(Press-News.org) Researchers at Lehigh University have identified for the first time that a performance gain in the electrical conductivity of random metal nanowire networks can be achieved by slightly restricting nanowire orientation. The most surprising result of the study is that heavily ordered configurations do not outperform configurations with some degree of randomness; randomness in the case of metal nanowire orientations acts to increase conductivity.
The study, Conductivity of Nanowire Arrays under Random and Ordered Orientation Configurations, is published in the current issue of Nature's journal Scientific Reports. The research was carried out by Nelson Tansu, Daniel E. '39 and Patricia M. Smith Endowed Chair Professor in Lehigh's Center for Photonics and Nanoelectronics and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and lead author Milind Jagota, a Bethlehem-area high school student.
Transparent conductors are needed widely for flat screen displays, touch screens, solar cells, and light-emitting diodes, among many other technologies. Currently, Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) is the most widely used material for transparent conductors due to its high conductivity and high transparency. However, ITO-based technology has several issues. The material is scarce, expensive to manufacture and brittle, a particularly undesirable characteristic for anything being used in this modern age of flexible electronics.
Researchers searching for a replacement for ITO are increasingly employing random networks of metal nanowires to match ITO in both transparency and conductivity. Metal nanowire-based technologies display better flexibility and are more compatible with manufacturing processes than ITO films. The technology, however, is still in an early phase of development and performance must be improved. Current research is focused on the effect of rod orientation on conductivity of networks to improve performance.
In this work, Lehigh researchers developed a computational model for simulation of metal nanowire networks, which should speed the process towards idealizing the configuration of nanowires. The model predicts existing experimental results and previously published computational results.
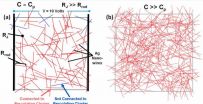
The researchers then used this model to extract results for the first time on how conductivity of random metal nanowire networks is affected by different orientation restrictions of varying randomness. Two different orientation configurations are reported.
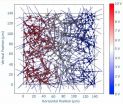
In the first, a uniform distribution of orientations over the range (?θ, θ) with respect to a horizontal line is used. In the second, a distribution of orientations over the range [?θ] _ [θ] is used, also with respect to a horizontal line. In each case θ is gradually decreased from 90° to 0°. Conductivity is measured both in directions parallel and perpendicular to alignment.
Researchers found that a significant improvement in conductivity parallel to direction of alignment can be obtained by slightly restricting orientation of the uniform distribution. This improvement, however, comes at the expense of a larger drop in perpendicular conductivity. The general form of these results matches that demonstrated by researchers experimenting with carbon nanotube films. Surprisingly, it was found that the highly ordered second case is unable to outperform isotropic networks for any value of θ; thus demonstrating that continuous orientation configurations with some degree of randomness are preferable to highly ordered configurations.
Prior research in this field has studied the effects of orientation on conductivity of 3D carbon nanotube composites, finding that a slight degree of alignment improves conductivity. Computational models have been used to study how percolation probability of 2D random rod dispersions is affected by rod orientation. Others have developed a more sophisticated computational model capable of calculating conductivity of 3D rod dispersions, again finding that a slight degree of axial alignment improves conductivity.
"Metal nanowire networks show great potential for application in various forms of technology," said Jagota. "This computational model, which has proven itself accurate through its good fit with previously published data, has demonstrated quantitatively how different orientation configurations can impact conductivity of metal nanowire networks."
"Restriction of orientation can improve conductivity in a single direction by significant amounts, which can be relevant in a variety of technologies where current flow is only required in one direction," said Tansu. "Surprisingly, heavily controlled orientation configurations do not exhibit superior conductivity; some degree of randomness in orientation in fact acts to improve conductivity of the networks. This approach may have tremendous impacts on improving current spreading in optoelectronics devices, specifically on deep ultraviolet emitter with poor p-type contact layer."
INFORMATION:
This work is supported in part by the National Science Foundation, the Daniel E. '39 and Patricia M. Smith Endowed Chair Professorship Fund, and Center for Photonics and Nanoelectronics at Lehigh University.
Tansu's research team at Lehigh works in the Laboratory for Emerging Photonics and Nanostructures and focuses on the physics and device technologies of semiconductor nanostructures for photonics and energy-efficiency applications. Tansu and his team employ fundamental knowledge derived from physics and chemistry in solving problems in engineering with technological impact. Several of the key applications they pursue include energy efficiency and renewable energy technologies including solid state lighting, solar cells, solar hydrogen, thermoelectricity, as well as deep UV emitters, terahertz photonics and semiconductor lasers for communications.
