(Press-News.org) Use of low-dose aspirin prior to a newer type of fecal occult blood test is associated with a higher sensitivity for detecting advanced colorectal tumors, compared to no aspirin use, according to a study in the December 8 issue of JAMA.
"Screening for colorectal cancer (CRC) and its precursors by fecal occult blood tests (FOBTs), which has been shown to reduce CRC incidence and mortality in randomized trials, is widely recommended and applied in an increasing number of countries. Screening is mostly done in age groups in which use of low-dose aspirin for primary or secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease is increasingly common. Use of low-dose aspirin increases the likelihood of gastrointestinal bleeding, especially upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Because of the increased risk of bleeding from sources other than colorectal neoplasms [tumors], concerns have been raised regarding possible adverse effects on specificity of FOBT-based screening for CRC," according to background information in the article. Potential false-positive test results due to increased risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding are expected to be of less concern for increasingly available immunochemical FOBTs (iFOBTs; a type of test to check for blood in the stool), but evidence is sparse about the performance of iFOBTs for patients who use low-dose aspirin.
Hermann Brenner, M.D., M.P.H., of the German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany, and colleagues assessed the association of use of low-dose aspirin with performance of 2 iFOBTs in a large sample of women and men who underwent CRC screening. The study, conducted from 2005 through 2009, included 1,979 patients (average age, 62.1 years): 233 regular users of low-dose aspirin (167 men, 67 women) and 1,746 who never used low-dose aspirin (809 men, 937 women). The researchers analyzed measures of sensitivity and specificity in detecting advanced colorectal neoplasms (colorectal cancer or advanced adenoma [a tumor that is not cancer]) with 2 quantitative iFOBTs (hemoglobin test and hemoglobin-haptoglobin [a protein] test).
Advanced neoplasms were found in 24 users (10.3 percent) and 181 nonusers (10.4 percent) of low-dose aspirin. The researchers found that for the hemoglobin test, sensitivity was 70.8 percent for low-dose aspirin users compared with 35.9 percent for nonusers; specificity was 85.7 percent for users compared with 89.2 percent for nonusers. For the hemoglobin-haptoglobin test, sensitivity was 58.3 percent for users compared with 32 percent for non-users and specificity was 85.7 percent for users compared with 91.1 percent for nonusers.
"We provide a detailed comparison of the diagnostic performance of 2 quantitative iFOBTs among users and non-users of low-dose aspirin in the target population for CRC screening. For both tests, sensitivity was markedly higher, while specificity was slightly lower among users of low-dose aspirin compared with nonusers," the authors write.
"… our study strongly suggests that use of low-dose aspirin does not hamper testing for fecal occult blood by immunochemical tests. On the contrary, our findings raise the hypothesis that test performance may be enhanced by temporary use of low-dose aspirin, a hypothesis that needs replication in larger samples and followed up in further research, ideally including randomized trials and different types of FOBTs."
###
(JAMA. 2010;304[22]:2513-2520. Available pre-embargo to the media at www.jamamedia.org)
Editor's Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
To contact Hermann Brenner, M.D., M.P.H., email h.brenner@dkfz.de.
For More Information: Contact the JAMA/Archives Media Relations Department at 312-464-JAMA or email: mediarelations@jama-archives.org.
END
DALLAS – Dec. 7, 2010 – A more sensitive version of a blood test typically used to confirm that someone is having a heart attack could indicate whether a seemingly healthy, middle-aged person has unrecognized heart disease and an increased risk of dying, UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have found.
In a study available online and in the Dec. 8 print issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, researchers found that a new, highly sensitive test for a protein called cardiac troponin T (cTnT) could detect the protein in about 25 percent of blood ...
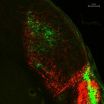
LA JOLLA, CA-Better known as the light sensor that sets the body's biological clock, melanopsin also plays an important role in vision: Via its messengers-so-called melanopsin-expressing retinal ganglion cells, or mRGCs-it forwards information about the brightness of incoming light directly to conventional visual centers in the brain, reports an international collaboration of scientists in this week's issue of PLoS Biology.
