A microscopic approach to the magnetic sensitivity of animals
Watching photochemical reactions respond to magnetic fields in tiny spaces
2015-06-04
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the University of Tokyo have succeeded in developing a new microscope capable of observing the magnetic sensitivity of photochemical reactions believed to be responsible for the ability of some animals to navigate in the Earth's magnetic field, on a scale small enough to follow these reactions taking place inside sub-cellular structures.
Several species of insects, fish, birds and mammals are believed to be able to detect magnetic fields - an ability known as magnetoreception. For example, birds are able to sense the Earth's magnetic field and use it to help navigate when migrating. Recent research suggests that a group of proteins called cryptochromes and particularly the molecule flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) that forms part of the cryptochrome, are implicated in magnetoreception. When cryptochromes absorb blue light, they can form what are known as radical pairs. The magnetic field around the cryptochromes determines the spins of these radical pairs, altering their reactivity. However, to date there has been no way to measure the effect of magnetic fields on radical pairs in living cells.
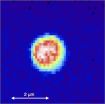
The research group of Associate Professor Jonathan Woodward at the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences are specialists in radical pair chemistry and investigating the magnetic sensitivity of biological systems. In this latest research, PhD student Lewis Antill made measurements using a special microscope to detect radical pairs formed from FAD, and the influence of very weak magnetic fields on their reactivity, in volumes less than 4 millionths of a billionth of a liter (4 femtoliters). This was possible using a technique the group developed called TOAD (transient optical absorption detection) imaging, employing a microscope built by postdoctoral research associate Dr. Joshua Beardmore based on a design by Beardmore and Woodward.
"In the future, using another mode of the new microscope called MIM (magnetic intensity modulation), also introduced in this work, it may be possible to directly image only the magnetically sensitive regions of living cells," says Woodward. "The new imaging microscope developed in this research will enable the study of the magnetic sensitivity of photochemical reactions in a variety of important biological and other contexts, and hopefully help to unlock the secrets of animals' miraculous magnetic sense."
INFORMATION:
Lewis Antill is a student on the new GPES (Graduate Program on Environmental Sciences) program, supported by a GPES specific MEXT scholarship. The research was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24350002.
Publication
Joshua P. Beardmore, Lewis M. Antill, and Jonathan R. Woodward, "Optical Absorption and Magnetic Field Effect Based Imaging of Transient Radicals" Angewandte Chemie International Edition. Early View: 2015/6/3, doi: 10.1002/anie.201502591
Links
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo
Organization for Programs on Environmental Sciences (OPES), Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo
Woodward Laboratory, Organization for Programs on Environmental Sciences (OPES), Graduate School of Arts and Sciences, The University of Tokyo
Associate Professor Jonathan R. Woodward
Graduate School of Arts and Sciences
The University of Tokyo
3-8-1 Komaba, Meguro-ku, Tokyo, 153-8902, Japan
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 2,000 international students. Find out more at http://www.u-tokyo.ac.jp/en/ or follow us on Twitter at @UTokyo_News_en.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-04
The advent of online social networks has led to the rapid development of tools for understanding the interactions between members of the network, their activity, the connections, the hubs and nodes. But, any relationships between lots of entities, whether users of Facebook and Twitter, bees in a colony, birds in a flock, or the genes and proteins in our bodies can be analyzed with the same tools.
Now, research published in International Journal of Data Mining and Bioinformatics shows how social network analysis can be used to understand and identify the biomarkers in ...
2015-06-04
SEATTLE - Physical activities, such as walking, as well as aerobics/calisthenics, biking, gardening, golfing, running, weight-lifting, and yoga/Pilates are associated with better sleep habits, compared to no activity, according to a new study from researchers at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. In contrast, the study shows that other types of physical activity - such as household and childcare -- work are associated with increased cases of poor sleep habits. The full results of the study (Abstract #0246) will be presented during the poster ...
