(Press-News.org) Road traffic noise is linked to a heightened risk of developing a mid-riff bulge, indicates research published online in Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Exposure to a combination of road traffic, rail, and aircraft noise may pose the greatest risk of acquiring a spare tyre--otherwise known as central obesity, and thought to be one of the most harmful types of fat deposition around the body--the findings suggest.
The researchers assessed how much road traffic, rail, and aircraft noise 5075 people living in five suburban and rural areas around Stockholm, Sweden, had been exposed to since 1999.
They did this, by using official figures on road and rail traffic noise levels and flow. This included information on ground surfaces, building heights, speed limits and noise barriers from the five municipalities. And they used national data on aircraft noise from Stockholm's main airport, Arlanda.
All the participants and had been part of the Stockholm Diabetes Prevention Program (1992-8), which aimed to look at risk factors for the development of diabetes and how best to prevent it.
Between 2002 and 2006, when they were aged between 43 and 66, they completed a detailed questionnaire covering lifestyle, current state of health, levels of psychological distress, insomnia and job strain. They were also asked about environmental noise pollution from road traffic, trains, and planes.
And they underwent a medical, which included blood pressure and a test for diabetes, as well as measures of central body fat (waist and hips and the waist:hip ratio), and overall obesity (weight and height to define the body mass index or BMI).
The researchers calculated that well over half (62%, 3127) had been regularly exposed to road traffic noise of at least 45 decibels (dB) while one in 20 had been exposed to similar levels of noise from trains. A further 1108 had been exposed to aircraft noise of more than 45 dB.
In all, just over half (54%, 2726) had been exposed to one source of traffic noise; 15% (740) to two sources; and 2% (90) to all three. Around a third (30%, 1519) had been exposed to levels below 45 dB, which were not considered to be harmful.
The analysis indicated no link between road traffic noise and BMI. But there was an association between road traffic noise and waist size, with a 0.21 cm increase for every additional 5 dB increase in exposure, although this was only significant among women.
Similarly, there was a link to waist:hip ratio, with a change of 0.16 for every 5 dB increase in noise exposure to road traffic; this association was stronger in men.
A larger waist was significantly associated with exposure to any of the three sources of noise, but the link was strongest for aircraft noise; a larger waist:hip ratio was associated with road traffic and aircraft noise only.
There seemed to be a cumulative effect, however: the more sources of noise pollution a person was exposed to at the same time, the greater their risk of central obesity seemed to be.
The heightened risk of a larger waist rose from 25% among those exposed to only one source to almost double for those exposed to all three sources.
The findings were not influenced by socioeconomic factors, lifestyle, or exposure to ambient air pollution from local road traffic. But age was an influential factor, with associations between central obesity and road traffic noise only found for those below the age of 60.
This is an observational study so no definitive conclusions can be drawn about cause and effect, nor were the researchers able to assess levels of residential sound insulation or the location of the participants' bedrooms.
But noise exposure may be an important physiological stressor and bump up the production of the hormone cortisol, high levels of which are thought to have a role in fat deposition around the middle of the body, they suggest.
"This may explain why the effects of noise were mainly seen for markers of central obesity, such as waist circumference and waist-hip ratio, rather than for generalised obesity, measured by BMI," they write.
Traffic noise from any of the three sources may also affect metabolic as well as cardiovascular functions, through sleep disturbance, they suggest, altering appetite control and energy expenditure.
INFORMATION:
Patients aged 80 and above are significantly less likely to be investigated or aggressively treated after surgery than their younger counterparts, reveals a national audit of hospital deaths, published in the online journal BMJ Open.
This is despite the fact that the oldest old have higher rates of trauma and multiple underlying conditions on admission, say the Australian researchers.
Care in the oldest old may be less aggressive, or scaled down because the outcome is expected to be poor or treatment considered futile, they say. Perceived future quality of life issues ...
