(Press-News.org) Researchers from Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry are part of a team led by the University of Oxford, who have carried out new research that suggests mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT) could provide an alternative non-drug treatment for people who do not wish to continue long-term antidepressant treatment.
The results are published in "The Lancet".
The results come from the first ever large study to compare MBCT - structured training for the mind and body which aims to change the way people think and feel about their experiences - with maintenance antidepressant medication for reducing the risk of relapse in depression.
The study aimed to establish whether MBCT is superior to maintenance antidepressant treatment in terms of preventing relapse of depression. Although the findings show that MBCT isn't any more effective than maintenance antidepressant treatment in preventing relapse of depression, the results, combined with those of previous trials, suggest that MCBT may offer similar protection against depressive relapse or recurrence for people who have experienced multiple episodes of depression, with no significant difference in cost.
"Depression is a recurrent disorder. Without ongoing treatment, as many as four out of five people with depression relapse at some point,"
explained Willem Kuyken, lead author and Professor of Clinical Psychology at the University of Oxford in the UK.
"Currently, maintenance antidepressant medication is the key treatment for preventing relapse, reducing the likelihood of relapse or recurrence by up to two-thirds when taken correctly,"
added study co-author Professor Richard Byng, from the Plymouth University Peninsula Schools of Medicine and Dentistry, UK.
"However, there are many people who, for a number of different reasons, are unable to keep on a course of medication for depression. Moreover, many people do not wish to remain on medication for indefinite periods, or cannot tolerate its side effects."*
MBCT was developed to help people who have experienced repeated bouts of depression by teaching them the skills to recognise and to respond constructively to the thoughts and feelings associated with relapse, thereby preventing a downward spiral into depression.
In this trial, which was conducted from the University of Exeter, UK, 424 adults with recurrent major depression and taking maintenance antidepressant medication were recruited from 95 primary care general practices across the South West of England. Participants were randomly assigned to come off their antidepressant medication slowly and receive MBCT (212 participants) or to stay on their medication (212 participants).
Participants in the MBCT group attended eight 2 ¼ hour group sessions and were given daily home practice. After the group they had the option of attending four follow-up sessions over a 12-month period. The MBCT course consists of guided mindfulness practices, group discussion and other cognitive behavioural exercises. Those in the maintenance antidepressant group continued their medication for two years.
All trial participants were assessed at regular intervals over two years for a major depressive episode using a psychiatric diagnostic interview tool--the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV.
Over two years, relapse rates in both groups were similar (44 per cent in the MBCT group vs 47 per cent in the maintenance antidepressant medication group). Although five adverse events were reported, including two deaths, across both groups, they were not judged to be attributable to the interventions or the trial.
According to study co-author Professor Sarah Byford, from the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience (IoPPN) at King's College London, UK:
"As a group intervention, mindfulness-based cognitive therapy was relatively low cost compared to therapies provided on an individual basis and, in terms of the cost of all health and social care services used by participants during the study, we found no significant difference between the two treatments." *
According to Professor Kuyken:
"Whilst this study doesn't show that mindfulness-based cognitive therapy works any better than maintenance antidepressant medication in reducing the rate of relapse in depression, we believe these results suggest a new choice for the millions of people with recurrent depression on repeat prescriptions."
Study participant Mr Nigel Reed from Sidmouth, Devon, UK, commented that:
"Mindfulness gives me a set of skills which I use to keep well in the long term. Rather than relying on the continuing use of antidepressants mindfulness puts me in charge, allowing me to take control of my own future, to spot when I am at risk and to make the changes I need to stay well."
Writing in a linked Comment, Professor Roger Mulder from the University of Otago in New Zealand said:
"Because [mindfulness-based cognitive therapy] is a group treatment which reduces costs and the number of trained staff needed it may be feasible to offer MBCT as a choice to patients in general practice...We therefore have a promising relatively new treatment which is reasonably cost effective and applicable to the large group of patients with recurrent depression."
INFORMATION:
Fragments of asteroids regularly land on Earth as meteorites. If you examine such a find, you can see that it comprises millimetre-sized round stones, known as chondrules. These small particles are believed to be the original building blocks of the solar system. However, the research community has not previously been able to explain how the chondrules formed asteroids. A new study shows that asteroids were formed by capturing chondrules with the help of gravitational force.
