(Press-News.org) An intervention to connect low-income uninsured and Medicaid patients to a reliable source of primary health care shows promise for reducing avoidable use of hospital emergency departments in Maryland. A University of Maryland School of Public Health study evaluating the results of the intervention was published this week in the May issue of the journal Health Affairs.
For twenty years, use of hospital emergency departments has been on the rise in the United States, particularly among low-income patients who face barriers to accessing health care outside of hospitals including not having an identifiable primary health care provider. Almost half of emergency room visits are considered "avoidable." The Emergency Department-Primary Care Connect Initiative of the Primary Care Coalition, which ran from 2009 through 2011, linked low-income uninsured and Medicaid patients to safety-net health clinics.
"Our study found that uninsured patients with chronic health issues - such as those suffering from hypertension, diabetes, asthma, COPD, congestive heart failure, depression or anxiety -- relied less on the emergency department after they were linked to a local health clinic for ongoing care," says Dr. Karoline Mortensen, assistant professor of health services administration at the University of Maryland School of Public Health and senior researcher. "Connecting patients to primary care and expanding the availability of these safety-net clinics could reduce emergency department visits and provide better continuity of care for vulnerable populations."
Funded by a grant from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services and the Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene, the initiative engaged all five of the hospitals operating in Montgomery County, Maryland at the time, and four safety-net clinics serving low-income patients. Using "patient navigators," individuals trained to help patients find the care they need and can afford, these hospitals referred more than 10,000 low-income, uninsured and Medicaid patients who visited emergency departments to four local primary care clinics, with the goal of encouraging them to establish an ongoing relationship with the clinic and reduce their reliance on costly emergency department care.
Two hospitals in Montgomery County who participated in the intervention continued the program after the initial grant period concluded because of the benefits they saw for patients and for reducing emergency department visits and associated costs. These hospitals are currently testing a new version of the intervention specifically deigned to link emergency department patients with behavioral health conditions to appropriate community-based services.
While hospital administrators and health policy experts throughout the country are recognizing that access to primary care improves continuity of care for patients and reduces avoidable use of emergency departments, the implications of this project are particularly important for hospitals in Maryland, which are now operating under a unique all-payer model for hospital payments. Within this new payment structure, Maryland hospitals will have to meet ambitious spending, quality of care, and population health goals. Reducing avoidable use of emergency departments can help in reaching these goals.
The project provides promise not only for hospitals in Maryland but throughout the nation to improve health care experiences and outcomes for their patients. Shared learning systems were an integral component of the project so participants were learning from each other and sharing best practices throughout the project and that learning has now been documented and can be replicated in other communities.
"This was an incredibly rewarding project to work on," says Barbara H. Eldridge, Manager of Quality Improvement at the Primary Care Coalition. "We created a learning system that permits us to sustain improved communication between patients and their providers, between hospital discharge planners and community based clinics, and across five hospitals operating in Montgomery County." The initiative has proven successful in Montgomery County, Maryland and is being replicated in communities in other parts of the country.
INFORMATION:
"Linking Uninsured Patients Treated In The Emergency Department To Primary Care Shows Some Promise In Maryland" was written by Theresa Y. Kim, Karoline Mortensen, and Barbara Eldridge and published in the journal Health Affairs. http://content.healthaffairs.org/content/34/5/796.abstract
About the UMD School of Public Health authors:
Thesesa Kim is a doctoral student and Karoline Mortensen is an assistant professor in the Department of Health Services Administration in the University of Maryland School of Public Health. The UMD School of Public Health's mission is to promote and protect the health and well-being of the diverse communities throughout Maryland, the nation and the world through interdisciplinary education, research, practice, leadership and public policy. Learn more: http://sph.umd.edu
The Primary Care Coalition of Montgomery County is making health care happen. PCC works with clinics, hospitals, health care providers, and other community partners to coordinate health services for low-income, uninsured residents of Montgomery County, Maryland and the National Capital Area. Our vision is a community in which all residents will have the opportunity to live healthy lives. PCC is a 501(c) (3) nonprofit organization.
