(Press-News.org) Simple steps that include the consistent use of experienced medical teams for a single type of surgery, preemptive antibiotics before the procedure, less reliance on potent opioids during recovery and urging patients to get out of bed and move around sooner can not only prevent infections, blood clots and other serious complications in people undergoing colorectal operations, but can also accelerate recovery and reduce cost of care, according to results of an ongoing program at The Johns Hopkins Hospital.
The approach, dubbed Integrated Recovery Pathway, or IRP, and its impact on colorectal surgery care and cost are described online June 8 in the Journal of the American College of Surgeons under "articles in press."
For their analysis, Johns Hopkins researchers collected information on length of stay, surgical and urinary tract infections, and blood clots among 310 patients who had colorectal surgery before the IRP model was implemented. They then compared the data with outcomes of 330 patients who underwent treatment after the program launch.
The average length of stay in the pre-IRP group was seven days, compared with five days for those treated under the new model. The rate of surgical infections dropped from 19 percent to 7 percent, while the rate of deep-vein clots fell from 3.5 percent to 1.6 percent, as did urinary tract infections -- from 4 percent to 1.6 percent. The average cost of treatment decreased from nearly $11,000 to $9,000 per patient under the new protocol.
"Surgery is expensive and fraught with preventable harm, and attempts to make it safer should begin long before patients enter the OR and well after they leave it," says study senior author Elizabeth Wick, M.D., a colorectal specialist and associate professor of surgery at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "The IRP model is a means of anticipating and addressing well-established vulnerabilities, and taking advantage of opportunities along the entire continuum of clinical care to improve safety and overall outcomes."
The IRP approach doesn't so much require new treatments or new science, Wick adds, but consistent application of practices that are evidence based, engage patients and require accountability among clinicians at all levels.
"Avoiding preventable harm and improving outcomes are the cornerstones of quality improvement, but a comprehensive safety effort takes more than checklists," says Peter Pronovost, M.D., Ph.D., director of the Johns Hopkins Armstrong Institute for Patient Safety and Quality and co-author on the study. "They are rooted in a cultural shift and systematic solutions, and the findings of our study quantify the precise reduction in harm and cost and the improvements in patient scores as a result of such a cultural shift."
The key aspects of the IRP model included:
Adding oral antibiotics to the standard presurgical bowel cleanse
Asking patients to wipe their bodies with washcloths soaked in antiseptic solution prior to surgery
Use of epidural anesthesia in combination with intravenous anesthesia to minimize the need for inhaled gases and opioids, an approach that is far less taxing on the body's immune function and promotes faster recovery, the researchers say
Favoring nonopioid drugs to treat pain during recovery to ward off unwanted side effects, like nausea and constipation, which can slow recovery
Restricting the use of intravenous feeding in favor of resuming normal feeding earlier
Getting patients out of bed and moving around sooner to foster a faster return to independence
Preoperative patient education using information, supplies, checklists and instructions developed based on feedback from previous patients
"Questions like 'What do you wish someone had told you? What do you wish you knew going into surgery?' sound deceptively simple, but it's remarkable how much we learn by simply asking," Wick says.
Researchers believe the improvement in outcomes was at least in part fueled by efforts to involve patients more closely into decisions about their own care.
"Explaining to patients why they should take antibiotics before surgery or why we choose one pain medication over another can not only increase trust, but can also improve compliance," Wick says.
Building on ongoing efforts at Johns Hopkins to improve workplace culture, the IRP team established an accountability process that involved senior hospital leadership and frontline clinicians, including:
Real-time feedback on how well each medical team was doing and making swift adjustments where needed
Asking senior leaders and frontline clinicians to reflect on and openly discuss their roles and responsibilities
Creation of permanent clinical teams to boost cohesion and performance
"Prior to IRP, a pool of hundreds of anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists were randomly assigned to colorectal surgery, which compromised bonding and trust among team members and challenged their ability to implement interventions reliably and smoothly," says senior investigator Christopher Wu, M.D., professor of anesthesiology and critical care medicine at the Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine. "Under the IRP model, a small cadre of anesthesiologists, residents and nurse anesthetists are now permanently assigned to colorectal surgeries."
Researchers say the model's value has been sufficiently demonstrated to spark its rollout in July in gynecologic cancer surgery and urologic surgery. It is already being used in liver surgery.
"Given that 50 million people have surgery each year in the United States, the rapid application of IRP-style programs across the nation could yield serious improvements in patient safety and reduce the cost of care," Wick says.
INFORMATION:
Other investigators included Daniel Galante, Deborah Hobson, Jonathan Efron, Ken Lee and Sean Berenholtz, all of Johns Hopkins.