1. Appropriate duration of dual antiplatelet therapy still unclear
Free abstract: http://www.annals.org/article.aspx?doi=10.7326/M15-0083
URL goes live when embargo lifts
A systematic review of published evidence does little to clarify the appropriate duration of dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) following drug eluting stent placement. The evidence suggests that longer duration therapy decreases the risk for myocardial infarction, but increases the risk for major bleeding events, and may provide a slight increase in mortality. The results are published in Annals of Internal ...
Ovarian cancer is notoriously difficult to diagnose and treat, making it an especially fatal disease. Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Moores Cancer Center have now identified six mRNA isoforms (bits of genetic material) produced by ovarian cancer cells but not normal cells, opening up the possibility that they could be used to diagnose early-stage ovarian cancer. What's more, several of the mRNA isoforms code for unique proteins that could be targeted with new therapeutics. The study is published the week of May 25 by the Proceedings ...
Frailer older patients are at higher risk of readmission to hospital or death within 30 days after discharge from a general internal medicine ward, but health care professionals can assess who is at risk using the Clinical Frailty Scale, according to a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal)
Readmission within 30 days after hospital discharge is common and also costly for the health care system. Identifying at-risk patients and addressing the factors contributing to readmission can help reduce recurrences. However, current tools are not able to predict accurately ...
This news release is available in French. Scientists measuring brain activity have found that in many regions, such as the sensory or motor cortex, activity sometimes oscillates at different frequencies, forming wave-like patterns. Despite the fact that such oscillations are frequently observed, and present in many brain regions, their functional role remains unclear. Research done by Dr. Christopher Pack, from McGill University, who looked at such waves occurring in a region of the visual cortex of the brain, suggests these oscillations could have a role in resetting ...
Cold Spring Harbor, NY -- A team of scientists at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) has identified a set of genes that control stem cell production in tomato. Mutations in these genes explain the origin of mammoth beefsteak tomatoes. More important, the research suggests how breeders can fine-tune fruit size in potentially any fruit-bearing crop. The research appears online today in Nature Genetics.
In its original, wild form the tomato plant produces tiny, berry-sized fruits. Yet among the first tomatoes brought to Europe from Mexico by conquistador Hernan Cortez in ...
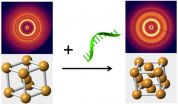
UPTON, NY -- Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have just taken a big step toward the goal of engineering dynamic nanomaterials whose structure and associated properties can be switched on demand. In a paper appearing in Nature Materials, they describe a way to selectively rearrange the nanoparticles in three-dimensional arrays to produce different configurations, or phases, from the same nano-components.
"One of the goals in nanoparticle self-assembly has been to create structures by design," said Oleg Gang, who led the work ...
New research conducted in a rural community in Pakistan highlights the crucial role that essential fatty acids play in human brain growth and function.
A team co-led by the University of Exeter, working with experts in Singapore, has published findings in Nature Genetics which show that mutations in the protein Mfsd2a cause impaired brain development in humans. Mfsd2a is the transporter in the brain for a special type of fat called lysophosphatidylcholines (LPCs) -- which are composed of essential fatty acids like omega-3. This shows the crucial role of these fats in ...
Having a healthy gut may well depend on maintaining a complex signaling dance between immune cells and the stem cells that line the intestine. Scientists at the Buck Institute are now reporting significant new insight into how these complex interactions control intestinal regeneration after a bacterial infection. It's a dance that ensures repair after a challenge, but that also goes awry in aging fruit flies -- the work thus offers important new clues into the potential causes of age-related human maladies, such as irritable bowel syndrome, leaky gut and colorectal cancer.
"We've ...
May 26, 2015, Shenzhen, China - Researchers from BGI reported the most complete haploid-resolved diploid genome (HDG) sequence based on de novo assembly with NGS technology and the pipeline developed lays the foundation for de novo assembly of genomes with high levels of heterozygosity. The latest study was published online today in Nature Biotechnology.
The human genome is diploid, and knowledge of the variants on each chromosome is important for the interpretation of genomic information. In this study, researchers presented the assembly of a haplotype-resolved diploid ...