More severe weather in store for middle states in US
2015-05-12
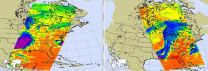
(Press-News.org) Today's imagery from NASA's AIRS instrument on the Aqua satellite indicates more severe weather is in store for the Midwest from Texas to Michigan. There is another extremely strong storm that is stretching from south to north and into Canada, and that system can be seen in this AIRS image from May 11, 2015. The first image (left) was taken at 3:35 am EDT, by the time the second image (right) was taken at 2:41 pm EDT the system had come together and was stretching across the nation vertically across the country.
Current weather forecasting predicts that Monday evening (5/11) will see very strong, severe weather whose activity will be further to the east than the previous storms from the past weekend. Tornado outbreaks are not expected with this system, but cannot be completely ruled out. The weather will still be severe including torrential rain, hail, high winds, and flash flooding. In this AIRS imagery, the very dark purple color is indicative of very cold air masses, a very compelling indication of strong convective storms.
Those persons in the affected areas should be on alert for severe weather and take necessary precautions.
INFORMATION:
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-12
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Researchers have discovered why many animal species can spend their whole lives outdoors with no apparent concern about high levels of solar exposure: they make their own sunscreen.
The findings, published today in the journal eLife by scientists from Oregon State University, found that many fish, amphibians, reptiles, and birds can naturally produce a compound called gadusol, which among other biologic activities provides protection from the ultraviolet, or sun-burning component of sunlight.
The researchers also believe that this ability may have ...
2015-05-12
Using a smart tablet and a red beam of light, Georgia Institute of Technology researchers have created a system that allows people to control a fleet of robots with the swipe of a finger. A person taps the tablet to control where the beam of light appears on a floor. The swarm robots then roll toward the illumination, constantly communicating with each other and deciding how to evenly cover the lit area. When the person swipes the tablet to drag the light across the floor, the robots follow. If the operator puts two fingers in different locations on the tablet, the machines ...
2015-05-12
Diet exerts a major impact on health and ageing. The nervous system plays an important role in this process but, thus far, how food signals are interpreted by the nervous system has been a mystery. This is an important question because the perception of food by the nervous system impacts not just ageing, but also other processes associated with health and disease, including metabolism, reproduction, and development.
A new study published in eLife by researchers from the MRC Centre for Developmental Neurobiology (MRC CDN) at the Institute of Psychiatry, Psychology & Neuroscience ...
2015-05-12
To measure distances in the Universe, astronomers use Cepheids, a family of variable stars whose luminosity varies with time. Their role as distance calibrators has brought them attention from researchers for more than a century. While it was thought that nearly everything was known about the prototype of Cepheids, named Delta Cephei, a team of researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), the Johns Hopkins University, and the European Space Agency (ESA), have now discovered that this star is not alone, but that it has a hidden companion. A revelation published in The ...
2015-05-12
MADISON, Wis. -- Expansion of cattle pastures has led to the destruction of huge swaths of rain forest in Brazil, home to the world's largest herd of commercial beef cattle. But a new study led by the University of Wisconsin-Madison's Holly Gibbs shows that market-driven "zero deforestation agreements" have dramatically influenced the behavior of ranchers and the slaughterhouses to which they sell.
Publishing today [May 12, 2015] in the journal Conservation Letters, the research team - including other UW-Madison scientists, the National Wildlife Federation, and IMAZON ...
2015-05-12
Scientists from Oregon State University have discovered that fish can produce their own sunscreen. They have copied the method used by fish for potential use in humans.
In the study published in the journal eLife, scientists found that zebrafish are able to produce a chemical called gadusol that protects against UV radiation. They successfully reproduced the method that zebrafish use by expressing the relevant genes in yeast. The findings open the door to large-scale production of gadusol for sunscreen and as an antioxidant in pharmaceuticals.
"The fact that the compound ...
2015-05-12
Extremely high levels of cardiovascular risk factors have been found in people with established psychosis, with central obesity evident in over 80 per cent of participants, in a study by researchers from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at the South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust (SLaM) and King's College London.
In the largest study of its kind in the UK, drawing on a sample of more than 400 outpatients with psychosis, it was discovered that nearly half of the sample were obese (48 per cent), with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or more. Additionally, nearly ...
2015-05-12
Around 55 million years ago, an abrupt global warming event triggered a highly corrosive deep-water current to flow through the North Atlantic Ocean. The origin of this corrosive water has puzzled scientists for a decade.
Now, researchers have discovered this current and how it formed. The findings, published today in Nature Geoscience, also have profound implications for the sensitivity of our current climate to carbon dioxide emissions.
The researchers explored the acidification of the ocean that occurred during a period known as the Paleocene Eocene Thermal Maximum ...
2015-05-11
A low platelet count can occur as the result of a variety of medical conditions and as a medication side effect. Platelet transfusion is often required for individuals with a critically low platelet level. Currently, the primary source of platelets is volunteer donors. Unfortunately, donated platelets have an extremely short shelf life and can be in limited supply. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation reports on a method to generate progenitor cells from murine embryonic stems that are able to produce a large number of functional platelets. Mitchell Weiss ...
2015-05-11
Bacterial meningitis is a life-threating infection of the central nervous system. Group B Streptococcus (GBS) is the leading cause of meningitis in newborn babies and can cause severe complications in those that survive the infection. GBS must cross the blood-brain-barrier (BBB) to cause disease but it is not clear how these organisms breach this barrier. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation identifies a pathway that is induced by GBS and disrupts junctions between cells. Kelly Doran and colleagues at San Diego State University determined that GBS induces ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] More severe weather in store for middle states in US