Body's 'serial killers' captured on film destroying cancer cells
2015-05-19
(Press-News.org) A dramatic video has captured the behaviour of cytotoxic T cells - the body's 'serial killers' - as they hunt down and eliminate cancer cells before moving on to their next target.
In a study published today in the journal Immunity, a collaboration of researchers from the UK and the USA, led by Professor Gillian Griffiths at the University of Cambridge, describe how specialised members of our white blood cells known as cytotoxic T cells destroy tumour cells and virally-infected cells. Using state-of-the-art imaging techniques, the research team, with funding from the Wellcome Trust, has captured the process on film.
"Inside all of us lurks an army of serial killers whose primary function is to kill again and again," explains Professor Griffiths, Director of the Cambridge Institute for Medical Research. "These cells patrol our bodies, identifying and destroying virally infected and cancer cells and they do so with remarkable precision and efficiency."
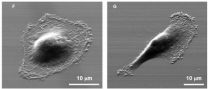
There are billions of T cells within our blood - one teaspoon full of blood alone is believed to have around 5 million T cells, each measuring around 10 micrometres in length, about a tenth the width of a human hair. Each cell is engaged in the ferocious and unrelenting battle to keep us healthy. The cells, seen in the video as orange or green amorphous 'blobs' move around rapidly, investigating their environment as they travel.
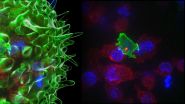
When a cytotoxic T cell finds an infected cell or, in the case of the film, a cancer cell (blue), membrane protrusions rapidly explore the surface of the cell, checking for tell-tale signs that this is an uninvited guest. The T cell binds to the cancer cell and injects poisonous proteins known as cytotoxins (red) down special pathways called microtubules to the interface between the T cell and the cancer cell, before puncturing the surface of the cancer cell and delivering its deadly cargo.
"In our bodies, where cells are packed together, it's essential that the T cell focuses the lethal hit on its target, otherwise it will cause collateral damage to neighbouring, healthy cells," says Professor Griffiths. "Once the cytotoxins are injected into the cancer cells, its fate is sealed and we can watch as it withers and dies. The T cell then moves on, hungry to find another victim."
The researchers captured the footage through high-resolution 3D time-lapse multi-colour imaging, making use of both spinning disk confocal microscopy and lattice light sheet microscopy. These techniques involves capturing slices through an object and 'stitching' them together to provide the final 3D images across the whole cell. Using these approaches the researchers have managed to elucidate the order the events leading to delivery of the lethal hit from these serial killers.
INFORMATION:
The video is available at https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ntk8XsxVDi0.
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-19
Decades' worth of textbook precepts about how our immune systems manage to avoid attacking our own tissues may be wrong.
Contradicting a long-held belief that self-reactive immune cells are weeded out early in life in an organ called the thymus, a new study by Stanford University School of Medicine scientists has revealed that vast numbers of these cells remain in circulation well into adulthood.
"This overturns 25 years of what we've been teaching," said Mark Davis, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology and director of Stanford's Institute for Immunity, Transplantation ...
2015-05-19
Scientists are reporting development of a new way to modify interleukin-2 (IL-2), a substance known as a cytokine that plays key roles in regulating immune system responses, in order to fine-tune its actions. Harnessing the action of IL-2 in a controllable fashion is of clinical interest with potential benefit in a range of situations, including transplantation and autoimmune disease. The modified IL-2 molecules inhibited the actions of endogenous IL-2, potentially more effectively than existing agents, as well as inhibited the actions of another interleukin, IL-15, with ...
2015-05-19
A team led by researchers from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) and the Ragon Institute of MGH, MIT and Harvard has found that the most common bacterial community in the genital tract among healthy South Africa women not only is significantly different from that of women in developed countries but also leads to elevated levels of inflammatory proteins. In a paper in the May 19 issue of Immunity, the investigators describe finding potential mechanisms by which particular bacterial species induce inflammation and show that the presence of those species and of elevated ...
2015-05-19
Ever since single-layer graphene burst onto the science scene in 2004, the possibilities for the promising material have seemed nearly endless. With its high electrical conductivity, ability to store energy, and ultra-strong and lightweight structure, graphene has potential for many applications in electronics, energy, the environment, and even medicine.
Now a team of Northwestern University researchers has found a way to print three-dimensional structures with graphene nanoflakes. The fast and efficient method could open up new opportunities for using graphene printed ...
2015-05-19
HIV infections continue to rise in a new generation of young, gay, bisexual and other men who have sex with men (YMSM) despite three decades of HIV prevention as well as recent availability of biomedical technologies to prevent infection. In the U.S., it is estimated that 63% of incident HIV infections in 2010 were among YMSM despite the fact that they represent a very small portion of the population. Given this heightened risk for HIV seroconversion among YMSM, researchers at New York University's Center for Health, Identity, Behavior & Prevention Studies (CHIBPS) sought ...
2015-05-19
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- Why do some cancer cells break away from a tumor and travel to distant parts of the body? A team of oncologists and engineers from the University of Michigan teamed up to help understand this crucial question.
Cancer becomes deadly when it spreads, or metastasizes. Not all cells have the same ability to travel through the body, but researchers don't understand why.
In a paper published in Scientific Reports, researchers describe a new device that is able to sort cells based on their ability to move. The researchers were then able to take the sorted ...
2015-05-19
Run far or run fast? That is one of the questions NASA is trying to answer with one of its latest studies--and the answers may help keep us in shape on Earth, as well as in space. Even with regular exercise, astronauts who spend an extended period of time in space experience muscle weakening, bone loss, and decreased cardiovascular conditioning. This is because they no longer have to work against gravity in everyday living.
NASA's Human Research Program Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training study, known as iRAT, completed recently to evaluate the use of high intensity ...
2015-05-19
Human error is estimated to cause more than 90% of traffic accidents, a percentage that might be drastically reduced by the implementation of self-driving cars featuring smart systems that control most aspects of driving. Although the potential benefits of self-driving cars have been widely touted, their success on the roadways of the near future is largely reliant on whether or not drivers are willing to trust these smart systems enough to hand over the wheel. A new study published in Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society evaluated whether ...
2015-05-19
A University of Colorado Cancer Center study published in the journal Nicotine & Tobacco Research shows a new dimension to the marginalization of smokers: people who smoke are less likely to vote than their non-smoking peers.
"One on hand, the result is intuitive. We know from previous research that smokers are an increasingly marginalized population, involved in fewer organizations and activities and with less interpersonal trust than nonsmokers. But what our research suggests is that this marginalization may also extend beyond the interpersonal level to attitudes toward ...
2015-05-19
PUYALLUP, Wash. -- Farmers' markets wanting to increase purchases by customers should consider accepting more than just cash or checks as payment, according to Washington State University researchers.
"Customers are willing to buy more if they have other payment options," said Karina Gallardo, a WSU associate professor and extension specialist in the School of Economic Sciences. "They may not necessarily pay more, but they'll buy more."
That's one of the results of a study recently published in the International Food and Agribusiness Management Review.
Gallardo and her ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Body's 'serial killers' captured on film destroying cancer cells