How atmospheric rivers form
Rivers of moist air transporting water vapor from tropics to Europe and other midlatitude lands may be linked to 'Lagrangian coherent structures' high in atmosphere
2015-06-09
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, DC, June 9, 2015 - If you want to assign blame on an overcast day, then cast your eyes on the tropics. Water vapor originating from the Earth's tropics is transported to midlatitudes on long filaments of flowing air that intermittently travel across the world's oceans. When these airy tendrils make landfall, they can cause severe floods and other extreme weather events. Yet despite the importance of these "atmospheric rivers" for the global water and heat cycles, the mechanism behind their formation is still a mystery.
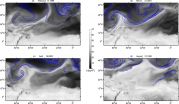
But a new study, published this week in the journal Chaos, from AIP Publishing, suggests that unusually persistent spatial structures that self-assemble high up in the atmosphere serve as "tracer patterns" around which atmospheric rivers grow. Based on simulations using real weather data in the Atlantic Ocean, the work was focused specifically on the transport of water from the tropics of the Caribbean to the Iberian Peninsula in Spain, but it suggests a more general way to study the transport of tropical water vapor globally.
These so-called Lagrangian coherent structures have been observed shaping other natural phenomena, including volcanic ash clouds and plankton blooms.
"Given that atmospheric rivers over the Atlantic and Pacific oceans appear as coherent filaments of water vapor lasting for up to a week, and that Lagrangian coherent structures have turned out to explain the formation of other geophysical flows, we wondered whether Lagrangian coherent structures might somehow play a role in the formation of atmospheric rivers," said study coauthor Vicente Perez-Munuzuri, a physicist at the University of Santiago de Compostela in Spain.
Through computer simulations, Perez-Munuzuri and his colleagues have shown that Lagrangian coherent structures and atmospheric rivers could indeed be linked. Using publically available data about wind speed and water vapor flux from real-world atmospheric rivers over the Atlantic, the scientists created a computer model consisting of thousands of moving virtual air particles and found a close match between the complex swirls -- the Lagrangian coherent structures -- made by the air particles and the patterns made by the real atmospheric rivers.
"The Lagrangian coherent structures serve as a kind of temporary scaffolding around which an atmospheric river can grow and lengthen," Perez-Munuzuri said.
The team thinks Lagrangian coherent structures could provide a better way of identifying and classifying atmospheric rivers. "To date, most methods used to identify atmospheric rivers are based on their water vapor flux or wind speed," Perez-Munuzuri said. "Here we show that the rivers can be classified by whether or not they start as Lagrangian coherent structures and also what shapes those structures take."
INFORMATION:
The article, "Lagrangian coherent structures along Atmospheric Rivers," is authored by Daniel Garaboa, Jorge Eiras-Barca, Florian Huhn and Vicente Pérez-Muñuzuri. It will appear in the journal CHAOS on June 9, 2015 (DOI: 10.1063/1.4919768). After that date, it can be accessed at: http://scitation.aip.org/content/aip/journal/chaos/25/6/10.1063/1.4919768.
The authors of this paper are affiliated with the University of Santiago de Compostela and ETH Zurich.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
CHAOS is devoted to increasing the understanding of nonlinear phenomena in all disciplines and describing their manifestations in a manner comprehensible to researchers from a broad spectrum of disciplines. See http://chaos.aip.org
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2015-06-09
Between 1993 and 2012, the incidence rate of acute traumatic spinal cord injury remained relatively stable in the U.S., although there was an increase among older adults, mostly associated with an increase in falls, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Traumatic spinal cord injury leads to chronic impairment and disability. Despite the substantial effects of this injury on health-related quality of life and health care spending, contemporary data on trends in incidence, causes, and medical care are limited, ...
2015-06-09
A control system that incorporated electrical signals generated during muscle contractions and gait information resulted in improved real-time control of a powered prosthetic leg for different modes of walking (such as on level ground or descending stairs), according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Most prosthetic lower limbs are mechanically passive (cannot provide power) and so do not restore full function. Leg prostheses that provide power are becoming available; however, different ambulation modes require ...
