(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio - Researchers have uncovered the first evidence of a genetic link between prodigy and autism.
The scientists found that child prodigies in their sample share some of the same genetic variations with people who have autism.
These shared genetic markers occur on chromosome 1, according to the researchers from The Ohio State University and Nationwide Children's Hospital in Columbus.
The findings confirm a hypothesis made by Joanne Ruthsatz, co-author of the study and assistant professor of psychology at Ohio State's Mansfield campus.
In a previous study, Ruthsatz and a colleague had found that half of the prodigies in their sample had a family member or a first- or second-degree relative with an autism diagnosis.
"Based on my earlier work, I believed there had to be a genetic connection between prodigy and autism and this new research provides the first evidence to confirm that," Ruthsatz said.
The new study appears online in the journal Human Heredity.
While this study provides a solid basis for identifying a linkage, there is a lot more to be learned, said co-author Christopher Bartlett, a principal investigator at Nationwide Children's Hospital and associate professor of pediatrics at Ohio State.
"We haven't identified the mutations, but we found that there's something in this region of chromosome 1 that is the same with both prodigies and their family members with autism," Bartlett said.
These findings are the first step toward answering the big question, Ruthsatz said.
"We now know what connects prodigy with autism. What we want to know is what distinguishes them. We have a strong suspicion that there's a genetic component to that, as well, and that's the focus of our future work," she said.
The Human Heredity study involved five child prodigies and their families that Ruthsatz has been studying, some for many years. Each of the prodigies had received national or international recognition for a specific skill, such as math or music. All took tests to confirm their exceptional skills.
The researchers took saliva samples from the prodigies, and from between four and 14 of each prodigy's family members. Each prodigy had between one and five family members in the study who had received a diagnosis on the autism spectrum.
DNA was extracted from the saliva and the researchers sequenced the exome - the segment of DNA containing the 1 to 2 percent of genes that make proteins. (This is less expensive and complex than sequencing the entire genome.) The researchers plan to follow up with full genome sequencing, which will reveal more information about genetic mutations that the prodigies share with people with autism.
"What we found here was just an indication that there's something similar in the genetic makeup of prodigies and their family members with autism. There's a lot more that needs to be studied," Bartlett said.
In her earlier work, Ruthsatz found that while both prodigies and people with autism share better than average scores on tests that measure attention to detail, prodigies scored higher among those two groups. And prodigies really excelled when it came to working memory, with all that she studied scoring in the 99th percentile.
"We believe that there may some gene or genes for working memory that may be a key part of helping to create prodigies," Ruthsatz said.
"Prodigies seem to have some protective genes that are saving them from the deficits associated with autism and only allowing the talent you see in savants to shine through. That's what we're looking to identify."
In the meantime, the researchers caution that they haven't found any "smoking gun."
"The testing we did here wouldn't help anyone tell if he or she was going to be a prodigy or have autism," Bartlett said.
"We didn't find the exact genes or mutations involved. It is a good start, but it is just a start."
INFORMATION:
Other co-authors on the study were Stephen Petrill, professor of psychology at Ohio State; and Ning Li and Samuel Wolock of Nationwide Children's Hospital.
Support for the study came from the Marci and Bill Ingram Research Fund for Autism Spectrum Disorders.
Contact: Joanne Ruthsatz, 419-755-4117; Ruthsatz.4@osu.edu
Christopher Bartlett, 614-355-5625; Christopher.Bartlett@nationwidechildrens.org
Written by Jeff Grabmeier, 614-292-8457; Grabmeier.1@osu.edu
WASHINGTON - Vehicle cost, current battery technology, and inadequate consumer knowledge are some of the barriers preventing widespread adoption of plug-in electric vehicles, says a new congressionally mandated report from the National Research Council. Developing less expensive, better performing batteries is essential to reducing overall vehicle cost, and a market strategy is needed to create awareness and overcome customer uncertainty. The report recommends a range of incentives that the federal government can offer to address these and other barriers.
The report ...
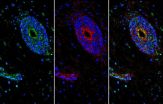
The brain is a privileged organ in the body. So vital to life, the brain is protected from alterations elsewhere in the body by a highly regulated gateway known as the blood-brain barrier, which allows only selected molecules to pass through.