2015-06-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - A new Cornell study of New York state apple orchards finds that pesticides harm wild bees, and fungicides labeled "safe for bees" also indirectly may threaten native pollinators.
The research, published June 3 in Proceedings of the Royal Society B, finds the negative effects of pesticides on wild bees lessens in proportion to the amount of natural areas near orchards.
Thirty-five percent of global food production benefits from insect pollinators, and U.S. farmers have relied exclusively on European honeybees, whose populations have been in decline for ...
2015-06-04
CINCINNATI - Researchers have identified that parent-reported responses to a questionnaire called the Pediatric Eosinophilic Esophagitis Symptom Score (PEESS® v2.0) correspond to clinical and biologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) - a severe and often painful food allergy that renders children unable to eat a wide variety of foods.
This study, published online in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, was led by researchers at Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center.
Eosinophils are normal cellular components of the blood, but when the body ...
2015-06-04
ITHACA, N.Y. - Ask a plant researcher how the sex of a cucumber plant is determined and the person will tell you, "It's complicated." Depending on a complex mix of genetic and environmental factors, cucumbers can be seven different sexes. Some high-yield cucumber varieties produce only female flowers, and a new study identifies the gene duplication that causes this unusual trait.
The study, led by Zhangjun Fei of the Boyce Thompson Institute at Cornell University, and Sanwen Huang of the Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, in Beijing, appeared recently in The Plant ...
2015-06-04
Chicago - June 4, 2015 - It may be better for patients to resume taking their blood pressure medication sooner after surgery than previously thought. A new study published in the Online First edition of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), found resuming angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), common medications used to treat high blood pressure, within two days after surgery decreased death rates in the first month following surgery.
"Sometimes doctors briefly stop ARB medications around the time of ...
2015-06-04
A 333-million year old broken bone is causing fossil scientists to reconsider the evolution of land-dwelling vertebrate animals, says a team of palaeontologists, including QUT evolutionary biologist Dr Matthew Phillips, and colleagues at Monash University and Queensland Museum.
Analysis of a fractured and partially healed radius (front-leg bone) from Ossinodus pueri, a large, primitive, four-legged (tetrapod), salamander-like animal, found in Queensland, pushes back the date for the origin of demonstrably terrestrial vertebrates by two million years, said Dr Phillips, ...
2015-06-04
Research by Catherine Klein, an undergraduate in Bristol's School of Earth Sciences, shows that fossils from the previously unstudied Woodleaze Quarry belong to a new species of the 'Gloucester lizard' Clevosaurus (named in 1939 after Clevum, the Latin name for Gloucester).
In the Late Triassic, the hills of the South West of the UK formed an archipelago that was inhabited by small dinosaurs and relatives of the Tuatara, a living fossil from New Zealand. The limestone quarries of the region have many caves or fissures containing sediments filled with the bones of abundant ...
2015-06-04
New research has revealed that parasitic 'vampire' plants that attach onto and derive nutrients from another living plant may benefit the abundance and diversity of surrounding vegetation and animal life.
By altering the densities of the hemiparasite (a parasitic plant that also photosynthesises) Rhinanthus minor, in the Castle Hill National Nature Reserve in Sussex, ecologists from the Universities of York, Sussex and Lincoln were able to assess the impacts of the 'vampire' plants on the biodiversity of a species-rich semi-natural grassland. The scientists compared ...
2015-06-04
NORTH GRAFTON, Mass. (June 4, 2015)--Birds, like people, can suffer from conditions where a blood transfusion is a necessary life-saving measure. But in many instances, unless an avian donor is readily available, accessing blood is impossible because of the challenges associated with storing the species' red blood cells.
New research published in the American Journal of Veterinary Research has found that a substance called dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) shows promise as a potential cryopreservant for freezing avian blood.
"Birds are susceptible to various causes of blood ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A microscopic approach to the magnetic sensitivity of animals
Watching photochemical reactions respond to magnetic fields in tiny spaces