1. The "Radial Paradox": Higher Femoral Access Site Complications Offsets Radial Benefits
Growing acceptance of radial access during cardiac catheterisation to reduce access site complications may contribute to a loss of experience with femoral access, potentially increasing vascular complications when the femoral technique is used. Montreal Heart Institute researchers compared contemporary and historical patient cohorts (n=17,059) and found that vascular access complications today, using the femoral artery approach--used typically as a back-up method--are more common ...
No one health issue has the most impact on human health, or engenders more debate about how to tackle it, than obesity.
It has become the scourge of the health agenda, especially in the west, and it is a growing problem. According to the latest figures from the World Health Organisation, almost three-quarters of British men and two-thirds of women will be overweight or obese by 2030 - a staggering 39 million adults in total. We have one of the worst obesity records in Europe, with just six of the 52 countries in the WHO's European region with worse obesity rates for women.
We ...
Spider silk has long been noted for its graceful structure, as well as its advanced material properties: Ounce for ounce, it is stronger than steel.
MIT research has explained some of the material's mysteries, which could help design synthetic resources that mimic the extraordinary properties of natural silk. Now, scientists at MIT have developed a systematic approach to research its structure, blending computational modeling and mechanical analysis to 3D-print synthetic spider webs. These models offer insight into how spiders optimize their own webs.
"This is the ...
This news release is available in Spanish. The mission of neural stem cells located in the hippocampus, one of the main regions of the brain, is to generate new neurons during the adult life of mammals, including human beings, of course, and their function is to participate in certain types of learning and responses to anxiety and stress. Using an epilepsy model in genetically modified mice, the researchers have discovered that hippocampal neural stem cells stop generating new neurons and are turned into reactive astrocytes, a cell type that promotes inflammation and ...
A research team based at the University of Eastern Finland and the Turku Centre for Biotechnology have found new ways to block a pathway that may be responsible for several brain disorders, which could open the door to developing better treatments.
The protein NOS-1 generates nitric oxide, a chemical signal that is linked to neurological disorders from neurodegeneration, stroke and chronic pain sensitivity to anxiety and depressive disorders. These are now among the most common causes of disability and mortality, but decades of efforts have not led to a safe drug that ...
WASHINGTON, DC (May 15, 2015) -- More than half of popular probiotics contain traces of gluten, according to an analysis performed by investigators at the Celiac Disease Center at Columbia University Medical Center (CUMC). Tests on 22 top-selling probiotics revealed that 12 of them (or 55%) had detectable gluten.
Probiotics are commonly taken by patients for their theoretical effect in promoting gut health, though evidence of benefits is limited to a few clinical situations. "Many patients with celiac disease take dietary supplements, and probiotics are particularly popular," ...
SALT LAKE CITY, Utah, May 15, 2015 -- Myriad Genetics, Inc. (NASDAQ: MYGN) today presented clinical data for its Prolaris test at the 2015 American Urological Association (AUA) Annual Meeting being held May 15 to 19 in New Orleans, La. The results highlighted and underscored the significant ability of the Prolaris test to help physicians improve care for men diagnosed with prostate cancer.
In this pioneering study, Myriad presented important new clinical validation data that establishes an active surveillance (AS) threshold for men with localized prostate cancer. Specifically, ...
Research published today in the journal Analyst has demonstrated a new, noninvasive test that can detect cocaine use through a simple fingerprint. For the first time, this new fingerprint method can determine whether cocaine has been ingested, rather than just touched.
Led by the University of Surrey, a team of researchers from the Netherlands Forensic Institute (NL), the National Physical Laboratory (UK), King's College London (UK) and Sheffield Hallam University (UK), used different types of an analytical chemistry technique known as mass spectrometry to analyse the ...
Great Neck, NY - While the consequences of osteoporosis are worse in men than women - including death - older males are far less likely to take preventive measures against the potentially devastating bone-thinning disease or accept recommendations for screening, according to startling new research by North Shore-LIJ Health System geriatricians.
Geriatric fellow Irina Dashkova, MD, designed and led a cross-sectional survey of 146 older adults in New York and Florida that showed stunning gender differences in perspectives, beliefs and behaviors surrounding osteoporosis, ...
Great Neck, NY - With an aging Baby Boomer population and increasing numbers of childless and unmarried seniors, nearly one-quarter of Americans over age 65 are currently or at risk to become "elder orphans," a vulnerable group requiring greater awareness and advocacy efforts, according to new research by a North Shore-LIJ geriatrician and palliative care physician.
A case study and literature review by Maria Torroella Carney, MD, chief of geriatric and palliative medicine at the North Shore-LIJ Health System, zeroes in on staggering data on the prevalence and risks ...