(Press-News.org) Lawrence Livermore researchers have determined that a tunnel bomb explosion by Syrian rebels was less than 60 tons as claimed by sources.
Using seismic stations in Turkey, Livermore scientists Michael Pasyanos and Sean Ford created a method to determine source characteristics of near earth surface explosions. They found the above-ground tunnel bomb blast under the Wadi al-Deif Army Base near Aleppo last spring was likely not as large as originally estimated and was closer to 40 tons.
Seismology has long been used to determine the source characteristics of underground explosions, such as yield and depth, and plays a prominent role in nuclear explosion monitoring. But now some of the same techniques have been modified to determine the strength and source of near and above-ground blasts.
The new method to track above-ground explosions serves as a forensic tool for investigators and governmental agencies seeking to understand the precise cause of an explosion.
"The technique accounts for the reduction in amplitudes as the explosion depth approaches the free surface and less energy is coupled into the ground," said Michael Pasyanos, an LLNL geophysicist and lead author of a paper appearing in an upcoming issue of Geophysical Research Letters.
The team, also made up LLNL scientist Sean Ford, used the method on a series of shallow explosions in New Mexico where the yields and depths were known.
Pasyanos and Ford's examination of source characteristics of near-surface explosions is an extension of the regional amplitude envelope method. This technique was developed and applied to North Korean nuclear explosions, then applied to chemical explosions and nuclear tests in Nevada.
"The technique takes an earthquake or explosion source model and corrects for the wave propagation to generate predicted waveform envelopes at any particular frequency band," Pasyanos said.
Methods for determining the yields of contained events range from teleseismic amplitudes and P-wave spectra to regional P-wave amplitudes and magnitudes. Pasyanos developed a method to characterize underground explosions based on regional amplitude envelopes across a broad range of frequencies. One advantage of the method is that examining the signal over a wide frequency band can reduce some of the strong tradeoffs between yield and depth, Pasyanos said
"By allowing the methodology to consider shallow, uncontained events just below, at, or even above the Earth's surface, we make the method relevant to new classes of events including mining events, military explosions, industrial accidents, plane crashes or potential terrorist attacks." Pasyanos said. "A yield estimate is often very important to investigators and governmental agencies seeking to understand the precise cause of an explosion."
For the Syrian explosion, the team did not have local seismic data from Syria, but it was well recorded by regional stations from the Continental Dynamics: Central Anatolian Tectonics (CD-CAT) deployment in Turkey.
If the explosion occurred well above the surface, a yield of 100 tons TNT equivalent would be required to produce the observed seismic signal.
"Given the video footage of the explosion, however, we know that it was neither at nor above the free surface, nor fully coupled," Ford said. "We estimate a chemical yield ranging from 6 and 50 tons depending on the depth, with the best estimate between 20-40 tons. Including independent information on the depth, we could narrow this considerably. If, for instance, we definitively knew that the explosion occurred at 2 meters below the surface, then we would estimate the yield at 40 tons."
The team found that though there are expected tradeoffs between yield and depth/height, when constrained by other information, the yields are consistent with ground truth yields in tests in New Mexico and reasonable values from what Pasyanos and Ford know about in Syria.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency.
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
This news release is available in French. Montreal, May 21, 2015 - A new study published by the team of Naguib Mechawar, Ph.D., a researcher at the Douglas Institute (CIUSSS de l'Ouest-de-l'île-de-Montréal) and Associate Professor in the Department of Psychiatry at McGill University, suggests that the integration of new neurons in the adult brain is a phenomenon more generally compromised in the brains of depressed patients.
This new work confirms that neurogenesis in the human olfactory bulb is a marginal phenomenon in adults. These findings shed light ...
Alexandria, VA - In the years following the 1986 Chernobyl nuclear disaster, forest fires billowed plumes of contaminated smoke, carrying radioactive particles throughout Europe on the wind. Now, researchers fear that a shift to a hotter, drier climate in Eastern Europe could increase the frequency of these fires.
