Controlling typhoid bacterium key to prevent gallbladder cancer in India and Pakistan
2015-05-28
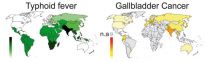
(Press-News.org) Controlling bacterial infections responsible for typhoid fever could dramatically reduce the risk of gallbladder cancer in India and Pakistan, according to a study published by Cell Press May 28th in Cell Host & Microbe. The findings establish for the first time the causal link between bacterial infection and gallbladder cancer, explaining why this type of cancer is rare in the West but common in India and Pakistan, where typhoid fever is endemic. Public policy changes inspired by this research could have an immediate impact on preventing a type of cancer that currently has a very poor prognosis.
"While viruses are among the established causal factors for particular cancers, bacteria are largely ignored as direct contributors," says senior study author Jacques Neefjes of the Netherlands Cancer Institute. "Accepting that bacterial infections can directly contribute to cancer formation makes these tumors in principle preventable. If Salmonella Typhi infections are cured immediately with antibiotics and chronic infections are prevented, or if vaccination programs to eradicate S. Typhi work, we would expect a major reduction in the incidence of a tumor that represents the third most common gastrointestinal tumor in India and Pakistan."
Gallbladder cancer is hard to diagnose in its early stages because there are no signs or symptoms. By the time the cancer is detected, it is often too late to save patients' lives. Because the prognosis of gallbladder cancer is so poor, Neefjes, Tiziana Scanu of the Netherlands Cancer Institute, and Gopal Nath of Banaras Hindu University set out to gain insight into how to combat this tumor by identifying causal factors underlying its unique global distribution. The researchers quickly zeroed in on S. Typhi because this typhoid-causing bacterium is endemic in India and has been associated with gallbladder cancer in epidemiological studies. Moreover, proteins that Salmonella injects into host cells activate cancer-related signaling pathways called AKT and MAPK, which support not only bacterial infection and survival, but also the growth and proliferation of cancer cells.
To explore the role of S. Typhi in cancer in the new study, Neefjes and Scanu compared tumor samples from Indian and Dutch patients with gallbladder cancer. While both groups showed signs of AKT and MAPK activation and an inactive, mutant TP53 cancer gene, only Indian patients showed strong evidence of S. Typhi infection and over-activating mutations in a cancer gene called c-Myc. To mimic the features of the tumor samples from India, the researchers transplanted Salmonella-infected cells with mutations affecting TP53 and c-Myc activity into mice. These mice later developed tumors, demonstrating that Salmonella causes cancer in genetically at-risk hosts as a result of the collateral damage induced by its normal infection cycle.
Additional experiments suggested that Salmonella infection sets genetically predisposed host cells on the cancerous path by secreting proteins that increase AKT and MAPK activity, which remains elevated and perpetuates the cancer trajectory long after the bacteria have disappeared. These same two host signaling pathways are activated by bacterial pathogens implicated in cervical and lung cancer, suggesting that a direct contribution of bacteria to tumor formation could be more common than previously anticipated. "The findings also suggest that the use of antibiotic treatment to control these bacterial infections may come too late for individuals who have already developed cancer," Scanu says. "Instead, the main goal should be prevention through proper treatment with antibiotics, vaccination programs, or better sanitary conditions."
In future studies, the researchers will investigate whether Salmonella contributes to tumors in other tissues, identify other cancer-causing bacteria, and determine how these pathogens leave an imprint of infection in host cells. But policymakers do not have to wait for answers to these questions before taking action to save countless lives. "Our findings may now be used to urge policymakers to take appropriate measures to eliminate or better control these infections," Neefjes says. "If typhoid fever is controlled, gallbladder carcinoma in India and Pakistan could be prevented and become as rare as in the Western world."
INFORMATION:
Cell Host & Microbe, Scanu et al. "Salmonella manipulation of host signaling pathways provokes cellular transformation associated with gallbladder carcinoma" http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.chom.2015.05.002
Cell Host & Microbe, published by Cell Press, is a monthly journal that publishes novel findings and translational studies related to microbes (which include bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses). The unifying theme is the integrated study of microbes in conjunction and communication with each other, their host, and the cellular environment they inhabit. For more information, please visit http://www.cell.com/cell-host-microbe. To receive media alerts for Cell Host & Microbe or other Cell Press journals, contact press@cell.com.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-05-28
The chemical rapamycin is used clinically as an immunosuppressant and as an anti-cancer agent that works by inactivating a protein named TOR (Target Of Rapamycin). This protein is essential for the growth of normal cells, but is hyperactive in tumor cells. To be able to carry out its various growth-related tasks, TOR needs to assemble into one of two larger protein complexes named TORC1 and TORC2. Curiously, whereas TORC1 is inhibited by rapamycin, TORC2 is unaffected by this drug. The team of Robbie Loewith, professor in biology at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, ...