In certain diseases, however, such as multiple sclerosis, the barrier can be improperly breached. These "leaks" can allow immune cells and inflammatory molecules to pass through, causing inflammation that leads to neuronal damage.
In a new study, researchers have made insights into how the blood-brain barrier, or BBB, is maintained, ...
The widespread use of cloth masks by healthcare workers may actually put them at increased risk of respiratory illness and viral infections and their global use should be discouraged, according to a UNSW study.
The results of the first randomised clinical trial (RCT) to study the efficacy of cloth masks were published today in the journal BMJ Open.
The trial saw 1607 hospital healthcare workers across 14 hospitals in the Vietnamese capital, Hanoi, split into three groups: those wearing medical masks, those wearing cloth masks and a control group based on usual practice, ...
(Boston)-- Individuals with mild Traumatic Brain Injury (mTBI), particularly those who have had loss of consciousness (LOC), show structural brain abnormalities in their white matter as measured by Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI).
These findings, which appear in the journal NeuroImage: Clinical, is the only study to date to demonstrate that mTBI with LOC is associated with brain abnormalities that lead to decreased performance in verbal memory.
Blast-related TBI has been a common injury among returning troops due to the widespread use of improvised explosive devices ...
WASHINGTON (April 22, 2015) -- New research published this week in Nature has found several drugs could lead to new treatment options for multiple sclerosis (MS), including two drugs that effectively treat MS at the source, in vivo. When administered at the peak of disease, these two drugs showed a striking reversal of disease severity.
At the pathological level, MS is a disease in which the immune system attacks the protective myelin sheath, a type of insulation that covers nerves, ultimately disrupting communication between the brain and the body and leading to nerve ...
April 22, 2014 (SILVER SPRING, Md.) - Ebola survivors experienced negative health effects that persisted more than two years after the 2007-2008 Bundibugyo ebolavirus (BDBV) outbreak in Uganda that claimed 39 lives. These findings are detailed in a paper published online today in Lancet ID. This represents the largest long-term study to-date on Ebola survivors, and examines health events more than two years after initial exposure to BDBV.
"Defining EVD-related health consequences could help improve patient care for survivors," said Dr. Hannah Kibuuka, the principal ...
As baby boomers age, the number of people diagnosed with Parkinson's disease is expected to increase. Patients who develop this disease usually start experiencing symptoms around age 60 or older. Currently, there's no cure, but scientists are reporting a novel approach that reversed Parkinson's-like symptoms in rats. Their results, published in the journal ACS Nano, could one day lead to a new therapy for human patients.
Rajnish Kumar Chaturvedi, Kavita Seth, Kailash Chand Gupta and colleagues from the CSIR-Indian Institute of Toxicology Research note that among other ...
If you've studied ingredient labels on food packaging, you've probably noticed that soy lecithin is in a lot of products, ranging from buttery spreads to chocolate cake. Scientists have now found a potential new role for this all-purpose substance: dispersing crude oil spills. Their study, which could lead to a less toxic way to clean up these environmental messes, appears in ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering.
Ram B. Gupta and colleagues explain that applying chemical dispersants is one of the most effective ways to help get rid of oil spills quickly. The dispersants ...
For years, health advocates have been pushing to ban some flame retardants for their potentially harmful effects, especially on young children and infants. Now scientists report these compounds could play a role in a common health problem for one of our most beloved pets: cats. In the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology, a new study found that cats with hyperthyroidism had high levels of certain flame retardants, hinting at a possible link.
Jessica Norrgran and colleagues explain that more than 10 percent of older cats develop hyperthyroidism, a hormonal disorder ...
In the last 10 years, computer security researchers have shown that malicious hackers don't need to see your data in order to steal your data. From the pattern in which your computer accesses its memory banks, adversaries can infer a shocking amount about what's stored there.
The risk of such attacks is particularly acute in the cloud, where you have no control over whose applications are sharing server space with yours. An antagonist could load up multiple cloud servers with small programs that do nothing but spy on other people's data.
Two years ago, researchers in ...