(Press-News.org) For the first time, scientists have imaged thunder, visually capturing the sound waves created by artificially triggered lightning. Researchers from Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) are presenting the first images at a joint meeting of American and Canadian geophysical societies in Montreal, Canada, May 3-7.
"Lightning strikes the Earth more than 4 million times a day, yet the physics behind this violent process remain poorly understood," said Dr. Maher A. Dayeh, a research scientist in the SwRI Space Science and Engineering Division. "While we understand the general mechanics of thunder generation, it's not particularly clear which physical processes of the lightning discharge contribute to the thunder we hear. A listener perceives thunder largely based upon the distance from lightning. From nearby, thunder has a sharp, cracking sound. From farther away, it has a longer-lasting, rumbling nature."
Although people see it as a flashing bolt, lightning begins as a complex process of electrostatic charges churning around in storm clouds. These charges initiate step leaders, branching veins of electricity propagating down, which subsequently lead to a main discharge channel. That channel opens a path to nearly instantaneous return strokes, which form the lightning flash as we see it. By studying the acoustic power radiated from different portions of the lightning channel, researchers can learn more about the origins of thunder as well as the energetic processes associated with lightning.
"Thunder and lightning are fascinating, wild, and unpredictable," said Dayeh. "Because of their erratic nature, the phenomena are best studied using triggered events." The technique involves launching a small rocket trailing a grounded copper wire into thunderclouds. The copper wire provides a conductive channel and creates a predictable path for lightning, allowing scientists to precisely focus their instruments and perform repeatable experiments close to the discharge channel. Using SwRI internal research funding, Dayeh led a proof-of-concept experiment to image the acoustic signature of thunder. SwRI conducted experiments at the International Center for Lightning Research and Testing at the University of Florida, Gainesville, taking advantage of the state's claim to the most lightning strikes per year in the U.S.
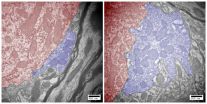
Dayeh designed a large, sophisticated array of microphones to study the acoustic signature of thunder. Fifteen microphones, spaced one meter apart, were lined up 95 meters away from the rocket launch pad where the triggered lightning would strike. To image the vertical profile of the bolt, he used post-signal processing techniques and directional amplification of the data signals captured by the microphone array.
"At first I thought the experiment didn't work," said Dayeh. "The initial constructed images looked like a colorful piece of modern art that you could hang over your fireplace. But you couldn't see the detailed sound signature of lightning in the acoustic data."
However, when Dayeh looked at the different sound frequency bands, he saw that the images cleared up at higher frequencies. The technique revealed a distinct signature of thunder generated by the lightning strike. Future experiments could allow scientists to study the probable acoustic signatures of current pulses, step leader branches, and discharge channel zigzags independently.
On May 5 at 11:30 a.m. EDT, a press conference will highlight this research at the 2015 Joint Assembly at the Palais des congrès de Montréal, located at 201 Viger Street West, Montreal, Canada. This meeting is cosponsored by the American Geophysical Union, Canadian Geophysical Union, the Geological Association of Canada, and the Mineralogical Association of Canada. For this research, Dayeh collaborated with groups from the University of New Hampshire, Florida Institute of Technology, and the University of Florida.
INFORMATION:
Employing online training programs to teach psychotherapists how to use newer evidence-based treatments can be as successful as in-person instruction, according to a new RAND Corporation study.
Psychotherapy treatments can lag years behind what research has shown to be effective because there simply are not enough clinicians trained in new methods. That means that many people with mental health disorders are not getting the most effective nonpharmacological treatments, RAND researchers say.
For one such treatment, Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy to treat bipolar ...
Tropical Storm Noul is still threatening Yap Island located in the Caroline Islands of the western Pacific Ocean, and a part of the Federated States of Micronesia. Micronesia has posted a typhoon warning for the tiny island. The storm is currently 22 miles south-southwest of Ulithi (one of the outer islands of the State of Yap) and is moving west at 2 knots per hour. Maximum sustained winds for the storm is 55 knots gusting to 70 knots and maximum wave height is 20 feet.
Noul is moving to the west and is expected to veer west northwest and later to the northwest. ...
After gobbling the fourth Oreo in a row while bathed in refrigerator light, have you ever thought, "That wasn't enough," and then proceeded to search for something more?
Researchers at BYU have shed new light on why you, your friends, neighbors and most everyone you know tend to snack at night: some areas of the brain don't get the same "food high" in the evening.
In a newly published study, exercise sciences professors and a neuroscientist at BYU used MRI to measure how people's brains respond to high- and low-calorie food images at different times of the day. The ...
Anxiety disorders affect approximately one in six adult Americans, according to the National Institute of Mental Health. The most well-known of these include panic disorder, post-traumatic stress disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and social anxiety disorder. But what of brief bouts of anxiety caused by stressful social situations?
A new study by Tel Aviv University researchers, published recently in the Journal of Oral Rehabilitation, finds that anxiety experienced in social circumstances elevates the risk of bruxism - teeth grinding which causes tooth wear and ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. -- Cells that relay information from the ear to the brain can change in significant ways in response to the noise level in the environment.
That's one major finding of a study out today in the Early Edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Expose the cells to loud sounds for a prolonged period of time, and they alter their behavior and even their structure in a manner that may aid hearing in the midst of noise. End the ruckus, and the cells change again to accommodate for quieter environs.
"The brain is amazingly adaptable: The ...
A multidisciplinary team of Johns Hopkins researchers has developed two new strategies to treat depression in young people using the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) class of medications. These strategies, published May 5 in the journal Translational Psychiatry, incorporate a new understanding of how to mitigate the risk of suicide while on SSRI treatment.
"These medications have to be dosed in a careful way," says senior investigator Adam Kaplin, M.D., Ph.D., an assistant professor of psychiatry and neurology at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. ...
(Winston-Salem, N.C. - May 5, 2015) - Researchers from Wake Forest University and the University of Utah are the first to successfully fabricate halide organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite field-effect transistors and measure their electrical characteristics at room temperature.
"We designed the structure of these field-effect transistors that allowed us to achieve electrostatic gating of these materials and determine directly their electrical properties," said lead author, Oana Jurchescu, an assistant professor of physics at Wake Forest. "Then we fabricated these transistors ...
HOUSTON -- ( May 5, 2015 ) -- The effectiveness of cancer vaccines could be dramatically boosted by first loading the cancer antigens into silicon microparticles, report scientists from Houston Methodist and two other institutions in an upcoming Cell Reports (early online).
Model studies showed that microparticles loaded with an antigen, HER2, not only protected the antigen from premature destruction, but also stimulated the immune system to recognize and relentlessly attack cancer cells overexpressing the HER2 antigen.
"We could completely inhibit tumor growth after ...
An intervention to connect low-income uninsured and Medicaid patients to a reliable source of primary health care shows promise for reducing avoidable use of hospital emergency departments in Maryland. A University of Maryland School of Public Health study evaluating the results of the intervention was published this week in the May issue of the journal Health Affairs.
For twenty years, use of hospital emergency departments has been on the rise in the United States, particularly among low-income patients who face barriers to accessing health care outside of hospitals ...
The rainfall accumulation analysis above was computed from data generated by the Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) during the period from April 28 to May 3, 2015. During this period IMERG algorithms continuously merged and interpolated satellite passive microwave precipitation estimates and microwave-calibrated infrared (IR) satellite estimates over the entire globe.
Rainfall from cyclone Quang fell over the west coast and a non-tropical system pounded the east coast of Australia simultaneously during the past weekend. Cyclone Quang formed in the South ...