Surgical outcomes (deep vein thrombosis, urinary tract infections and surgical site infections) were tracked with the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program®.
Johns Hopkins Medicine
Media Relations and Public Affairs
Media contacts:
Ekaterina Pesheva, (410) 502-9433, epeshev1@jhmi.edu,
Lisa Broadhead, (410) 637-6294, lbroadh1@jhmi.edu
In a small clinical trial, scientists at Johns Hopkins' Kimmel Cancer Center and James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute found that men with advanced prostate cancer and detection of androgen receptor splice variant-7 (AR-V7) respond to chemotherapy just as well as men who lack the variant.
The findings, the researchers say, may be significant for patients who carry the AR-V7 variant, because they are more likely to develop resistance to one of two hormone drugs routinely used to treat their disease. Results of the trial are published online in the June 4 issue of JAMA ...
Young adults who use social media to quit smoking are twice as successful in their efforts as those who use a more traditional method, according to new research from the University of Waterloo.
The study, published last week in Nicotine & Tobacco Research, compared the success of the social media-based campaign Break It Off with Smokers' Helpline, a telephone hotline for young adults looking to quit smoking.
After three months in the program, 32 per cent of smokers who used Break It Off apps and web tools had quit smoking, compared to 14 per cent of their peers who ...
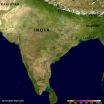
Monsoon rainfall, although a little later than normal, started on June 5, 2015, in southern India. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) core satellite gathered rainfall data that was used to create an animation that shows where the precipitation fell as the season started.
Due to El Nino conditions some meteorologists predict that monsoon rainfall will be below normal this year. Cooling rainfall comes to the country after high temperatures preceding the monsoon have caused the reported deaths of more than 2,300 people.
Data from the NASA's Integrated Multi-satellitE ...
The remnants of former Hurricane Blanca are blanking out over the northern part of Mexico's Baja California today, June 9. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of Blanca's remnants revealing a disorganized storm. All watches and warnings have been dropped.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite took an image of Blanca's remnants as it continued moving over the northern Baja California peninsula on June 9 at 1245 UTC (8:45 a.m. EDT). The clouds associated with the remnants were over the northern Baja and over the northern portion of mainland Mexico. The western-most ...
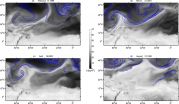
WASHINGTON, DC, June 9, 2015 - If you want to assign blame on an overcast day, then cast your eyes on the tropics. Water vapor originating from the Earth's tropics is transported to midlatitudes on long filaments of flowing air that intermittently travel across the world's oceans. When these airy tendrils make landfall, they can cause severe floods and other extreme weather events. Yet despite the importance of these "atmospheric rivers" for the global water and heat cycles, the mechanism behind their formation is still a mystery.
But a new study, published this week ...
Between 1993 and 2012, the incidence rate of acute traumatic spinal cord injury remained relatively stable in the U.S., although there was an increase among older adults, mostly associated with an increase in falls, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Traumatic spinal cord injury leads to chronic impairment and disability. Despite the substantial effects of this injury on health-related quality of life and health care spending, contemporary data on trends in incidence, causes, and medical care are limited, ...
A control system that incorporated electrical signals generated during muscle contractions and gait information resulted in improved real-time control of a powered prosthetic leg for different modes of walking (such as on level ground or descending stairs), according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Most prosthetic lower limbs are mechanically passive (cannot provide power) and so do not restore full function. Leg prostheses that provide power are becoming available; however, different ambulation modes require ...
Among applicants to U.S. medical schools, those with disabilities who obtained extra test administration time for the Medical College Admission Test in use from 1991 to January 2015 had no significant difference in rate of medical school admission but had lower rates of passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination Step examinations and of medical school graduation, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Individuals with documented mental and physical disabilities may receive testing accommodations ...
Following implementation of rotavirus vaccination in 2006, all-cause acute gastroenteritis hospitalization rates among U.S. children younger than 5 years of age declined by 31 percent - 55 percent in each of the post-vaccine years from 2008 through 2012, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA.
Eyal Leshem, M.D., of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues examined both all-cause gastroenteritis and rotavirus-related hospitalizations among children younger than 5 years from 2000 through 2012. The researchers analyzed State ...
Did the cross-country drive that you planned using an online mapping service take twice as long as expected?
In a new study published in the Articles in Advance section of Transportation Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS), Microsoft researchers working on a project for Bing Maps explain how they developed the first routing engine that satisfies a large number of algorithmic requirements that overcome barriers to generating directions on multi-stage trips like coast-to-coast drives.
Customizable Route Planning ...