The findings reveal a new role for mRGCs during image-forming vision and suggest that these cells could make a significant contribution to assessing ...
Patients who need assistance to breathe through mechanical ventilation may benefit from listening to music, a new review published in The Cochrane Library shows. The researchers found that music listening may relax patients, potentially resulting in fewer complications.
Mechanical ventilation often causes major distress and anxiety in patients. The sensation of breathlessness, frequent suctioning, inability to talk, uncertainty regarding surroundings or condition, discomfort, isolation from others, and fear all contribute to high levels of anxiety. Medications administered ...
Immunotherapy given as pills or drops under the tongue is a safe and effective way to treat hayfever-like allergies caused by pollen and dust mites, according to a new Cochrane Systematic Review. The researchers say the approach is an attractive alternative to immunotherapy injections in children.
Common treatments for hayfever-like symptoms caused by allergies include antihistamines and nasal corticosteroids. If these prove unsuccessful, doctors may recommend immunotherapy, a desensitisation approach that involves exposing patients to increasing doses of an allergen. ...
Vitamin A supplements are still an effective way to reduce childhood death and disease. A new study by Cochrane researchers strongly endorses the continuation of vitamin A supplementation programmes, which reduce the incidence of measles and diarrhoea and ultimately save lives.
Vitamin A deficiency is a common problem in low and middle income countries. People whose diets do not include enough of the vitamin may have impaired body functions, and be more susceptible to blindness, infection and early death. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends vitamin A supplements ...
HACKENSACK, N.J. (December 7, 2010 at 7:30am) — The John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center announced today important research findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH) taking place December 4-7, 2010 in Orlando, Florida. The ASH meeting is the world's leading scientific gathering of hematologists and hematology researchers.
Research highlights from the 40 abstracts from the John Theurer Cancer Center include a comparison of treatment with stem cell transplantation versus continued combination drug ...
Sophia Antipolis, 8 December 2010: The prevalence of smoking and exposure to tobacco smoke among men in France has fallen by more than 15 per cent since the mid 1980s, but over the same 20-year period has increased among women. As a result, investigators from the World Health Organization French MONICA (MONItoring trends and determinants in CArdiovascular disease) centre say the divergent smoking trends predict changes in death rates from coronary heart disease in French men and women since 1985 - estimated as a decline in men of 10-15 per cent, but an increase among women ...
"Mobility is hugely important in terms of older people being able to remain independent," explains Dr Lynn McInnes. "Reduced mobility can restrict a person's social life as well as limiting their access to shops, leisure and other activities. People fear not being able to look after themselves and being a burden on others. Often a cause of this dependence is a decline in mobility."
The study used innovative methods, such as location awareness technologies for mapping the mobility of the oldest-old members (75 years and over) of an existing 25-year longitudinal study ...
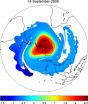
Washington, D.C. (December 7, 2010) -- Geophysical phenomena such as the dynamics of the atmosphere and ocean circulation are typically modeled mathematically by tracking the motion of air or water particles. These mathematical models define velocity fields that, given (i) a position in three-dimensional space and (ii) a time instant, provide a speed and direction for a particle at that position and time instant.
"Geophysical phenomena are still not fully understood, especially in turbulent regimes," explains Gary Froyland at the School of Mathematics and Statistics ...
Washington, D.C. (December 7, 2010) -- You've seen it in movies: the human-like, robot assassin quickly regenerates its structure after being damaged beyond recognition. This "Terminator" scenario is becoming less far-fetched as recent advances in structural health monitoring systems have led to a variety of ways to identify damage to a structural system.
Now, in the Journal of Applied Physics, researchers at Arizona State University have created a material that may be able to not only sense damage in structural materials, such as cracking in a fiber-reinforced composite, ...