Scientists discover key to what causes immune cell migration to wounds
2015-05-28
(Press-News.org) Immune cells play an important role in the upkeep and repair of our bodies, helping us to defend against infection and disease. Until now, how these cells detect a wounded or damaged site has largely remained a mystery. New research, led by University of Bristol academics in collaboration with a team from the University of Sheffield, has identified the triggers which lead these cells to react and respond in cell repair.
It is hoped the findings, published in Current Biology, could help scientists design therapies to manipulate the cell repair process and direct immune cells away from sites where they are doing damage, such as tumours, and send them to places where they are needed.
Previous studies had found that the earliest signal produced at a wound site responsible for attracting immune cells to the damaged site is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). However, it was still unclear how these cells detect this chemical, and what signaling occurs in these cells downstream of H2O2 detection to power their rapid migration.
Using the common fruitfly (Drosophila melanogaster) and timelapse microscopy, the team led by Professor Will Wood at the University of Bristol were able to study the process in situ and identify what causes the cells to migrate to sites of damage where they then detect, ingest and degrade debris, dying cells and invading pathogens.
After dissecting the signaling occurring in immune cells responding to wound induced (H2O2), the team found that it involved a well-established immune signalling pathway used in vertebrate adaptive immune responses. The results suggest that adaptive immune signalling pathways important in distinguishing self from non-self in vertebrates appear to have evolved from a more ancient response designed to distinguished 'damaged self' from 'healthy self'.
Will Wood, Professor of Developmental Biology, in Bristol's School for Cellular and Molecular Medicine, and the study's lead author, said: "While inflammation is critical to prevent infection, too much of a response by immune cells can cause or worsen a wide range of human diseases and conditions including autoimmunity, atherosclerosis, cancer and chronic inflammation.
"This research is therefore critical for improving human health as it enables us to discover novel points of intervention to manipulate immune cell behaviour and allow us to design therapies to direct immune cells away from sites where they are doing damage and send them into places where they are needed."
INFORMATION:
Paper:
Draper/CED-1 mediates an ancient damage response to control inflammatory blood cell migration in vivo by Iwan Robert Evans, Frederico Salgueiro Lopes Matias Rodrigues, Emma Louise Armitage and Will Wood in Current Biology.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-28
Flies might be smarter than you think. According to research reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on May 28, fruit flies know what time of day it is. What's more, the insects can learn to connect different scents with the sweet reward of sugar, depending on the hour: menthol in the morning and mushrooms in the afternoon.
Researchers say that the findings show the surprising mental abilities of animals, no matter how small.
"If even the fly, with its miniature brain, has the sense of time, most animals may have it," says Martin Heisenberg of Rudolf Virchow ...
2015-05-28
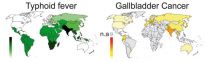
Controlling bacterial infections responsible for typhoid fever could dramatically reduce the risk of gallbladder cancer in India and Pakistan, according to a study published by Cell Press May 28th in Cell Host & Microbe. The findings establish for the first time the causal link between bacterial infection and gallbladder cancer, explaining why this type of cancer is rare in the West but common in India and Pakistan, where typhoid fever is endemic. Public policy changes inspired by this research could have an immediate impact on preventing a type of cancer that currently ...
2015-05-28
The chemical rapamycin is used clinically as an immunosuppressant and as an anti-cancer agent that works by inactivating a protein named TOR (Target Of Rapamycin). This protein is essential for the growth of normal cells, but is hyperactive in tumor cells. To be able to carry out its various growth-related tasks, TOR needs to assemble into one of two larger protein complexes named TORC1 and TORC2. Curiously, whereas TORC1 is inhibited by rapamycin, TORC2 is unaffected by this drug. The team of Robbie Loewith, professor in biology at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, ...
2015-05-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke Medicine researchers have found that bladder cells have a highly effective way to combat E. coli bacteria that cause urinary tract infections (UTIs).
In a study published online May 28, 2015, in the journal Cell, Duke researchers and their colleagues describe how bladder cells can physically eject the UTI-causing bacteria that manage to invade the host cell.
This response is analogous to having indigestion and vomiting to rid the stomach of harmful substances.
The finding suggests there may be a potential way to capitalize on this natural tendency ...
2015-05-28
New research suggests that European and Asian (Eurasian) peoples originated when early Africans moved north - through the region that is now Egypt - to expand into the rest of the world. The findings, published in the American Journal of Human Genetics, answer a long-standing question as to whether early humans emerged from Africa by a route via Egypt, or via Ethiopia.
The extensive public catalogue of the genetic diversity in Ethiopian and Egyptian populations developed for the project also now provides a valuable, freely available, reference panel for future medical ...
2015-05-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Some decisions arouse far more anxiety than others. Among the most anxiety-provoking are those that involve options with both positive and negative elements, such choosing to take a higher-paying job in a city far from family and friends, versus choosing to stay put with less pay.
MIT researchers have now identified a neural circuit that appears to underlie decision-making in this type of situation, which is known as approach-avoidance conflict. The findings could help researchers to discover new ways to treat psychiatric disorders that feature impaired ...
2015-05-28
La Jolla, Calif., May 28, 2015 - A new collaborative study led by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), published today in Cell Reports, provides new insight into the molecular changes that lead to resistance to a commonly prescribed group of drugs called BRAF inhibitors. The findings suggest that targeting newly discovered pathways could be an effective approach to improving the clinical outcome of patients with BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma tumors.
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, killing more than 8,000 people ...
2015-05-28
This news release is available in French.
One night of poor sleep significantly decreases performance on intelligence tests in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and also in neurotypical children (without ASD). This is the conclusion made by researchers at the Hôpital Rivière-des-Prairies, affiliated with the Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Université de Montréal.
For a paper published in the International Journal of Psychophysiology, the researchers observed the EEG measures of 13 autistic children ...
2015-05-28
Ex-prisoners with a history of risky drug use, mental illness or poverty are more likely to end up back behind bars. Those who are obese, are chronically ill or have attempted suicide are more likely to remain in the community. These are some of the findings from an exploratory study into health-related factors that could be used to predict whether a person released from prison will end up in custody again. It was led by Emma Thomas of the University of Melbourne in Australia and is published in Springer's journal Health & Justice, an open access journal.
In many countries, ...
2015-05-28
A citizen science programme reveals the protection measures for the Montagu's harrier in the cereal crop season in France to be ineffective if nests are not protected to decrease predation after harvesting. A study has been published as a result of this voluntary fieldwork, with the participation of the Hunting Resources Research Institute, which proposes fencing off the nests as a way of mitigating the damage and optimising conservation efforts in different areas.
Over the last decade there has been an explosion in the so-called citizen science programmes, in which people ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists discover key to what causes immune cell migration to wounds