The rainfall accumulation analysis above was computed from data generated by the Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) during the period from April 28 to May 3, 2015. During this period IMERG algorithms continuously merged and interpolated satellite passive microwave precipitation estimates and microwave-calibrated infrared (IR) satellite estimates over the entire globe.
Rainfall from cyclone Quang fell over the west coast and a non-tropical system pounded the east coast of Australia simultaneously during the past weekend. Cyclone Quang formed in the South ...
A pilot study has found that participating in a nine-week training program including elicitation of the relaxation response had a significant impact on clinical symptoms of the gastrointestinal disorders irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease and on the expression of genes related to inflammation and the body's response to stress. The report from investigators at the Benson-Henry Institute at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE, is the first to study the ...
Out loud, someone says, "The man is catching a fish." The same person then takes pen to paper and writes, "The men is catches a fish."
Although the human ability to write evolved from our ability to speak, writing and talking are now such independent systems in the brain that someone who can't write a grammatically correct sentence may be able say it aloud flawlessly, discovered a team led by Johns Hopkins University cognitive scientist Brenda Rapp.
In a paper published this week in the journal Psychological Science, Rapp's team found it's possible to damage the speaking ...
Environmental factors similar to those affecting the present day Great Barrier Reef have been linked to a major slowdown in its growth eight thousand years ago, research led by the University of Sydney, Australia shows.
"Poor water quality, increased sediments and nutrients - conditions increasingly being faced by the modern day reef - caused a delay in the Reef's growth of between seven hundred and two thousand years duration," said Belinda Dechnik, from the University of Sydney's School of Geosciences and lead author of an article published in Marine Geology in May. ...
Why does a species not adapt to an ever-wider range of conditions, gradually expanding its geographical range? In their paper published on May 5 in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences), Jitka Polechova and Nick Barton at the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (IST Austria) seek to answer this question, which lies at the interface between ecology and evolution. The theory presented by Polechova and Barton suggests that any natural population is liable to form sharp margins.
J.B.S. Haldane, one of the founders of population genetics, studied ...
In cooperation with a Swiss research team, geographers of Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have developed a novel measuring system relying on two different physical methods that promises to enhance forecasting of avalanches and spring floods. The method combines GPS and radar to measure snow properties also on the slopes.
Accurate forecasting of avalanches, and the risk of flooding in Alpine catchment areas during the spring thaw, primarily requires time-resolved data on snow volumes and the levels of liquid water in the snow cover. A research group led ...
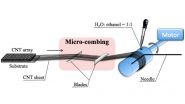
Researchers from North Carolina State University and China's Suzhou Institute of Nano-Science and Nano-Biotics have developed an inexpensive technique called "microcombing" to align carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which can be used to create large, pure CNT films that are stronger than any previous such films. The technique also improves the electrical conductivity that makes these films attractive for use in electronic and aerospace applications.
"It's a simple process and can create a lightweight CNT film, or 'bucky paper,' that is a meter wide and twice as strong as previous ...
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative condition that strikes at the heart of what makes us human: the ability to think, to feel, to remember and to communicate with those around us. The tragedy is compounded by the fact that there is currently no cure, no treatment, and no diagnostic method capable of identifying Alzheimer's at its early stages.
A ground-breaking study has now, for the first time anywhere, characterized early-stage changes that occur inside individual, Alzheimer's-affected cells in the intact brain. Remarkably, the study indicates that even ...
How many websites have you clicked on recently that haven't converted their format to mobile, frustrating your efforts to get the information you need in an effective and timely way?
Now researchers from Northwestern University have unearthed some provocative facts on how consumers utilize their mobile devices to buy groceries. With the global market for smartphones predicted to reach two billion by 2016, their findings should convince retailers planning marketing strategies and advertising campaigns that they need to pay attention to mobile.
In "On the Go: How Mobile ...
PITTSBURGH (May 5, 2015) ... For decades, robots have advanced the efficiency of human activity. Typically, however, robots are formed from bulky, stiff materials and require connections to external power sources; these features limit their dexterity and mobility. But what if a new material would allow for development of a "soft robot" that could reconfigure its own shape and move using its own internally generated power?
By developing a new computational model, researchers at the University of Pittsburgh's Swanson School of Engineering have designed a synthetic polymer ...