2015-06-09
Among applicants to U.S. medical schools, those with disabilities who obtained extra test administration time for the Medical College Admission Test in use from 1991 to January 2015 had no significant difference in rate of medical school admission but had lower rates of passing the United States Medical Licensing Examination Step examinations and of medical school graduation, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA, a theme issue on the Americans with Disabilities Act.
Individuals with documented mental and physical disabilities may receive testing accommodations ...
2015-06-09
Following implementation of rotavirus vaccination in 2006, all-cause acute gastroenteritis hospitalization rates among U.S. children younger than 5 years of age declined by 31 percent - 55 percent in each of the post-vaccine years from 2008 through 2012, according to a study in the June 9 issue of JAMA.
Eyal Leshem, M.D., of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues examined both all-cause gastroenteritis and rotavirus-related hospitalizations among children younger than 5 years from 2000 through 2012. The researchers analyzed State ...
2015-06-09
Did the cross-country drive that you planned using an online mapping service take twice as long as expected?
In a new study published in the Articles in Advance section of Transportation Science, a journal of the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS), Microsoft researchers working on a project for Bing Maps explain how they developed the first routing engine that satisfies a large number of algorithmic requirements that overcome barriers to generating directions on multi-stage trips like coast-to-coast drives.
Customizable Route Planning ...
2015-06-09
Rochester, MN, June 9, 2015 - U.S. government-issued dietary recommendations continue to evolve over time. In a special article published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings, an obesity theorist and cardiovascular health researchers claim that the main source of dietary information used by the U.S. Government's 2015 Dietary Guidelines Advisory Committee (DGAC) is scientifically flawed because the underlying data are primarily informed by memory-based dietary assessment methods (M-BMs) (eg, interviews and surveys). In an editorial response nutrition experts suggest that the purported ...
2015-06-09
Reacting positively to stressful situations may play a key role in long-term health, according to researchers.
In a study measuring adults' reactions to stress and how it affects their bodies, researchers found that adults who fail to maintain positive moods such as cheerfulness or calm when faced with the minor stressors of everyday life appear to have elevated levels of inflammation. Furthermore, women can be at heightened risk.
Inflammatory responses are part of the body's ability to protect itself via the immune system. However, chronic -- long-term -- inflammation ...
2015-06-09
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that insomnia decreases empathy in health care workers and may lead to adverse clinical outcomes and medical errors.
Results show that subjects with an Insomnia Severity Index ISI of greater than 8, scored significantly higher across all four subscales of empathy.
"Insomnia affects empathy in health care workers which can lead to adverse clinical outcomes,"
said lead author Venkatesh Basappa Krishnamurthy, MD, assistant professor, Sleep Research and Treatment Center, department of psychiatry, Penn State College of Medicine in Hershey, ...
2015-06-09
DARIEN, IL - A new study suggests that the timing of exposure to moderate levels of light may influence body mass index (BMI) and body fat.
Results show that people with more exposure to moderate or higher intensity light earlier in the day had lower body mass index and percent body fat than those with more of their moderate or higher intensity light exposure later in the day.
"These results emphasize the importance of getting the majority of your exposure to moderate or higher intensity light during the morning and provide further support that changes to environmental ...
2015-06-09
Teenagers who are incarcerated tend to have substantially worse outcomes later in life than those who avoid serving time for similar offenses, according to a distinctive new study co-authored by an MIT scholar.
"We find that kids who go into juvenile detention are much less likely to graduate from high school and much more likely to end up in prison as adults," says Joseph Doyle, an economist at the MIT Sloan School of Management and co-author of a new paper detailing the results of the study.
Indeed, the research project, which studied the long-term outcomes of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] How atmospheric rivers form
Rivers of moist air transporting water vapor from tropics to Europe and other midlatitude lands may be linked to 'Lagrangian coherent structures' high in atmosphere