"The chondrules are of exactly the right size to be slowed down by the gas that orbited the young ...
Researchers at the Institut Hospital del Mar d'Investigacions Mèdiques (IMIM) have identified a new way of treating colorectal cancer. In the study published in the journal Science Signaling, the team led by LLuís Espinosa, investigator of IMIM's research group into stem cells and cancer, have shown that inhibition of endosomal activity is a potential therapeutic strategy for the treatment of cancers with the BRAF mutated gene. This discovery is an important step in the personalisation of the treatment of colorectal cancer, as the presence of this mutation is ...
Bethesda, MD (April 22, 2015) -- The May issues of AGA's journals -- Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology and Gastroenterology -- highlight important research updates on the most deadly forms of liver disease. Here's what you need to know:
Researchers confirm that NAFLD worsens heart disease.
One specific cardiovascular disease risk factor -- psychological distress -- is linked to death from liver disease in a large, general population sample.
Improvements in cirrhosis care have contributed to a 41 percent decrease in inpatient mortality.
For access to any of ...
Researchers from North Carolina State University have discovered that electron spin brings a previously unknown degree of order to the high entropy alloy nickel iron chromium cobalt (NiFeCrCo) - and may play a role in giving the alloy its desirable properties.
"High entropy alloys have garnered a lot of attention over the past 10 years because they have remarkable properties," says Doug Irving, an associate professor of materials science and engineering at NC State and corresponding author of a paper describing the work. High entropy alloys are materials that consist ...
COLUMBUS, Ohio--An international research team is bringing a new weapon to bear against invasive earthworms.
The ongoing research project at The Ohio State University, the University of Alberta and Simon Fraser University uses statistical analysis to forecast one worm species' spread, in hopes of finding ways to curtail it.
Most recently, they've focused on the boreal forest of northern Alberta. No native worms live in the forest whatsoever; the region had been worm-free since the last ice age 11,000 years ago, until invasive European species began working their way ...
Alternative variations from popular artists' videos may reach an audience of millions, shows the new study from Finland's Aalto University.
Music is the most popular YouTube content by several measures, including video views and search activity. The world's first academic study on YouTube music consumption by Aalto University in Finland shows that one reason for its popularity lies in users' own video. People re-use original music by popular artists to create their own alternative video variations, which may reach an audience of millions and can be found alongside any ...
TORONTO, April 22, 2015--In a study to ascertain whether breast arterial calcification (BAC) detected with digital mammography correlates to chest CT findings of coronary artery calcification (CAC), researchers have discovered a striking relationship between the two factors. In 76% of the study cohort, women who had a BAC score of 0 also had a CAC score of 0. As the BAC score increases, there is a concomitant increase in the CAC score.
The findings indicate that the presence of BAC could play a significant role in identifying women who may benefit from coronary artery ...
The exoplanet 51 Pegasi b [1] lies some 50 light-years from Earth in the constellation of Pegasus. It was discovered in 1995 and will forever be remembered as the first confirmed exoplanet to be found orbiting an ordinary star like the Sun [2]. It is also regarded as the archetypal hot Jupiter -- a class of planets now known to be relatively commonplace, which are similar in size and mass to Jupiter, but orbit much closer to their parent stars.
Since that landmark discovery, more than 1900 exoplanets in 1200 planetary systems have been confirmed, but, in the year of the ...
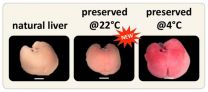
People waiting for organ transplants may soon have higher hopes of getting the help that they need in time. Researchers at the RIKEN Center for Developmental Biology have developed a new technique that extends the time that donor organs last and can also resuscitate organs obtained after cardiac arrest. The work published in Scientific Reports details a procedure that cools organs down to 22 °C (71.6 °F) and slows down organ function while still supplying oxygen, resulting in more successful transplants than the current standard methods. Team leader Takashi Tsuji ...
Real or counterfeit? Northwestern University scientists have invented sophisticated fluorescent inks that one day could be used as multicolored barcodes for consumers to authenticate products that are often counterfeited. Snap a photo with your smartphone, and it will tell you if the item is real and worth your money.
Counterfeiting is very big business worldwide, with $650 billion per year lost globally, according to the International Chamber of Commerce. The new fluorescent inks give manufacturers and consumers an authentication tool that would be very difficult for ...