...
2015-04-22
Actor Stephen McGann, who plays GP Dr Patrick Turner in the hit BBC period drama Call the Midwife, has described the steps taken by the writers, production team and actors to ensure the series has sufficient medical accuracy and authenticity. In an essay published today by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, McGann writes of the unique insight that the role of Dr Turner has given him into questions regarding the way popular culture portrays medics and medicine. While working on Call the Midwife, McGann's interest in the relationship between medical science and ...
2015-04-22
The widely held belief that depression is due to low levels of serotonin in the brain - and that effective treatments raise these levels - is a myth, argues a leading psychiatrist in The BMJ this week.
David Healy, Professor of Psychiatry at the Hergest psychiatric unit in North Wales, points to a misconception that lowered serotonin levels in depression are an established fact, which he describes as "the marketing of a myth."
The serotonin reuptake inhibiting (SSRI) group of drugs came on stream in the late 1980s, nearly two decades after first being mooted, writes ...
2015-04-22
The UK government plan to fund and to increase participation in rugby in schools has not been informed by injury data, warn experts in The BMJ this week.
Professor Allyson Pollock and colleagues at Queen Mary University of London say the government "should ensure the safety and effectiveness of (school) sports" and call for injury surveillance and prevention programmes to be established to help reduce injury rates.
The high rates of injury in rugby union and rugby league for professional and amateur players, including children, are well established and a cause for medical ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] User creativity made YouTube the world's biggest music service
Alternative variations from popular artists' videos may reach an audience of millions, shows the new study from Finland's Aalto University