Tropical Storm Dolphin threatening Micronesia
2015-05-11
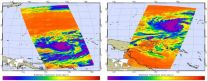
(Press-News.org) The MODIS instrument on the Aqua satellite captured this image of Tropical Storm Dolphin riding roughshod over the Federated States of Micronesia. Dolphin strengthened to tropical storm status between Bulletin 272 and 273 (1620 GMT and 2200 GMT) of the Joint Typhoon Weather Center on May 09, 2015.
The AIRS instrument on Aqua captured the images below of Dolphin between 10:59 pm EDT on May 9 and 11:00 am May 10 (02:59 UTC/15:17 UTC).
Dolphin is currently located (as of 5:00am EDT/0900 GMT) 464 miles ENE of Chuuk moving northwest at 9 knots (10 mph). It is expected to start to strengthen after a day or so. Dolphin is expected to reach 120 knots (138 mph) after 5 days, as it approaches Guam. Its maximum sustained winds are 45 knots with gusts to 55 knots (51 to 63 mph). The Federated States of Micronesia and the Northern Mariana Islands are both in the sights of Dolphin. Residents of Fananu in Chuuk State and the Marianas should monitor 07W carefully.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-11
New York, NY - The United States has a serious shortage of organs for transplants, resulting in unnecessary deaths every day. However, a fairly simple and ethical change in policy would greatly expand the nation's organ pool while respecting autonomy, choice, and vulnerability of a deceased's family or authorized caregiver, according to medical ethicists and an emergency physician at NYU Langone Medical Center.
The authors share their views in a new article in the May 11 online edition of the Journal of American Medical Association's "Viewpoint" section.
"The U.S. ...
2015-05-11
Hepatitis B stimulates processes that deprive the body's immune cells of key nutrients that they need to function, finds new UCL-led research funded by the Medical Research Council and Wellcome Trust.
The work helps to explain why the immune system cannot control hepatitis B virus infection once it becomes established in the liver, and offers a target for potential curative treatments down the line. The research also offers insights into controlling the immune system, which could be useful for organ transplantation and treating auto-immune diseases.
Worldwide 240 million ...
2015-05-11
A new study published in the journal Nature Climate Change shows that, when looking at the production site alone, growing biofuel crops can have a significant impact on climate depending on location and crop type. The study is the first geographically explicit life cycle assessment to consider the full range of greenhouse gases emissions from vegetation and soil carbon stock to nitrogen fertilizer emissions in all locations in the world.
In the last couple of years, research has begun to raise questions about the sustainability of biofuels. Life cycle assessments--a method ...
2015-05-11
CAMBRIDGE, MD (May 11, 2015)--A recent study of harmful algal blooms in the Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries by the University of Maryland Center for Environmental Science show a marked increase in these ecosystem-disrupting events in the past 20 years that are being fed by excess nitrogen runoff from the watershed. While algal blooms have long been of concern, this study is the first to document their increased frequency in the Bay and is a warning that more work is needed to reduce nutrient pollution entering the Bay's waters.
The Chesapeake Bay and its tributaries ...
2015-05-11
University of Melbourne animal welfare researcher Dr Jean-Loup Rault says the prospect of robopets and virtual pets is not as far-fetched as we may think.
His paper in the latest edition of Frontiers in Veterinary Science argues pets will soon become a luxury in an overpopulated world and the future may lie in chips and circuits that mimic the real thing.
"It might sound surreal for us to have robotic or virtual pets, but it could be totally normal for the next generation," Dr Rault said.
"It's not a question of centuries from now. If 10 billion human beings live ...
2015-05-11
ATLANTA--Confirming what many parents already know, researchers at Georgia State University and the University of Washington have discovered that toddlers, especially those with siblings, understand how the sounds they make affect people around them.
The findings are published in the Journal of Cognition and Development.
There has been limited research on what children understand about what others hear, with previous studies focusing only on whether a sound could be heard. This study takes a new approach to learning what children understand about sound by introducing ...
2015-05-11
ANN ARBOR--Climate helps drive the erosion process that exposes economically valuable copper deposits and shapes the pattern of their global distribution, according to a new study from researchers at the University of Idaho and the University of Michigan.
Nearly three-quarters of the world's copper production comes from large deposits that form about 2 kilometers (1.2 miles) beneath the Earth's surface, known as porphyry copper deposits. Over the course of millions to tens of millions of years, they are exposed by erosion and can then be mined.
Brian Yanites of the ...
2015-05-11
In a sobering finding for global health authorities and governments around the world, a group of leading epidemiologists say two in three deaths globally -- or 40 million people -- go unreported. And one in three births -- another 40 million people -- go unregistered.
University of Melbourne Laureate Professor Alan Lopez, one of The Lancet series lead authors, has been leading a global campaign to improve how countries capture civil registration and vital statistics (CRVS). The four-paper Lancet series promote the case to change CRVS systems to collect more reliable ...
2015-05-11
A new study links a father's age at birth to the risk that his child will develop blood and immune system cancers as an adult, particularly for only children. The study, which appears in the American Journal of Epidemiology, found no association between having an older mother and these cancers.
The proportion of parents who delay having children until age 35 or older continues to increase, but the long-term health consequences for these children are still emerging. Studies suggest higher risk of several conditions including several childhood and adult-onset cancers in ...
2015-05-11
DURHAM, N.H. -- The underlying physical process that creates striking "breaking wave" cloud patterns in our atmosphere also frequently opens the gates to high-energy solar wind plasma that perturbs Earth's magnetic field, or magnetosphere, which protects us from cosmic radiation. The discovery was made by two University of New Hampshire space physicists, who published their findings in the online journal Nature Communications Monday, May 11, 2015.
The phenomenon involves ultra low-frequency Kelvin-Helmholtz waves, which are ubiquitous throughout the universe and create ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Tropical Storm Dolphin threatening Micronesia


