(Press-News.org) There's an urgent demand for new antimicrobial compounds that are effective against constantly emerging drug-resistant bacteria. Two robotic chemical-synthesizing machines, named Symphony X and Overture, have joined the search. Their specialty is creating custom nanoscale structures that mimic nature's proven designs. They're also fast, able to assemble dozens of compounds at a time.
The machines are located in a laboratory on the fifth floor of the Molecular Foundry, a DOE Office of Science User Facility at Berkeley Lab. They make peptoids, which are synthetic versions of peptides. Nature uses peptides to build proteins, the workhorses of biology. Your body makes its own peptides to fight infections, and many antimicrobial drugs are based on peptides.
Despite their potency, peptide-based antimicrobials can degrade quickly in the bloodstream, limiting their effectiveness. Peptoids, being synthetic, are much more durable, which is one of the reasons why researchers have explored their use as antimicrobials for the past several years.
Recently, scientists from Denmark's Roskilde University used Symphony X and Overture to make dozens of peptoids that are designed to target bacteria. They created peptoids that mimic the structure and function of peptide-based antimicrobials. These drugs have an overall positive charge and water-repelling characteristics, two traits that enable them to disrupt a bacterium's membrane and kill it.
The trick was assembling a peptoid in which these traits are distributed throughout its structure in such a way that the peptoid is most effective at killing harmful bacteria without hurting other cells.
Often, such fine-tuning involves creating compounds one at a time and then testing them, a slow process with many dead-ends. Fortunately, Symphony X and Overture can churn out between 24 and 96 peptoids at a time. This means that many versions can be tested simultaneously.
"Peptoids are modular. We can control every position in their structure chemically and we can create peptoids with very specific traits and functions," says Ron Zuckermann, who directs the Molecular Foundry's Biological Nanostructures Facility and a pioneer of peptoid research.
"And because we can assemble many similar peptoids at the same time, we can test a hypothesis more thoroughly, in this case focusing on how to create peptoids that mimic antimicrobial peptides," Zuckermann adds.
Using Symphony X and Overture, Biljana Mojsoska, a graduate student at Roskilde University, created a family of several dozen peptoids, each with a slightly different distribution of charge and water-repelling traits. Peptoids are composed of non-natural amino acids that are strung together in a chain. The peptoids in this research were about ten amino acids long.
After assembling the peptoids at the Molecular Foundry, Mojsoska and Prof. Havard Jenssen studied them in their lab in Denmark to determine which versions work best at killing bacteria while not hurting red blood cells. Two promising candidates rose to the top.
"This paper demonstrated the biological compatibility of peptoids compared to antimicrobial peptide analogs," says Mojsoska. "Through various structural modifications, we were able to tune the structure of tryptophan and lysine-rich peptoids with regards to the hydrophobic content so that we could obtain antimicrobial peptoids with low toxicity profiles."
Adds Zuckermann, "This is a great example of what the Molecular Foundry offers. One of our long-term goals is to build functional nanoscale structures that are shaped and act like biological structures, but are made of more rugged materials. In this case it's antimicrobials, but it could be electrolytes for batteries, membranes for separations, or other applications."
Next, Mojsoska and colleagues plan to investigate the peptoids' mode of action against specific kinds of bacteria.
INFORMATION:
The research was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research.
An abstract of the research is here: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25941221
More about the Molecular Foundry: http://foundry.lbl.gov/
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory addresses the world's most urgent scientific challenges by advancing sustainable energy, protecting human health, creating new materials, and revealing the origin and fate of the universe. Founded in 1931, Berkeley Lab's scientific expertise has been recognized with 13 Nobel prizes. The University of California manages Berkeley Lab for the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Science. For more, visit http://www.lbl.gov.
DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit the Office of Science website at science.energy.gov/.
GAINESVILLE, Fla. -- If a picture is worth a thousand words, UF Health Type 1 diabetes researchers and their colleagues have tapped into an encyclopedia, revealing new insights into how young people cope with the disease.
The sophisticated scientific instrument? A camera.