2015-05-28
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke Medicine researchers have found that bladder cells have a highly effective way to combat E. coli bacteria that cause urinary tract infections (UTIs).
In a study published online May 28, 2015, in the journal Cell, Duke researchers and their colleagues describe how bladder cells can physically eject the UTI-causing bacteria that manage to invade the host cell.
This response is analogous to having indigestion and vomiting to rid the stomach of harmful substances.
The finding suggests there may be a potential way to capitalize on this natural tendency ...
2015-05-28
New research suggests that European and Asian (Eurasian) peoples originated when early Africans moved north - through the region that is now Egypt - to expand into the rest of the world. The findings, published in the American Journal of Human Genetics, answer a long-standing question as to whether early humans emerged from Africa by a route via Egypt, or via Ethiopia.
The extensive public catalogue of the genetic diversity in Ethiopian and Egyptian populations developed for the project also now provides a valuable, freely available, reference panel for future medical ...
2015-05-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Some decisions arouse far more anxiety than others. Among the most anxiety-provoking are those that involve options with both positive and negative elements, such choosing to take a higher-paying job in a city far from family and friends, versus choosing to stay put with less pay.
MIT researchers have now identified a neural circuit that appears to underlie decision-making in this type of situation, which is known as approach-avoidance conflict. The findings could help researchers to discover new ways to treat psychiatric disorders that feature impaired ...
2015-05-28
La Jolla, Calif., May 28, 2015 - A new collaborative study led by researchers at Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute (Sanford-Burnham), published today in Cell Reports, provides new insight into the molecular changes that lead to resistance to a commonly prescribed group of drugs called BRAF inhibitors. The findings suggest that targeting newly discovered pathways could be an effective approach to improving the clinical outcome of patients with BRAF inhibitor-resistant melanoma tumors.
Melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer, killing more than 8,000 people ...
2015-05-28
This news release is available in French.
One night of poor sleep significantly decreases performance on intelligence tests in children with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and also in neurotypical children (without ASD). This is the conclusion made by researchers at the Hôpital Rivière-des-Prairies, affiliated with the Institut universitaire en santé mentale de Montréal and Université de Montréal.
For a paper published in the International Journal of Psychophysiology, the researchers observed the EEG measures of 13 autistic children ...
2015-05-28
Ex-prisoners with a history of risky drug use, mental illness or poverty are more likely to end up back behind bars. Those who are obese, are chronically ill or have attempted suicide are more likely to remain in the community. These are some of the findings from an exploratory study into health-related factors that could be used to predict whether a person released from prison will end up in custody again. It was led by Emma Thomas of the University of Melbourne in Australia and is published in Springer's journal Health & Justice, an open access journal.
In many countries, ...
2015-05-28
A citizen science programme reveals the protection measures for the Montagu's harrier in the cereal crop season in France to be ineffective if nests are not protected to decrease predation after harvesting. A study has been published as a result of this voluntary fieldwork, with the participation of the Hunting Resources Research Institute, which proposes fencing off the nests as a way of mitigating the damage and optimising conservation efforts in different areas.
Over the last decade there has been an explosion in the so-called citizen science programmes, in which people ...
2015-05-28
EUGENE, Ore. -- (May 28, 2015) -- Men and women often enter relationships with different long-term goals. In the animal world, differences in approaches to reproductive success can lead to sexual conflict.
Male fruit flies, for example, transfer proteins during mating that can alter the timing of a female's egg laying and her tendency to later mate with other males. Some of these male-derived proteins also migrate from the female's reproductive tract to her brain.
Now, in a new study, scientists of the University of Oregon and Bowdoin College show that sexual conflicts ...
2015-05-28
CHICAGO -- Researchers from the Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania and Penn's Perelman School of Medicine will present results from several clinical trials and other key studies during the 2015 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting from May 29 through June 2.
Results of Phase II Trial Show Successful Antitumor Response Rate in Patients with Advanced BRCA-Related Ovarian Cancer
Olaparib, an experimental twice-daily oral cancer drug, produces significant antitumor responses in more than a third of patients with BRCA-related ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Controlling typhoid bacterium key to prevent gallbladder cancer in India and Pakistan