Researchers from the University of South Carolina in Columbia used satellite imagery of fires in the 2000s and field measurements of radioisotope levels to model changes in the distribution of radiation over the region. The researchers found that fires likely ...
Researchers have developed a model to assess how dams affect the viability of sea-run fish species that need to pass dams as they use both fresh and marine waters during their lifetimes. NOAA's Northeast Fisheries Science Center (NEFSC) and Greater Atlantic Regional Fisheries Office (GARFO) have partnered on this project to test how varying passage efficiency at dams related to survival rates for these species.
Using a model of endangered Atlantic salmon in Maine's Penobscot River as a case study, NOAA researchers found that abundance, distribution and number of fish ...
Hamilton, ON (May 21, 2015) - Scientists at McMaster University have discovered how to make adult sensory neurons from human patients simply by having them roll up their sleeve and providing a blood sample.
Specifically, stem cell scientists at McMaster can now directly convert adult human blood cells to both central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) neurons as well as neurons in the peripheral nervous system (rest of the body) that are responsible for pain, temperature and itch perception. This means that how a person's nervous system cells react and respond to ...
One of the reasons pluripotent stem cells are so popular in medical research is that they can be differentiated into any cell type. However, typical differentiation protocols lead to a heterogeneous population from which the desired type must be purified. Normally, antibodies that react to surface receptors unique to the desired cell are used for this purpose. However, in many cases the purification levels remain poor and the cells can be damaged. New RNA technology produced at CiRA may avoid these problems.
Professor Hirohide Saito at the Dept. of Reprogramming Science ...
Receptors carrying built-in decoys are the latest discovery in the evolutionary battle between plants and pathogens. The decoy domains within the receptor detect pathogens and raise the cell's alarm when there is an infection.
Plants display component parts of their immune system on receptors to trick pathogens into binding with them, which then triggers defence mechanisms. The discovery comes from Professor Jonathan Jones' group at The Sainsbury Laboratory, published in the high-impact journal Cell with a companion paper on a similar discovery from the Deslandes group ...
Almost 90 per cent of men with advanced prostate cancer carry genetic mutations in their tumours that could be targeted by either existing or new cancer drugs, a landmark new study reveals.
Scientists in the UK and the US have created a comprehensive map of the genetic mutations within lethal prostate cancers that have spread around the body, in a paper being hailed as the disease's 'Rosetta Stone'.
Researchers say that doctors could now start testing for these 'clinically actionable' mutations and give patients with advanced prostate cancer existing drugs or drug combinations ...
May 21, 2015 - A University of Wyoming faculty member led a research team that discovered a certain type of soil bacteria can use their social behavior of outer membrane exchange (OME) to repair damaged cells and improve the fitness of the bacteria population as a whole.
Daniel Wall, a UW associate professor in the Department of Molecular Biology, and others were able to show that damaged sustained by the outer membrane (OM) of a myxobacteria cell population was repaired by a healthy population using the process of OME. The research revealed that these social organisms ...
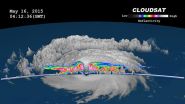
When Dolphin was a typhoon on May 16, NASA's CloudSat satellite completed a stunning eye overpass of Typhoon Dolphin in the West Pacific at 0412 UTC (12:12 a.m. EDT). By May 22, Dolphin's remnants were moving through the Northern Pacific.
NASA's CloudSat satellite sends pulses of microwave energy through the clouds, and some of the energy in the pulses is reflected back to the spacecraft. The time delay between when the pulse is sent and when the reflected energy is received back at the spacecraft is mapped into a distance of the cloud from the surface of the Earth, and ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - Last year, researchers at the University of Missouri published a study on genetic diversity in American black bears in Missouri, Arkansas and Oklahoma and determined that conservation management is needed to maintain healthy populations in the region. Now, those scientists have expanded the study to include black bears throughout North America. They discovered that black bears in Alaska are more closely related to bears in the eastern regions of the U.S. and Canada than those located in western regions. Details from the study revealed ancient movement patterns ...