INFORMATION:
About The University of Texas at Arlington
The University of Texas at Arlington is a comprehensive research institution of more than 50,000 students in campus-based and online degree programs and is the second largest institution in The University of Texas System. The Chronicle of Higher Education ranked UT Arlington as one of the 20 fastest-growing public research universities in the nation in 2014. U.S. News & World Report ranks UT Arlington fifth in the nation for undergraduate diversity. The University is a Hispanic-Serving Institution and is ranked as a "Best for Vets" college by Military Times magazine. Visit http://www.uta.edu to learn more, and find UT Arlington rankings and recognition at http://www.uta.edu/uta/about/rankings.php.
Household items, toys key to infant motor skill development, research finds
2015-06-04
(Press-News.org) ARLINGTON, Texas -- Toys, appliances, and even a sofa and coffee table can impact the way or when a baby first crawls, walks or achieves other growth milestones, but a new UT Arlington study finds that many parents are unaware of the significant role household items play in their infant's motor skill development.
Priscila Caçola, an assistant professor of kinesiology in the UT Arlington College of Nursing and Health Innovation, co-developed a simple questionnaire for caregivers of infants aged 3 to 18 months that she says can aid in the evaluation of toys and other items in the home known as home affordances.
The study, called "Further Development and Validation of the Affordances in the Home Environment for Motor Development-Infant Scale (AHEMD-IS)," appears in a recent issue of the journal Physical Therapy.
The questionnaire is called the Affordances in the Home Environment for Motor Development-Infant Scale, or AHEMD-IS, and is now being used by physical and occupational therapists worldwide. Caçola said the tool could help parents better assess items for motor skill development or help infants do something like learning to walk.
"When parents buy toys, they're rarely thinking 'I wonder if this is going to be great for my child's fine or gross motor skills,' but if they look at each AHEMD-IS question and each separation of the question, they can choose to buy toys that are different or that offer different opportunities for their infants," said Caçola, who also serves as director of the UT Arlington Department of Kinesiology's Little Mavs Movement Academy.
"Parents, doctors or other infant caregivers might ask 'What does a toy or a coffee table do?' Well, depending on the space between the couch and the coffee table, it could be the first distance that the child wants to cross," Caçola said. "If a toy is cranked and pops up, the child might want to go grab it, which could lead the child to walking. But the challenge is the thing that stimulates that child to begin walking."
Caçola said the AHEMD-IS would be especially important when you consider infants that are premature, low birth-weight or have a condition that could impair motor skill development.
Gross motor skills commonly refer to movements involving larger muscles, like those in the arms, legs, feet or the whole body used for walking, jumping and so forth. Fine motor skills generally refer to movements involving smaller muscles, like those in the hands, wrists and fingers that are used for holding a crayon or toy. The two skills can overlap, for example, when a child is taking something off a shelf and using both large muscles to walk to the shelf and small muscles used to grasp for the toy with fingers.
David Keller, chair of the Department of Kinesiology, called Caçola's research and the AHEMD-IS measurement helpful for all children and said it "offers significant practical implications for the development of screening, diagnostic and intervention protocols associated with motor skills."
Carl Gabbard, Texas A&M University professor of health and kinesiology, Maria I.L. Montebelo, Universidade Metodista de Piracicaba (Brazil) professor of mathematical sciences, and Denise C.C. Santos, University of Michigan professor of human movement sciences, joined Caçola in the study.
The researchers surveyed parents of more than 400 infants over five years in three Brazilian states, using the AHEMD-IS. They focused on four categories, including physical space in the home, variety of stimulation, gross-motor toys and fine-motor toys. Parents were asked questions like whether there was enough space for the child in the home to play or move around freely; does the home include a special space for toys where the child can choose what to play with and get it without help; and whether the parents regularly played games with their child to practice movements such as 'clap hands,' 'wave,' 'crawl,' 'walk,' etc.
Based on questionnaire responses, expert opinion and other variables, researchers found the AHEMD-IS to be a reliable and valid instrument for parents, doctors or other child caregivers in assessing objects in the home environment that promote infant motor development.
"Developing a child's motor skills is extremely important because motor development is actually the mediator of cognitive, social and emotional development," Caçola said. "Good motor skills predict a whole lot later in life, so it might be something that all of us should be concerned about early in a child's life."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
This week from AGU: Gulf of Mexico erosion, Grand Canyon sandbars, rainfall fluctuations
2015-06-04
From AGU's blogs: Flooding, erosion risks rise as Gulf of Mexico waves loom larger
Waves in the northern Gulf of Mexico are higher than they were 30 years ago, contributing to a greater risk of coastal erosion and flooding in Florida, Alabama, Mississippi and Louisiana, according to a new study in Geophysical Research Letters.