More than 13,000 children and teens are diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes each year. To find out more about their experiences as they live with this chronic disorder, a group of diabetes researchers from three universities, including the University of Florida, gave 40 adolescents disposable cameras and ...
People with achromatopsia, an inherited eye disorder, see the world literally in black and white. Worse yet, their extreme sensitivity to light makes them nearly blind in bright sunlight. Now, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and Shiley Eye Institute at UC San Diego Health System have identified a previously unknown gene mutation that underlies this disorder.
The study published online June 1 in the journal Nature Genetics.
"There are whole families with this sort of vision problem all over the world," said Jonathan Lin, MD, ...
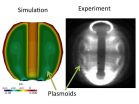
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) have for the first time simulated the formation of structures called "plasmoids" during Coaxial Helicity Injection (CHI), a process that could simplify the design of fusion facilities known as tokamaks. The findings, reported in the journal Physical Review Letters, involve the formation of plasmoids in the hot, charged plasma gas that fuels fusion reactions. These round structures carry current that could eliminate the need for solenoids - large magnetic coils that wind down the center ...
There is a wealth of published information describing interactions between drugs used to treat cardiovascular disease and the genetic variations that can affect how patients respond to them. But few heart specialists make routine use of this potentially life-saving data.
To help physicians make better-informed clinical decisions, researchers from the University of Chicago and Stanford University combed through scientific literature on the pharmacogenomics of 71 leading cardiovascular drugs and compiled summaries, published in the June issue of the Mayo Clinic Proceedings.
"Tens ...
Academic programs that provide alternatives to traditional remedial education help students succeed at community colleges, but different programs result in a range of outcomes for various sub-populations of students. Drew Allen, a New York University doctoral student and director of the Office of Research, Evaluation, and Program Support at the City University of New York (CUNY), devoted his doctoral research to the evaluation of three current programmatic approaches at CUNY community colleges.
Entering community college students are often required to take remedial, ...
Some female members of a critically endangered species of sawfish are reproducing in the wild without sex. The discovery, reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on June 1, marks the first time living offspring from "virgin births" have been found in a normally sexually reproducing vertebrate in the wild, the researchers say.
Earlier evidence that vertebrates might sometimes reproduce via a process called parthenogenesis had primarily come from isolated examples of captive animals--including birds, reptiles, and sharks. In those instances, the animals in question ...
Despite guideline recommendations to limit medical tests before low-risk surgeries, electrocardiograms (ECGs) and chest x-rays are still performed frequently, found a study in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
Evidence indicates that for patients undergoing low-risk surgery, routine testing does not improve outcomes and can actually lead to surgical delays, patient anxiety and other issues. The Choosing Wisely campaign, which started in the United States and spread to Canada and other countries, aims to raise awareness of unnecessary tests and procedures among ...
Radon gas is a silent health threat, and Canada needs to align its guidelines for acceptable radon levels with World Health Organization (WHO) limits, argues an editorial in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal).
"We are left in an odd situation in Canada," writes Dr. Diane Kelsall, Deputy Editor, CMAJ. "Drivers and passengers are required to wear seat belts, which are estimated to save about 1000 lives per year. Smoke alarms are required in most jurisdictions, reducing the annual rate of fire-related deaths from 130 per million households by about two-thirds. Yet, ...
ROSEMONT, Ill.--Woman in general have a higher incidence of osteoporosis-related hip fractures yet, conversely, they have a lower rate of mortality than men with the same fracture, according to a study in the June 2015 issue of the Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons (JAAOS). In addition, doctors don't always recognize or treat osteoporosis in men as often as they do in women.
"Male and Female Differences Matter in Musculoskeletal Disease" details the differences between how common musculoskeletal disorders manifest themselves in males versus females. ...
ROCHESTER, Minn. -- Why are major surgical errors called "never events?" Because they shouldn't happen -- but do. Mayo Clinic researchers identified 69 never events among 1.5 million invasive procedures performed over five years and detailed why each occurred. Using a system created to investigate military plane crashes, they coded the human behaviors involved to identify any environmental, organizational, job and individual characteristics that led to the never events. Their discovery: 628 human factors contributed to the errors overall, roughly four to nine per event. ...