From Eos.org: Building Sandbars in the Grand Canyon
Annual controlled floods from one of America's largest dams are rebuilding the sandbars of the iconic Colorado River, according to a new article by U.S. Geological Survey scientists in Eos. ...
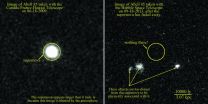
Exiled stars explode far from home
2015-06-04
Sharp images obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope confirm that three supernovae discovered several years ago exploded in the dark emptiness of intergalactic space, having been flung from their home galaxies millions or billions of years earlier.
Most supernovae are found inside galaxies containing hundreds of billions of stars, one of which might explode per century per galaxy.
These lonely supernovae, however, were found between galaxies in three large clusters of several thousand galaxies each. The stars' nearest neighbors were probably 300 light years away, nearly ...
CU Anschutz study shows low-cost weight loss program has long-term results
2015-06-04
AURORA, Colo. June 3 -- As America's obesity epidemic continues to grow, a new study from the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus shows that a low-cost, non-profit weight loss program offers the kind of long-term results that often elude dieters.
'We know that people lose weight and then gain it back,' said study author Nia S. Mitchell, M.D., MPH, a researcher with the Division of General Internal Medicine at the Anschutz Health and Wellness Center at CU Anschutz. 'In this case, we found that people who renewed their annual membership in the program lost a ...
New tool brings standards to epigenetic studies
2015-06-04
One of the most widely used tools in epigenetics research - the study of how DNA packaging affects gene expression - is chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), a technique that allows researchers to examine interactions between specific proteins and genomic regions. However, ChIP is a relative measurement, and has significant limitations that can lead to errors, poor reproducibility and an inability to be compared between experiments.
To address these issues, scientists from the University of Chicago have developed a new technique that calibrates ChIP experiments with an ...
Developing delirium in the ICU linked to fatal outcomes
2015-06-04
About one-third of patients admitted to an intensive care unit (ICU) will develop delirium, a condition that lengthens hospital stays and substantially increases one's risk of dying in the hospital, according to a new study led by Johns Hopkins Medicine researchers appearing in the British Medical Journal.
"Every patient who develops delirium will on average remain in the hospital at least one day longer," says one of the study's authors, Robert Stevens, M.D., a specialist in critical care and an associate professor at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. ...
Thirty years of AIDS data highlight survival gains, room for improvement
2015-06-04
[EMBARGOED UNTIL THURSDAY, JUNE 4] Although treatment advances have dramatically reduced deaths from opportunistic infections related to AIDS, a new study drawing on 30 years of data from more than 20,000 patients in San Francisco suggests there is still ample room to improve. About a third--35 percent--of AIDS patients diagnosed with their first opportunistic infection from 1997 to 2012 in that city died within five years, according to the study, published in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
"While recent research suggests that many opportunistic infections in the ...
Is dietary supplementation appropriate for children with autism spectrum disorder?
2015-06-04
Philadelphia, PA, June 4, 2015 - Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are often picky eaters, which can lead parents to suspect that their children might not be getting adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals. This sometimes leads parents of children with ASD to try nutritional supplements and dietary regimens such as gluten-free and casein-free (GFCF) diets without professional supervision. In the largest study of its kind, published in the Journal of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, researchers report that these well-intentioned efforts can result in ...
Hubble observes chaotic dance of Pluto's moons
2015-06-04
In a new study, scientists have gathered all available NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope data on the four outer moons of Pluto to analyse the system in more depth than ever before. The observations show that at least two of Pluto's moons are not neatly rotating on their axes but are in chaotic rotation while orbiting around Pluto and its companion Charon. The study also hints that one of the moons has a mysterious jet-black colouring. These surprising results appear in the 4 June issue of the journal Nature.
Almost every moon in the Solar System, including our moon, rotates ...
Ancient El Niños triggered Baja bunny booms
2015-06-04
SALT LAKE CITY, June 4, 2015 - At times during the past 10,000 years, cottontails and hares reproduced like rabbits and their numbers surged when the El Niño weather pattern drenched the Pacific Coast with rain, according to a University of Utah analysis of 3,463 bunny bones.
The study of ancient rabbit populations at a Baja California site may help scientists better understand how mammals that range from the coast to the interior will respond to climate change, says anthropology doctoral student Isaac Hart. He is first author of the study to be published in the ...
University of East Anglia researcher finds rare Vietnamese rabbit
2015-06-04
A rare and elusive rabbit has been found, held and photographed by a researcher from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
The Annamite Striped rabbit, found in the forests of Laos and Vietnam, was first documented by rabbit expert Dr Diana Bell and colleagues from UEA's School of Biological Sciences in the journal Nature in 1999. It has rarely been seen since.
Researcher Sarah Woodfin, who is studying for a Masters in Applied Ecology and Conservation at UEA, set out on a three-month expedition to track the recently-discovered rabbit and study its habitat.
But she ...